Verbs_-_English_8_2
... regular verb generally regular verbs forms its past and past that end in e drop the participle by adding –d or e –ed before adding –ing. to the base form. ...
... regular verb generally regular verbs forms its past and past that end in e drop the participle by adding –d or e –ed before adding –ing. to the base form. ...
Grammar Troublesome Verbs
... • Watch out for lie/lay. • Consider the meanings of these two verbs to check that you are using the correct one. Lie means “rest or recline.” Lay means “put or place.” Try substituting these meanings for the verbs. ...
... • Watch out for lie/lay. • Consider the meanings of these two verbs to check that you are using the correct one. Lie means “rest or recline.” Lay means “put or place.” Try substituting these meanings for the verbs. ...
Les Verbes -ER
... Regular verbs all follow the same pattern of conjugation A conjugation fomrula is “stem + endings” ...
... Regular verbs all follow the same pattern of conjugation A conjugation fomrula is “stem + endings” ...
ON TARGET 2 : UNIT 5
... form is positive: She told the manager the truth and she is not sorry about this fact.) She regrets not telling the manager the truth.( -ing form is negative: She did not tell the manager the truth and she is sorry about this fact.) ...
... form is positive: She told the manager the truth and she is not sorry about this fact.) She regrets not telling the manager the truth.( -ing form is negative: She did not tell the manager the truth and she is sorry about this fact.) ...
File - TEC English class Black
... We made enough food. Is the audio loud enough? Are we writing nicely enough? 1. I am not enjoying my job at the moment because I have____________________. (work) 2. I don't like the soup because there is____________________in it. (salt) 3. Her English is not good. She makes____________________. (mis ...
... We made enough food. Is the audio loud enough? Are we writing nicely enough? 1. I am not enjoying my job at the moment because I have____________________. (work) 2. I don't like the soup because there is____________________in it. (salt) 3. Her English is not good. She makes____________________. (mis ...
Verbs
... provide examples of verb conjugations but they usually focus on irregular verbs. After all, since the vast majority of verbs are “regular,” they would waste a lot of ink showing you the usual way, word after word. So, they tend to show you the irregular patterns, largely as a space saver and often, ...
... provide examples of verb conjugations but they usually focus on irregular verbs. After all, since the vast majority of verbs are “regular,” they would waste a lot of ink showing you the usual way, word after word. So, they tend to show you the irregular patterns, largely as a space saver and often, ...
8th GRADE SPANISH Ch 7-2 GRAMMAR NOTES
... ¿Vas a hacer la tarea? (Are you going to do the homework) Note: the ir is conjugated, NOT what one is going to do 2. Pensar to plan or to intend: Pensar (is an e - ie stem-changing verb) When saying that one plans or intends to do something use pensar + infinitive construction: Pienso hacer la tarea ...
... ¿Vas a hacer la tarea? (Are you going to do the homework) Note: the ir is conjugated, NOT what one is going to do 2. Pensar to plan or to intend: Pensar (is an e - ie stem-changing verb) When saying that one plans or intends to do something use pensar + infinitive construction: Pienso hacer la tarea ...
VERB PHRASE
... (at 5 o’clock I was watching TV) (when he entered the classroom, she was explaining grammar) 2.) activity in progress within some time interval (I was watching TV for 3 hours – from 1 to 3) (Last night – all the night – I was watching TV) 3.) two activities that were in progress simultaneously (when ...
... (at 5 o’clock I was watching TV) (when he entered the classroom, she was explaining grammar) 2.) activity in progress within some time interval (I was watching TV for 3 hours – from 1 to 3) (Last night – all the night – I was watching TV) 3.) two activities that were in progress simultaneously (when ...
Jeopardy: Subjects, Verbs, Fragments, & Run-Ons
... I really like to go shopping; however, I don’t like to go it with my sister. I really like to go shopping. However, I don’t like to go it with my sister. (however is one of the transitions used with a semicolon before and a comma after…see pg 553 for ...
... I really like to go shopping; however, I don’t like to go it with my sister. I really like to go shopping. However, I don’t like to go it with my sister. (however is one of the transitions used with a semicolon before and a comma after…see pg 553 for ...
DocDroid
... nu mi-amintesc să fi văzut acest film niciodată — I don't remember ever seeing this film Prezent (Present) In most cases, the subjunctive forms of verbs in 1st and 2nd persons, singular and plural, are the same as their present tense counterparts. (One exception that comes to mind is the verb a fi, ...
... nu mi-amintesc să fi văzut acest film niciodată — I don't remember ever seeing this film Prezent (Present) In most cases, the subjunctive forms of verbs in 1st and 2nd persons, singular and plural, are the same as their present tense counterparts. (One exception that comes to mind is the verb a fi, ...
Tense, modality, and aspect define the status of the main verb
... • This agreement is partially based on the category of number, that is, whether the noun is singular or plural. It is also based on the category of person, which covers the distinctions of first person, second person and third person (involving any others). The different forms of English pronouns ca ...
... • This agreement is partially based on the category of number, that is, whether the noun is singular or plural. It is also based on the category of person, which covers the distinctions of first person, second person and third person (involving any others). The different forms of English pronouns ca ...
Types of Verbs
... TYPES OF VERBS Before you begin the verb tense lessons, it is extremely important to understand that NOT all English verbs are the same. English verbs are divided into three groups: ...
... TYPES OF VERBS Before you begin the verb tense lessons, it is extremely important to understand that NOT all English verbs are the same. English verbs are divided into three groups: ...
Name: Period: ______ Grammar Unit 3: Verbs Study Guide A verb is
... The past tenses convey actions and conditions that came to an end in the past. The past tense shows actions that began and were completed in the past. Example sentence: __________________________________________________________________ The past perfect tense places the actions before other past acti ...
... The past tenses convey actions and conditions that came to an end in the past. The past tense shows actions that began and were completed in the past. Example sentence: __________________________________________________________________ The past perfect tense places the actions before other past acti ...
Study Sheet: Dossier #1 (Episode #1) - Request a Spot account
... Using the present conditionnel to make a polite request or suggestion Pourriez-vous m’indiquer où se trouve la Tour Eiffel, s’il vous plaît? Je prendrais la soupe à l’oignon, s’il vous plaît. Auriez-vous l’heure, s’il vous plaît? The conditional is formed like the future tense (futur simple). Just l ...
... Using the present conditionnel to make a polite request or suggestion Pourriez-vous m’indiquer où se trouve la Tour Eiffel, s’il vous plaît? Je prendrais la soupe à l’oignon, s’il vous plaît. Auriez-vous l’heure, s’il vous plaît? The conditional is formed like the future tense (futur simple). Just l ...
Writing Clinic – Session 1
... with, it pulled, and the style my mother had chosen was not easy wither. She was not really a good sewer. She liked to make things; this is different. Whenever she could she tried to skip basting and pressing and she took no pride in the fine points of tailoring, the finishing of buttonholes and the ...
... with, it pulled, and the style my mother had chosen was not easy wither. She was not really a good sewer. She liked to make things; this is different. Whenever she could she tried to skip basting and pressing and she took no pride in the fine points of tailoring, the finishing of buttonholes and the ...
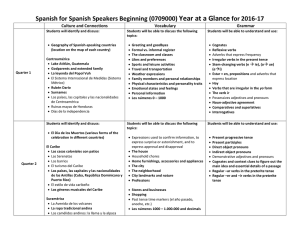
Spanish for Spanish Speakers Beginning (0709000) Year at a
... vocabulary give great opportunities to practice reading and listening using authentic texts and resources. Also, include opportunities for discussion and interpersonal speaking, as well as oral and written presentations to prepare for Pre-AP. ...
... vocabulary give great opportunities to practice reading and listening using authentic texts and resources. Also, include opportunities for discussion and interpersonal speaking, as well as oral and written presentations to prepare for Pre-AP. ...
Finite and Non
... verb to paint, which is being used as an adjective. A verbal is another name for a non-finite verb.) ...
... verb to paint, which is being used as an adjective. A verbal is another name for a non-finite verb.) ...
The Verb Train: Teaching Ancient Greek Verbs at Secondary
... The sounds used in the program are limited so that the learner is not distracted, especially in the computer lab. Yet the complete absence of music and sounds would be dissatisfying and would impede the comprehension of the message. There are analogue sounds that are a direct reference to the real w ...
... The sounds used in the program are limited so that the learner is not distracted, especially in the computer lab. Yet the complete absence of music and sounds would be dissatisfying and would impede the comprehension of the message. There are analogue sounds that are a direct reference to the real w ...
BE Verb
... Can have alternative form: IOs can be replaced by PPs introduced by “to” or “for” “The board gave a raise to the ...
... Can have alternative form: IOs can be replaced by PPs introduced by “to” or “for” “The board gave a raise to the ...
Slide 1
... that one action in the past occurred before another action in the past. It is formed by adding the auxiliary verb had before the main verb. For example, if Myron called his mother before he told his friends she had said he couldn't go to the concert, you would use the past perfect tense for the verb ...
... that one action in the past occurred before another action in the past. It is formed by adding the auxiliary verb had before the main verb. For example, if Myron called his mother before he told his friends she had said he couldn't go to the concert, you would use the past perfect tense for the verb ...
U.7 – imperativi The imperative is the command form of the verb
... I. To form the formal (Lei) imperative: 1. Think of the “io” form of the verb. 2. Take off the “o” and the end. 3. Add the “opposite” ending. –ARE verbs change to an “i” ending ex: parlare – think of “parlo” – switch the “o” to “i” – imperative = “parli” –ERE and –IRE verbs change to an “a” ending e ...
... I. To form the formal (Lei) imperative: 1. Think of the “io” form of the verb. 2. Take off the “o” and the end. 3. Add the “opposite” ending. –ARE verbs change to an “i” ending ex: parlare – think of “parlo” – switch the “o” to “i” – imperative = “parli” –ERE and –IRE verbs change to an “a” ending e ...
English auxiliary verbs
... Possibility - It is possible that he will jump Permission - He has permission to jump ...
... Possibility - It is possible that he will jump Permission - He has permission to jump ...
perfect - Frenchteacher.net
... agrees with the subject (masculine, feminine, singular or plural endings). ...
... agrees with the subject (masculine, feminine, singular or plural endings). ...