perfect - Frenchteacher.net
... agrees with the subject (masculine, feminine, singular or plural endings). ...
... agrees with the subject (masculine, feminine, singular or plural endings). ...
1. to 7. verbs
... A) I have finished / had finished / will have finished my homework. B) I _____________________________________________ to France. C) They ___________________________________________________diligently to get full scholarships. D) We ________________________________________________ to prepare our Litt ...
... A) I have finished / had finished / will have finished my homework. B) I _____________________________________________ to France. C) They ___________________________________________________diligently to get full scholarships. D) We ________________________________________________ to prepare our Litt ...
Slide 1
... IE present stem: accented, the vowel *e IE perfect stem: unaccented, the vowel reduced (dynamic accent) or changed in the direction of *o (pitch accent) ...
... IE present stem: accented, the vowel *e IE perfect stem: unaccented, the vowel reduced (dynamic accent) or changed in the direction of *o (pitch accent) ...
Show Don`t Tell
... Does this show or tell? – Not very vivid…in fact it’s dull. – So…change it to action to show he is a monster. ...
... Does this show or tell? – Not very vivid…in fact it’s dull. – So…change it to action to show he is a monster. ...
How to memorize the “être” verbs?
... A way to help memorizing these verbs is to imagine a hiker coming to a mountain with a house on top: being born in her village (naître), then coming to the mountain from her village (venir), arriving to the mountain (arriver), climbing on it (monter), going through a cave (passer), then going to the ...
... A way to help memorizing these verbs is to imagine a hiker coming to a mountain with a house on top: being born in her village (naître), then coming to the mountain from her village (venir), arriving to the mountain (arriver), climbing on it (monter), going through a cave (passer), then going to the ...
Lesson #7
... Note also that past tense modals can express the future: • I could have a rum and coke tonight. (past tense, simple aspect: expresses the future) And the present: • I could be having a rum and coke (but I’m here teaching English instead). (past tense, progressive aspect: expresses the present that ...
... Note also that past tense modals can express the future: • I could have a rum and coke tonight. (past tense, simple aspect: expresses the future) And the present: • I could be having a rum and coke (but I’m here teaching English instead). (past tense, progressive aspect: expresses the present that ...
SCHEMAS - SFU.ca
... person, deictic inflectional dimension that orients the speaker relative to the addressee and other participants not addressed tense, deictic inflectional dimension that relates the speaker’s time of utterance to the time of the content of the utterance aspect, verbal aspectual dimension that descri ...
... person, deictic inflectional dimension that orients the speaker relative to the addressee and other participants not addressed tense, deictic inflectional dimension that relates the speaker’s time of utterance to the time of the content of the utterance aspect, verbal aspectual dimension that descri ...
Parallel Structure
... rambling at the lec tern, that the end of class had arrived. Or you can revise the sentence so that all of the items in the list are nouns: Students gathered their pens , notebooks , and book bags as they tried to alert Professor Jones, rambling at the lec tern, that the end of class had arrived. ...
... rambling at the lec tern, that the end of class had arrived. Or you can revise the sentence so that all of the items in the list are nouns: Students gathered their pens , notebooks , and book bags as they tried to alert Professor Jones, rambling at the lec tern, that the end of class had arrived. ...
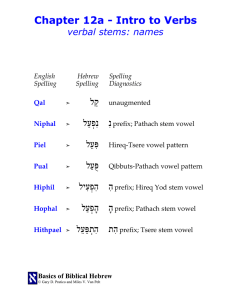
verbal stems: names
... הִ הִפְעִילprefix; Hireq Yod stem vowel הָ הָפְעַלprefix; Pathach stem vowel הִת הִתְפַּעֵלprefix; Tsere stem vowel ...
... הִ הִפְעִילprefix; Hireq Yod stem vowel הָ הָפְעַלprefix; Pathach stem vowel הִת הִתְפַּעֵלprefix; Tsere stem vowel ...
Which are these time forms and how are they used? (b)
... Which are these time forms and how are they used? (a) ...
... Which are these time forms and how are they used? (a) ...
VERBS
... Verbs have four principal parts that are used to form all tenses. The chart below show how the principal parts of most verbs are formed.. Principal Parts of Verbs Base Form ...
... Verbs have four principal parts that are used to form all tenses. The chart below show how the principal parts of most verbs are formed.. Principal Parts of Verbs Base Form ...
Exceptions in Direct and Indirect Speech for SSC
... Case 1: He said, “I saw the sun rising in the east.” He said that he had seen the sun rising in the east. Case 2: He said, “Sun rises in the East.” He said that Sun rises in the East. In case 1 and 2, the Reporting Verb is in the past tense (said) but still the tense of only Case 1 is changed. There ...
... Case 1: He said, “I saw the sun rising in the east.” He said that he had seen the sun rising in the east. Case 2: He said, “Sun rises in the East.” He said that Sun rises in the East. In case 1 and 2, the Reporting Verb is in the past tense (said) but still the tense of only Case 1 is changed. There ...
Checklist for Recognizing Complete Verbs
... These three tenses combine the features of the previous two. Notice that each tense below has the “had, have, has”+ the past participle “been” + an “ing” word (present participle). Present Perfect Progressive: I have been trying to reach you; you have been being difficult, she has been seeing a coun ...
... These three tenses combine the features of the previous two. Notice that each tense below has the “had, have, has”+ the past participle “been” + an “ing” word (present participle). Present Perfect Progressive: I have been trying to reach you; you have been being difficult, she has been seeing a coun ...
What is a Verb?
... grammatical structure of a sentence, but they do not tell us very much alone. We usually use helping verbs with main verbs. They "help" the main verb (which has the real meaning). ...
... grammatical structure of a sentence, but they do not tell us very much alone. We usually use helping verbs with main verbs. They "help" the main verb (which has the real meaning). ...
abandon the investigation
... regular verbs only and that irregular verbs form their past tenses differently (compare walk-walked, vs. eat-ate, or think-thought). The morpheme -ed is one realization of the abstract INFL with the feature [+past]. For irregular verbs the combination of this abstract INFL with the relevant verb giv ...
... regular verbs only and that irregular verbs form their past tenses differently (compare walk-walked, vs. eat-ate, or think-thought). The morpheme -ed is one realization of the abstract INFL with the feature [+past]. For irregular verbs the combination of this abstract INFL with the relevant verb giv ...
En mi tiempo libre PRESENT TENSE
... When the verb has the –AR, -ER, -IR ending it is called the INFINITIVE. When you remove the –AR, -ER, -IR it becomes THE STEM. ...
... When the verb has the –AR, -ER, -IR ending it is called the INFINITIVE. When you remove the –AR, -ER, -IR it becomes THE STEM. ...
NOMBRE: Hora: Imperfect Irregulars (ser, ir, ver)
... IMPERFECT IRREGULARS We talked about the past tense yesterday. One of the past tenses we discussed was the imperfect tense. The imperfect tense is the past tense that we use to talk about things that are not from a fixed moment in time. For example, the imperfect would be used for things I used to d ...
... IMPERFECT IRREGULARS We talked about the past tense yesterday. One of the past tenses we discussed was the imperfect tense. The imperfect tense is the past tense that we use to talk about things that are not from a fixed moment in time. For example, the imperfect would be used for things I used to d ...
Chapter 6, Greek Before Christmas
... Greek Before Christmas Greek present tense verbs always consist of two components: the present stem (which expresses the core meaning of the verb) and the personal ending (which functions like an English subject pronoun). Greek does not have a verb form that merely says “walk.” Instead, Greek has s ...
... Greek Before Christmas Greek present tense verbs always consist of two components: the present stem (which expresses the core meaning of the verb) and the personal ending (which functions like an English subject pronoun). Greek does not have a verb form that merely says “walk.” Instead, Greek has s ...
Participles
... participle is that form of the verb which is used like an adjective. l Since it is a verb, it has tense and voice. It can take a direct object, an indirect object, etc. l Since it is an adjective, it has case, number, and gender, and it will modify a noun. ...
... participle is that form of the verb which is used like an adjective. l Since it is a verb, it has tense and voice. It can take a direct object, an indirect object, etc. l Since it is an adjective, it has case, number, and gender, and it will modify a noun. ...
add an s
... • To make nouns plural Nouns ---add an s ch, sh, x, or z Add an es • If the word ends in y, look at the letter before the y – vowel Add an s ...
... • To make nouns plural Nouns ---add an s ch, sh, x, or z Add an es • If the word ends in y, look at the letter before the y – vowel Add an s ...
Lesson 13 Topic: Home-reading, Present and Past Participle. • Lead
... Notice that each present participle ends in ing. This is the case 100 percent of the time. On the other hand, you can see that past participles do not have a consistent ending. The past participles of all regular verbs end in ed; the past participles of irregular verbs, however, vary considerably. I ...
... Notice that each present participle ends in ing. This is the case 100 percent of the time. On the other hand, you can see that past participles do not have a consistent ending. The past participles of all regular verbs end in ed; the past participles of irregular verbs, however, vary considerably. I ...
Participles
... There are two types of participles in Spanish, the past participle and the present participle. You have already learned how to form the past participle. For regular verbs you add –ado to the stem of –ar verbs and –ido to the stem of –er or –ir verbs. And remember there are about 11 major irregular p ...
... There are two types of participles in Spanish, the past participle and the present participle. You have already learned how to form the past participle. For regular verbs you add –ado to the stem of –ar verbs and –ido to the stem of –er or –ir verbs. And remember there are about 11 major irregular p ...
Useful First-Conjugation Verbs Ending in
... essi they (masculine), and esse they (feminine). In English, subject pronouns must be used with verbs. In Italian, however, the forms of the verb change to show who the subject is, and pronouns are used only for emphasis or contrast. Italian verbs are divided into three groups, called conjugations. ...
... essi they (masculine), and esse they (feminine). In English, subject pronouns must be used with verbs. In Italian, however, the forms of the verb change to show who the subject is, and pronouns are used only for emphasis or contrast. Italian verbs are divided into three groups, called conjugations. ...
Participles - JJ Daniell Middle School
... pillow, and the cool muslin pillowcase touched both my ears as the back of my head sank into all those feathers. -A Day No Pigs Would Die ...
... pillow, and the cool muslin pillowcase touched both my ears as the back of my head sank into all those feathers. -A Day No Pigs Would Die ...
verb - Cloudfront.net
... grammatical structure of a sentence, but they do not tell us very much alone. We usually use helping verbs with main verbs. They "help" the main verb (which has the real meaning). ...
... grammatical structure of a sentence, but they do not tell us very much alone. We usually use helping verbs with main verbs. They "help" the main verb (which has the real meaning). ...