Muscle - Midlands State University
... Physiology The three types of muscle have significant differences, but all use the movement of actin against myosin to produce contraction and relaxation. In skeletal muscle, contraction is stimulated by electrical impulses transmitted by the nerves, the sensory nerves and motoneurons in particular ...
... Physiology The three types of muscle have significant differences, but all use the movement of actin against myosin to produce contraction and relaxation. In skeletal muscle, contraction is stimulated by electrical impulses transmitted by the nerves, the sensory nerves and motoneurons in particular ...
Nogo Receptor mRNA Expression in Intact and Regenerating CNS
... but not all, classes of neurons than in the white matter (Figs. 15–20). Strong Nogo mRNA expression was found in the neurons of the neocortex and hippocampal formation and many thalamic nuclei (Figs. 15, 17, and 18), including the TRN (arrows in Fig. 17). In the neostriatum, Nogo mRNA was widely exp ...
... but not all, classes of neurons than in the white matter (Figs. 15–20). Strong Nogo mRNA expression was found in the neurons of the neocortex and hippocampal formation and many thalamic nuclei (Figs. 15, 17, and 18), including the TRN (arrows in Fig. 17). In the neostriatum, Nogo mRNA was widely exp ...
Bridging Rate Coding and Temporal Spike Coding
... observed with a precision of milliseconds [1], suggesting the importance of precise spike timing in information processing. The precisely timed synchronous firing has also been found in different neural systems, and may represent coherent information with synchronous neurons forming a dynamical asse ...
... observed with a precision of milliseconds [1], suggesting the importance of precise spike timing in information processing. The precisely timed synchronous firing has also been found in different neural systems, and may represent coherent information with synchronous neurons forming a dynamical asse ...
autonomic nervous system
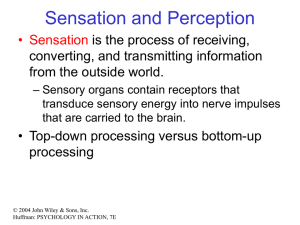
... • The autonomic nervous system contains both autonomic sensory and motor neurons. – Autonomic sensory input is not consciously perceived. • The autonomic motor neurons regulate visceral activities by either increasing (exciting) or decreasing (inhibiting) ongoing activities of cardiac muscle, smooth ...
... • The autonomic nervous system contains both autonomic sensory and motor neurons. – Autonomic sensory input is not consciously perceived. • The autonomic motor neurons regulate visceral activities by either increasing (exciting) or decreasing (inhibiting) ongoing activities of cardiac muscle, smooth ...
Lesson plans
... Activity 10. Draw a diagram relating nerve impulse and myelin. Draw a poster relating receptors, centres and effectors. Explain your diagram and poster to a partner(**). ...................................................................... 19 Activity 11. Now listen to your partner‟s explanation an ...
... Activity 10. Draw a diagram relating nerve impulse and myelin. Draw a poster relating receptors, centres and effectors. Explain your diagram and poster to a partner(**). ...................................................................... 19 Activity 11. Now listen to your partner‟s explanation an ...
GAIT AND LOCOMOTION
... • During normal level path unobstructed locomotion the cortical level involvement is minimal: when the animal is required to go over barriers in the travel path or is constrained to place its paws on a specific location (such as rungs of a ladder) the intensity (but not the phase) of the activity in ...
... • During normal level path unobstructed locomotion the cortical level involvement is minimal: when the animal is required to go over barriers in the travel path or is constrained to place its paws on a specific location (such as rungs of a ladder) the intensity (but not the phase) of the activity in ...
Slide Set 1: Anatomy and Physiology of Voice Production
... Some Questions • What is a voice disorder? • Is a voice disorder different form a speech disorder? • Is a voice disorder different from a resonance disorder? • How common are voice disorders? • Who gets a voice disorder? • Why might someone have a voice disorder? • How do you know if someone has a ...
... Some Questions • What is a voice disorder? • Is a voice disorder different form a speech disorder? • Is a voice disorder different from a resonance disorder? • How common are voice disorders? • Who gets a voice disorder? • Why might someone have a voice disorder? • How do you know if someone has a ...
SENSE AND THE SINGLE NEURON: Probing the Physiology of
... corresponds to the flash intensity at which the flashes are detected on half the trials and missed on the other half. This flash intensity is often taken as a measure of the detection threshold (although other percentage points may be chosen). A change in the detection threshold for a sensory stimul ...
... corresponds to the flash intensity at which the flashes are detected on half the trials and missed on the other half. This flash intensity is often taken as a measure of the detection threshold (although other percentage points may be chosen). A change in the detection threshold for a sensory stimul ...
Progress Report – Glover
... about the genetic regulation of neuronal type specification. As a first step, it is important to determine which transcription factors are expressed in or near specific identified neurons. To this end, Søviknes has successfully worked out parameters for double in situ hybridization experiments, and ...
... about the genetic regulation of neuronal type specification. As a first step, it is important to determine which transcription factors are expressed in or near specific identified neurons. To this end, Søviknes has successfully worked out parameters for double in situ hybridization experiments, and ...
Mirror Neurons and Mirror Systems in Monkeys and Humans
... Although single mirror neurons code the motor act that is going on in front of the observer, there is recent evidence that, thanks to the functional organization of the parietal and premotor mirror neurons, the observer is also able to understand why that motor act is done, in other terms, the goal ...
... Although single mirror neurons code the motor act that is going on in front of the observer, there is recent evidence that, thanks to the functional organization of the parietal and premotor mirror neurons, the observer is also able to understand why that motor act is done, in other terms, the goal ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Nerve Impulses •Action potential •The movement of ions initiates an action potential in the neuron due to a stimulus •A graded potential (localized depolarization) exists where the inside of the membrane is more positive and the outside is less positive ...
... Nerve Impulses •Action potential •The movement of ions initiates an action potential in the neuron due to a stimulus •A graded potential (localized depolarization) exists where the inside of the membrane is more positive and the outside is less positive ...
The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons 15
... A third component of visceral innervation, the enteric nervous system, also innervates smooth muscle and glands, specifically those within the digestive tract. The enteric nervous system regulates the activity of the digestive tract and functions completely independently of the CNS. Autonomic neuron ...
... A third component of visceral innervation, the enteric nervous system, also innervates smooth muscle and glands, specifically those within the digestive tract. The enteric nervous system regulates the activity of the digestive tract and functions completely independently of the CNS. Autonomic neuron ...
Grip Strength:
... • “….Anterior and middle deltoid activity decreased by 2% MVE, while posterior deltoid, infraspinatus and trapezius activity increased by 2% MVE and biceps brachii activity increased by 6% MVE.” Antony NT, Keir PJ. Effects of Posture, Movement and Hand Load on Shoulder Muscle Activity. Journal ...
... • “….Anterior and middle deltoid activity decreased by 2% MVE, while posterior deltoid, infraspinatus and trapezius activity increased by 2% MVE and biceps brachii activity increased by 6% MVE.” Antony NT, Keir PJ. Effects of Posture, Movement and Hand Load on Shoulder Muscle Activity. Journal ...
Document
... carried out by patterned movements for behaviors including the generation of speech content. (Sensory driven reflexes have only limited control by the MIND). The willful intent of MIND initiates self-serving motor control for survival and reproduction. MIND initiated voluntary actions operate throug ...
... carried out by patterned movements for behaviors including the generation of speech content. (Sensory driven reflexes have only limited control by the MIND). The willful intent of MIND initiates self-serving motor control for survival and reproduction. MIND initiated voluntary actions operate throug ...
Introductory Psychology Concepts
... Introductory Psychology Concepts: The Neuron and the Synapse Identify parts of the neuron and synapse and describe how they communicate information. ...
... Introductory Psychology Concepts: The Neuron and the Synapse Identify parts of the neuron and synapse and describe how they communicate information. ...
portada-contrapo 59(4) (Page 5)
... exposure to MCLR may cause renal toxic effects, including histopathological changes and modifications in the kidney functional parameters in rats (20) and fish (15). However, renal damage rarely occurs in mice. It is accepted that the cellular uptake of MCLR is mediated by a bile acid carrier system ...
... exposure to MCLR may cause renal toxic effects, including histopathological changes and modifications in the kidney functional parameters in rats (20) and fish (15). However, renal damage rarely occurs in mice. It is accepted that the cellular uptake of MCLR is mediated by a bile acid carrier system ...
full text pdf
... nerve fibres were very abundant in the SO ganglionated plexus. Some of them expressed simultaneously immunoreactivity for SP, and many SP-positive only nerve terminals were also found within the ganglia and in nerve bundles closely associated with the SO muscle. These CGRP and/or SP-positive fibres ...
... nerve fibres were very abundant in the SO ganglionated plexus. Some of them expressed simultaneously immunoreactivity for SP, and many SP-positive only nerve terminals were also found within the ganglia and in nerve bundles closely associated with the SO muscle. These CGRP and/or SP-positive fibres ...
pain impulses
... Increased sensitivity to pain after tissue injury Damaged tissue also releases molecules sa bradykinin that gate other channels/bind receptors Secretion of substances, substance P, bradykinin, prostaglandin that cause inflammation Can cause long lasting intracellular changes that increased sensitivi ...
... Increased sensitivity to pain after tissue injury Damaged tissue also releases molecules sa bradykinin that gate other channels/bind receptors Secretion of substances, substance P, bradykinin, prostaglandin that cause inflammation Can cause long lasting intracellular changes that increased sensitivi ...
Chapter 30
... c. smooth muscle cells connected by gap junctions in tissues (allow action potential to pass from one cell to next) - electrical synapse d. Single nucleus per cell ...
... c. smooth muscle cells connected by gap junctions in tissues (allow action potential to pass from one cell to next) - electrical synapse d. Single nucleus per cell ...
relation between cell size and response characteristics of
... stimulation. Of the 136 vestibulospinal neurons, 80 (58.8%) displayed a reliable periodic modulation of their firing rate during sinusoidal tilt at 0.026 Hz, 10” peak amplitude (see Fig. 3, 0). Among the remaining 56 units (41.2%), 48 did not satisfy the criteria for responsiveness (see Fig. 3, x). ...
... stimulation. Of the 136 vestibulospinal neurons, 80 (58.8%) displayed a reliable periodic modulation of their firing rate during sinusoidal tilt at 0.026 Hz, 10” peak amplitude (see Fig. 3, 0). Among the remaining 56 units (41.2%), 48 did not satisfy the criteria for responsiveness (see Fig. 3, x). ...
Basal Ganglia and Associated Pathways
... from the striatum (striosome). Clinically, this pathway is most important for its role in Parkinson’s disease. Note: it is important to keep in mind the distinction between the substantia nigra pars compacta which produces dopamine and is a source of input information to the basal ganglia, and the s ...
... from the striatum (striosome). Clinically, this pathway is most important for its role in Parkinson’s disease. Note: it is important to keep in mind the distinction between the substantia nigra pars compacta which produces dopamine and is a source of input information to the basal ganglia, and the s ...
Basal ganglia contributions to motor control: a - Research
... Disconnection of the BG skeletomotor circuit does not impair movement initiation or performance of an overlearned motor sequence, but selectively affects movement speed and extent. Animals moved a joystick (a, top) through a series of four out-and-back component movements ((b–d) red, blue, green, an ...
... Disconnection of the BG skeletomotor circuit does not impair movement initiation or performance of an overlearned motor sequence, but selectively affects movement speed and extent. Animals moved a joystick (a, top) through a series of four out-and-back component movements ((b–d) red, blue, green, an ...
Responses of the human motor system to observing actions across
... the same gestures performed by robotic arms did not. Although there is some evidence to suggest that certain types of robots may activate the action observation system in humans, the ability of robotic movements to do so appears to depend on the degree of naturalistic ‘‘humanness’’ of the robot. For ...
... the same gestures performed by robotic arms did not. Although there is some evidence to suggest that certain types of robots may activate the action observation system in humans, the ability of robotic movements to do so appears to depend on the degree of naturalistic ‘‘humanness’’ of the robot. For ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.