REVIEW THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... 41. _________________________ neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 42. The depolarization and repolarization of a neuron’s membrane is called a (n) 43. What are the spaces between adjacent neurons called? 44. A change in the environment that may be of sufficient strength to init ...
... 41. _________________________ neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 42. The depolarization and repolarization of a neuron’s membrane is called a (n) 43. What are the spaces between adjacent neurons called? 44. A change in the environment that may be of sufficient strength to init ...
Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... • Memory loss • Confusion • Problems speaking, understanding • Time/place? • Misplacing things • Mood swings • Personality change (suspiciousness) • Lack of interest ...
... • Memory loss • Confusion • Problems speaking, understanding • Time/place? • Misplacing things • Mood swings • Personality change (suspiciousness) • Lack of interest ...
Nervous System - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... ◊ Name a few important body functions that your nervous system controls on its own without you having to think about it much? ...
... ◊ Name a few important body functions that your nervous system controls on its own without you having to think about it much? ...
Diseases of peripheral nervous system. Myasthenic, myopatic
... Ca II+ homeostasis, proinflammatory cytokines, autoimmune mechanisms • genetic factors – familiar form is in ca.10%, hereditary occurence (AD, AR, X bound) The result is apoptosis (managed extinction) of motor neurons ...
... Ca II+ homeostasis, proinflammatory cytokines, autoimmune mechanisms • genetic factors – familiar form is in ca.10%, hereditary occurence (AD, AR, X bound) The result is apoptosis (managed extinction) of motor neurons ...
1. Impulse Conduction
... b) the inside of the cell now becomes more positive in relation to the outside c) Channels first open near the soma, then down the length of the axon as the action potential moves along ...
... b) the inside of the cell now becomes more positive in relation to the outside c) Channels first open near the soma, then down the length of the axon as the action potential moves along ...
Neurophysiology – Action Potential, Nerve Impulse, and Synapses
... 3. Temperature at which the nerve impulse is conducted. The speed of nerve impulse conduction is not related to the strength of the stimulus that triggered it. B. All-or-None Response and Stimulus Intensity 1. All or None Response Nerve impulse conduction is an all-or- none response. If a neuron res ...
... 3. Temperature at which the nerve impulse is conducted. The speed of nerve impulse conduction is not related to the strength of the stimulus that triggered it. B. All-or-None Response and Stimulus Intensity 1. All or None Response Nerve impulse conduction is an all-or- none response. If a neuron res ...
456 ss 96 final - People Server at UNCW
... 28. Which of the following is true of the primary visual cortex : a) it gives meaning to complex stimuli like faces b) it allocates a small proportion of its area to processing foveal vision c) it is not layered d) it is not organized in columns e) LGN inputs terminate at layer 4 29. The optic radia ...
... 28. Which of the following is true of the primary visual cortex : a) it gives meaning to complex stimuli like faces b) it allocates a small proportion of its area to processing foveal vision c) it is not layered d) it is not organized in columns e) LGN inputs terminate at layer 4 29. The optic radia ...
Nervous System
... Release of neurotransmitters from presynaptic vesicles requires an influx of calcium ions, Ca++ Postsynaptic membrane receptors bind the neurotransmitter and initiate the response Example: A neuromuscular junction and the ...
... Release of neurotransmitters from presynaptic vesicles requires an influx of calcium ions, Ca++ Postsynaptic membrane receptors bind the neurotransmitter and initiate the response Example: A neuromuscular junction and the ...
Action Potential Webquest
... 5. How does an action potential conduct along an axon? 6. Describe and draw an action potential. ...
... 5. How does an action potential conduct along an axon? 6. Describe and draw an action potential. ...
Ch 27 Neurones and Neural Pathways
... neurone and resynthesised into active neurotransmitter stored in vesicles ready for reuse. Mitochondria present in the presynaptic knob provide the energy. Noradrenaline is rebsorbed by the presynaptic membrane and stored in vesicles ready for reuse. ...
... neurone and resynthesised into active neurotransmitter stored in vesicles ready for reuse. Mitochondria present in the presynaptic knob provide the energy. Noradrenaline is rebsorbed by the presynaptic membrane and stored in vesicles ready for reuse. ...
Chapter 6 - Sensory - Austin Community College
... Afferent signals are not consciously recognized unless intense enough to cause pain or nausea from damaged viscera, fullness of bladder, angina pectoris (inadequate blood flow to heart) The efferent component consists of the autonomic motor neurons that excite or inhibit visceral activities of effec ...
... Afferent signals are not consciously recognized unless intense enough to cause pain or nausea from damaged viscera, fullness of bladder, angina pectoris (inadequate blood flow to heart) The efferent component consists of the autonomic motor neurons that excite or inhibit visceral activities of effec ...
Neurotoxicity
... Gamma- Diketones n-hexane Methyl n-butyl ketone • Sensorimotor polyneuropathy • Sensory numbness and paresthesia • Distal nerves affected first (distal axon swelling in both motor or sensory ...
... Gamma- Diketones n-hexane Methyl n-butyl ketone • Sensorimotor polyneuropathy • Sensory numbness and paresthesia • Distal nerves affected first (distal axon swelling in both motor or sensory ...
L7-Brainstem Student..
... • Trochlear nerve (CN IV) nucleus which also controls movements of some eye muscles . • Red Nucleus: gives out Sends Rubrospinal tract which is inhibitory to spinal Gamma Efferents neurons ( & stretch reflex /muscle tone ) • Substantia Nigra: Collection of neurons in the ventral portion of the midbr ...
... • Trochlear nerve (CN IV) nucleus which also controls movements of some eye muscles . • Red Nucleus: gives out Sends Rubrospinal tract which is inhibitory to spinal Gamma Efferents neurons ( & stretch reflex /muscle tone ) • Substantia Nigra: Collection of neurons in the ventral portion of the midbr ...
Sciatic nerve block - Anesthesia Slides, Presentations and
... • 22-gauge, 12-cm needle is inserted so that it contacts the femur at its medial border. Once the needle has contacted the femur, it is redirected slightly medially to slide off the medial surface of the femur. • At approximately 5 cm past the depth required to contact the femur, a paresthesia or m ...
... • 22-gauge, 12-cm needle is inserted so that it contacts the femur at its medial border. Once the needle has contacted the femur, it is redirected slightly medially to slide off the medial surface of the femur. • At approximately 5 cm past the depth required to contact the femur, a paresthesia or m ...
File
... • Both elicit different responses on various effectors Terminating Autonomic Neurotransmitter Actions • The enzyme acetylcholinesterase rapidly decomposes the acetylcholine that cholinergic fibers release. • Norepinephrine from adrenergic fibers is removed by active transport. ...
... • Both elicit different responses on various effectors Terminating Autonomic Neurotransmitter Actions • The enzyme acetylcholinesterase rapidly decomposes the acetylcholine that cholinergic fibers release. • Norepinephrine from adrenergic fibers is removed by active transport. ...
Document
... • The myelin sheath is made of fatty tissue, similar to plastic wire coating • This wrapping is never complete. Interspersed along the axon are gaps where there is no myelin – these are nodes of Ranvier. ...
... • The myelin sheath is made of fatty tissue, similar to plastic wire coating • This wrapping is never complete. Interspersed along the axon are gaps where there is no myelin – these are nodes of Ranvier. ...
phys Learning Objectives Chapter 5 [10-31
... injected automatically through the current electrode to maintain intracellular voltage at a steady zero level. Current electrode is connected to an oscilloscope that measures current flow. Selectively block one channel at a time – sodium blocked by tetrodotoxin applied to exterior of nerve fiber; p ...
... injected automatically through the current electrode to maintain intracellular voltage at a steady zero level. Current electrode is connected to an oscilloscope that measures current flow. Selectively block one channel at a time – sodium blocked by tetrodotoxin applied to exterior of nerve fiber; p ...
Ch. 7 - The Nervous System
... A stimulus depolarizes the neuron’s membrane 2. A depolarized membrane allows sodium (Na+) to flow inside the membrane C. Action potential 1. If the action potential (nerve impulse) starts, it is propagated over the entire axon 2. Impulses travel faster when fibers have a myelin sheath 3. The excha ...
... A stimulus depolarizes the neuron’s membrane 2. A depolarized membrane allows sodium (Na+) to flow inside the membrane C. Action potential 1. If the action potential (nerve impulse) starts, it is propagated over the entire axon 2. Impulses travel faster when fibers have a myelin sheath 3. The excha ...
Ch 3 Review
... reaches its threshold, or trigger point, for firing. The threshold for human neurons is approx -50 millivolts When a neuron reaches its threshold, an action potential, or nerve impulse, moves down the axon at up to 200 mph. ...
... reaches its threshold, or trigger point, for firing. The threshold for human neurons is approx -50 millivolts When a neuron reaches its threshold, an action potential, or nerve impulse, moves down the axon at up to 200 mph. ...
Frog Reflexes/synapses
... permeability of the muscle membrane to positive ions (via messenger-dependent Na+ channels). Na+ enters the muscle fiber, hypopolarizing the membrane. This local hypopolarization is called an end-plate potential. When the end-plate potential reaches threshold value, a muscle action potential is elic ...
... permeability of the muscle membrane to positive ions (via messenger-dependent Na+ channels). Na+ enters the muscle fiber, hypopolarizing the membrane. This local hypopolarization is called an end-plate potential. When the end-plate potential reaches threshold value, a muscle action potential is elic ...
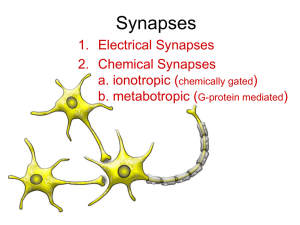
Synapses - Franklin College
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
Document
... gradients to create ION GRADIENTS batteries Pumps are driven by energy from ATP hydrolysis ELECTRICAL CURRENTS are generated by the opening of ION-SELECTIVE CHANNELS, allowing flow of current as ions down their concentration and electrical potential gradients ...
... gradients to create ION GRADIENTS batteries Pumps are driven by energy from ATP hydrolysis ELECTRICAL CURRENTS are generated by the opening of ION-SELECTIVE CHANNELS, allowing flow of current as ions down their concentration and electrical potential gradients ...
Biopsychology
... Are two kinds: 1. Hyperpolarization - increased polarity (voltage difference). 2. Depolarization - decreased polarity. Threshold Refers to the voltage level that needs to be reached for an action potential to occur. While the resting potential of the cell is about -70 mV, the threshold is ab ...
... Are two kinds: 1. Hyperpolarization - increased polarity (voltage difference). 2. Depolarization - decreased polarity. Threshold Refers to the voltage level that needs to be reached for an action potential to occur. While the resting potential of the cell is about -70 mV, the threshold is ab ...
What happens in a neuron
... 1.Multiple sclerosis (abbreviated to MS, known as disseminated sclerosis or encephalomyelitis disseminata) is an inflammatory disease in which parts of the brain and spinal cord are damaged, leading to slow signals, scarring as well as a broad spectrum of signs and symptoms. Disease onset usually oc ...
... 1.Multiple sclerosis (abbreviated to MS, known as disseminated sclerosis or encephalomyelitis disseminata) is an inflammatory disease in which parts of the brain and spinal cord are damaged, leading to slow signals, scarring as well as a broad spectrum of signs and symptoms. Disease onset usually oc ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.