4. Verbal Categories (Morphological forms. Transitivity. Reflexivity
... perfect, imperfect progressive, nonprogressive indicative, subjunctive, conditional ...
... perfect, imperfect progressive, nonprogressive indicative, subjunctive, conditional ...
Auxiliary verbs - Brilliance College
... My father has never visited the USA. How long have you been living in Germany? By this time next year I will have been learning English for 35 years! Auxiliary Verbs are the verbs be, do, have, will when they are followed by another verb (the full verb) in order to form a question, a negative senten ...
... My father has never visited the USA. How long have you been living in Germany? By this time next year I will have been learning English for 35 years! Auxiliary Verbs are the verbs be, do, have, will when they are followed by another verb (the full verb) in order to form a question, a negative senten ...
Auxiliary verbs - CareerCouncillor
... My father has never visited the USA. How long have you been living in Germany? By this time next year I will have been learning English for 35 years! Auxiliary Verbs are the verbs be, do, have, will when they are followed by another verb (the full verb) in order to form a question, a negative senten ...
... My father has never visited the USA. How long have you been living in Germany? By this time next year I will have been learning English for 35 years! Auxiliary Verbs are the verbs be, do, have, will when they are followed by another verb (the full verb) in order to form a question, a negative senten ...
the passive voice - Aula Virtual Maristas Mediterránea
... EXAMPLES: The queen opened the show. The show was opened by the queen. It is necessary. A police officer stopped John. John was stopped by a police officer. It is necessary Someone robbed me. I was robbed. It is not necessary. People speak English here. English is spoken here. It is not necessary. T ...
... EXAMPLES: The queen opened the show. The show was opened by the queen. It is necessary. A police officer stopped John. John was stopped by a police officer. It is necessary Someone robbed me. I was robbed. It is not necessary. People speak English here. English is spoken here. It is not necessary. T ...
MULTI-WORD VERBS
... They are a combination of a verb and a member of a closed set of adverbs. The most common verbs forming phrasal verbs are put, take, look, get, bring, go, come, wake, give … The most common adverbs are down, up, in on, out, off, back, forth, over, etc… (This is only an opinion based on frequency of ...
... They are a combination of a verb and a member of a closed set of adverbs. The most common verbs forming phrasal verbs are put, take, look, get, bring, go, come, wake, give … The most common adverbs are down, up, in on, out, off, back, forth, over, etc… (This is only an opinion based on frequency of ...
Infinitives - s3.amazonaws.com
... You already know the following things about infinitives : 1. They are the 2nd principle part of the verb 2. They always end in the letters “re” 3. They mean “to _____” ex. Amare = to love (make sure this is in your notes from earlier this year – if not write it down now!) ...
... You already know the following things about infinitives : 1. They are the 2nd principle part of the verb 2. They always end in the letters “re” 3. They mean “to _____” ex. Amare = to love (make sure this is in your notes from earlier this year – if not write it down now!) ...
multiword verbs - Professor Flavia Cunha
... IT IS TO PUT LONG, “HEAVY” ELEMENTS AT THE END OF CLAUSES AND SENTENCES RATHER THAN IN THE MIDDLE. ...
... IT IS TO PUT LONG, “HEAVY” ELEMENTS AT THE END OF CLAUSES AND SENTENCES RATHER THAN IN THE MIDDLE. ...
Hacer Ahora Miercoles, el 13 de abril
... Comer el desayuno/almuerzo/cena (to eat…) Estudiar el/la subject name (to study…) Jugar el name of sport (to play…) Caminar a la/al name of place (to walk to…) Ir a la/el name of place (to go to…) Escribir/Leer en la clase de subject name(To write/read in ___ class) Cocinar el desayuno/almuerzo/cena ...
... Comer el desayuno/almuerzo/cena (to eat…) Estudiar el/la subject name (to study…) Jugar el name of sport (to play…) Caminar a la/al name of place (to walk to…) Ir a la/el name of place (to go to…) Escribir/Leer en la clase de subject name(To write/read in ___ class) Cocinar el desayuno/almuerzo/cena ...
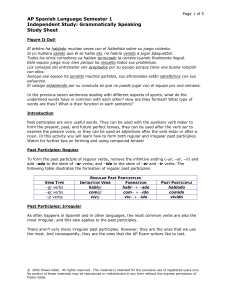
AP Spanish Language Semester 1 Independent Study
... underlined words have in common with each other? How are they formed? What type of words are they? What is their function in each sentence? Introduction Past participles are very useful words. They can be used with the auxiliary verb haber to form the present, past, and future perfect tenses, they c ...
... underlined words have in common with each other? How are they formed? What type of words are they? What is their function in each sentence? Introduction Past participles are very useful words. They can be used with the auxiliary verb haber to form the present, past, and future perfect tenses, they c ...
Dangling participles Source: www.englishgrammar.org Adjectives
... Standing at the gate, a scorpion stung the man. This sentence seems to suggest that it was the scorpion which stood at the gate. Actually, it was the man. He was stung by the scorpion when he was standing at the gate. Now another example is given below. Flitting from flower to flower, the girl watch ...
... Standing at the gate, a scorpion stung the man. This sentence seems to suggest that it was the scorpion which stood at the gate. Actually, it was the man. He was stung by the scorpion when he was standing at the gate. Now another example is given below. Flitting from flower to flower, the girl watch ...
Gustar with Infinitives
... • Each person in the group will write this person’s response. Remember to change the me to le because you’re talking about another person. ▫ Responses will look like this: A Maria le gusta más leer ...
... • Each person in the group will write this person’s response. Remember to change the me to le because you’re talking about another person. ▫ Responses will look like this: A Maria le gusta más leer ...
Infinitives - WaltripSpanish
... The most basic form of a verb is called the infinitive. In English, you can spot the infinitives because they usually have the word “to” in front of them: – To swim, to read, to write ...
... The most basic form of a verb is called the infinitive. In English, you can spot the infinitives because they usually have the word “to” in front of them: – To swim, to read, to write ...
Gerunds and Infinitives
... Running regularly will make you feel better. Studying requires most of my time during the day. The -ing form can also be called a present participle; however, the function is that of a verb when used in the present or past progressive: Example : The teacher is speaking to her students. If a gerund i ...
... Running regularly will make you feel better. Studying requires most of my time during the day. The -ing form can also be called a present participle; however, the function is that of a verb when used in the present or past progressive: Example : The teacher is speaking to her students. If a gerund i ...
Final Exam Review / SPANISH 2
... Negative:Use the present subjunctive of the verb in the tú form. To form the present subjunctive tense, you must first conjugate your verb in the first person or yo form. Second, replace the o with either –as (for verbs ending in –er or –ir) or –es (for verbs ending in –ar) ...
... Negative:Use the present subjunctive of the verb in the tú form. To form the present subjunctive tense, you must first conjugate your verb in the first person or yo form. Second, replace the o with either –as (for verbs ending in –er or –ir) or –es (for verbs ending in –ar) ...
Mikio Namoto 2.1 GroupI - Kyushu University Library
... do not allow them to have an infinitive as the direct object. After some verbs the gerund is more frequently used than the infinitive, and after other verbs the infinitive is preferred. According to Jespersen,2) after the verbs, hate and like, the infinitive is mostly used with reference to a specia ...
... do not allow them to have an infinitive as the direct object. After some verbs the gerund is more frequently used than the infinitive, and after other verbs the infinitive is preferred. According to Jespersen,2) after the verbs, hate and like, the infinitive is mostly used with reference to a specia ...
a pattern based approach for the derivation of base forms of verbs
... Assembling the participles and tenses of verb is performed based on the end patterns of the verb. Any participle or tense can be derived from any other participle or tense of the same base verb. There are a few exceptions that are ignored which are the following: “did", "should", "must", "could", "h ...
... Assembling the participles and tenses of verb is performed based on the end patterns of the verb. Any participle or tense can be derived from any other participle or tense of the same base verb. There are a few exceptions that are ignored which are the following: “did", "should", "must", "could", "h ...
TEACHING FRENCH USING MNENONIC - MN
... letters used that do not fit the acronym. Teachers should regularly repeat the devices in class and should require students to memorize them when feasible. Very often, after having taught one, I give extra credit on the next quiz to those who are able to reproduce the device and explain the grammati ...
... letters used that do not fit the acronym. Teachers should regularly repeat the devices in class and should require students to memorize them when feasible. Very often, after having taught one, I give extra credit on the next quiz to those who are able to reproduce the device and explain the grammati ...
A. To-infinitives
... Part 1: Wong Yuk Hung (27) Part 2: Yui Ka Yee (30) Part 3: Lin Lai Miu (14) ...
... Part 1: Wong Yuk Hung (27) Part 2: Yui Ka Yee (30) Part 3: Lin Lai Miu (14) ...
Past Perfect Tense
... Time words- tomorrow, next week, Thursday Time words are used with the present tense to express future time. Our show opens next week. Opens- present tense, next week -time words. Tomorrow we design scenery and rehearse. Next Friday our show is opening. (In this sentence the present progressive form ...
... Time words- tomorrow, next week, Thursday Time words are used with the present tense to express future time. Our show opens next week. Opens- present tense, next week -time words. Tomorrow we design scenery and rehearse. Next Friday our show is opening. (In this sentence the present progressive form ...
Lecture 5. Verbs and Verb Phrases I
... Nonfinite verb forms: o Nonfinite verb forms do not express tense (or mood, number, or person). o The infinitive (e.g. I can play the violin; I started to read when the light came on). o The present participle/-ing form (e.g. He is going to the lecture; Reading a good book is my favourite pastime). ...
... Nonfinite verb forms: o Nonfinite verb forms do not express tense (or mood, number, or person). o The infinitive (e.g. I can play the violin; I started to read when the light came on). o The present participle/-ing form (e.g. He is going to the lecture; Reading a good book is my favourite pastime). ...
Multisensory Grammar Activities Action Verbs
... as the subject and the verb in the predicate. Tell them to use the present-tense form of the verb. Then have students rewrite the same sentence in past tense and future tense. Tell students to underline each subject and circle each verb. (VISUAL; KINESTHETIC) 5. Invite volunteers to read their sente ...
... as the subject and the verb in the predicate. Tell them to use the present-tense form of the verb. Then have students rewrite the same sentence in past tense and future tense. Tell students to underline each subject and circle each verb. (VISUAL; KINESTHETIC) 5. Invite volunteers to read their sente ...
Verbals: Practice Quiz
... object, IO = indirect object, PN = predicate nominative, OP = object of preposition. Gerunds=Verbs that LOOK like Nouns STOP: Does the gerund answer “what” about an action verb? If so, you have a DO. Does the gerund identify the subject and come after a LV? If so, you have a PN. Does the gerund come ...
... object, IO = indirect object, PN = predicate nominative, OP = object of preposition. Gerunds=Verbs that LOOK like Nouns STOP: Does the gerund answer “what” about an action verb? If so, you have a DO. Does the gerund identify the subject and come after a LV? If so, you have a PN. Does the gerund come ...
The Ablative Absolute - The GCH Languages Blog
... In English we use the pluperfect tense to express an action which occurs before another action in the past. Latin, however, has a very neat way of expressing this time difference which follows the construction of the third sentence: With the city having been captured, the soldiers departed urbe cap ...
... In English we use the pluperfect tense to express an action which occurs before another action in the past. Latin, however, has a very neat way of expressing this time difference which follows the construction of the third sentence: With the city having been captured, the soldiers departed urbe cap ...
Painting with Five Basic Brush Strokes
... • Passive: The runaway horse was ridden into town by an old, white-whiskered rancher. • Active: An old, white-whiskered rancher rode the runaway horse into town. • Passive: The grocery store was robbed by two armed men. • Active: Two armed men robbed the grocery store. ...
... • Passive: The runaway horse was ridden into town by an old, white-whiskered rancher. • Active: An old, white-whiskered rancher rode the runaway horse into town. • Passive: The grocery store was robbed by two armed men. • Active: Two armed men robbed the grocery store. ...