Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... Hypothalamus releases hormones or releasing factors which in turn cause pituitary gland to release its hormones This is a slower communication process than the chemical communication that occurs between neurons. ...
... Hypothalamus releases hormones or releasing factors which in turn cause pituitary gland to release its hormones This is a slower communication process than the chemical communication that occurs between neurons. ...
1 - Lone Star College
... Sense of Smell, cont 2. How the brain receives odor information a. Nerve fibers lead to the olfactory bulb b. Combinations of activated receptor proteins account for different odors c. An odor’s signature is determined by which neurons are stimulated in the olfactory bulb d. Neurons send signals th ...
... Sense of Smell, cont 2. How the brain receives odor information a. Nerve fibers lead to the olfactory bulb b. Combinations of activated receptor proteins account for different odors c. An odor’s signature is determined by which neurons are stimulated in the olfactory bulb d. Neurons send signals th ...
M555 Medical Neuroscience
... gastrointestinal tract for newborns like J.G. This disorder involves the autonomic/enteric nervous systems and is one of the most common congenital anorectal malformations (1/5,500 births, four times more frequent in males). Neural crest may have failed to migrate toward the developing colon and rec ...
... gastrointestinal tract for newborns like J.G. This disorder involves the autonomic/enteric nervous systems and is one of the most common congenital anorectal malformations (1/5,500 births, four times more frequent in males). Neural crest may have failed to migrate toward the developing colon and rec ...
The Nervous System
... and are replaced, many neurons are never replaced when they die. In fact, you have fewer neurons when you are old compared to when you are young. On the other hand, data published in November 1998 show that in one area of the brain (the hippocampus), new neurons CAN grow in adult humans. Neurons can ...
... and are replaced, many neurons are never replaced when they die. In fact, you have fewer neurons when you are old compared to when you are young. On the other hand, data published in November 1998 show that in one area of the brain (the hippocampus), new neurons CAN grow in adult humans. Neurons can ...
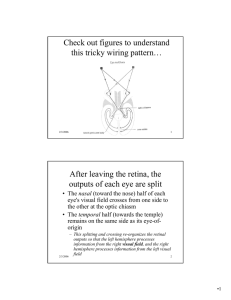
After leaving the retina, the outputs of each eye are split
... • Receptive fields often have a long, narrow bar of light (ON) and flanking (OFF) parts • Other types are the opposite (responding to dark bars) or simply respond to a light/dark edge ...
... • Receptive fields often have a long, narrow bar of light (ON) and flanking (OFF) parts • Other types are the opposite (responding to dark bars) or simply respond to a light/dark edge ...
Check out figures to understand this tricky wiring pattern… After
... • Receptive fields often have a long, narrow bar of light (ON) and flanking (OFF) parts • Other types are the opposite (responding to dark bars) or simply respond to a light/dark edge ...
... • Receptive fields often have a long, narrow bar of light (ON) and flanking (OFF) parts • Other types are the opposite (responding to dark bars) or simply respond to a light/dark edge ...
Research Proposal: Nivedita Chatterjee
... glial cells have been mapped fully and the data is available. In spite of being a relatively simple organism, it is capable of a surprising variety of behaviors. It shows adaptability to changing conditions as well as learning. I will be developing tools and strains which would allow studying change ...
... glial cells have been mapped fully and the data is available. In spite of being a relatively simple organism, it is capable of a surprising variety of behaviors. It shows adaptability to changing conditions as well as learning. I will be developing tools and strains which would allow studying change ...
lec12
... • This is more efficient than using a neuron for each fine cell. – It loses by needing 3 arrays – It wins by a factor of 3x3 per ...
... • This is more efficient than using a neuron for each fine cell. – It loses by needing 3 arrays – It wins by a factor of 3x3 per ...
as a PDF - University of Sussex
... However sparse coding is not the only way to reduce energy consumption by neurons using action potentials (APs). Changing the kinetics of the ion channels involved in generating the spike can reduce the energy requirements of the APs. Sengupta et al. [22] show that considerable differences in the re ...
... However sparse coding is not the only way to reduce energy consumption by neurons using action potentials (APs). Changing the kinetics of the ion channels involved in generating the spike can reduce the energy requirements of the APs. Sengupta et al. [22] show that considerable differences in the re ...
Somatosensory system
... -- Chemicals: histamine, bradykinin, substance P, ATP, serotonin, acetylcholine, acids, high K+ Three types: 1. Mechano-sensitive nociceptors (high threshold) 2. Thermo-sensitive nociceptors (high threshold) 3. Polymodal (chemo-sensitive) nociceptors ...
... -- Chemicals: histamine, bradykinin, substance P, ATP, serotonin, acetylcholine, acids, high K+ Three types: 1. Mechano-sensitive nociceptors (high threshold) 2. Thermo-sensitive nociceptors (high threshold) 3. Polymodal (chemo-sensitive) nociceptors ...
Lecture Exam #3 Review Slides
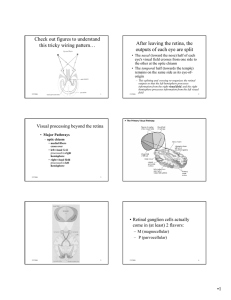
... • Definition: the area of the retina (or visual field) in which light signals evoke responses • It’s a property of the cell, not a cell or a part of the cell • It depends largely on the synaptic inputs to the cell and to some degree the biophysical property of the cell itself ...
... • Definition: the area of the retina (or visual field) in which light signals evoke responses • It’s a property of the cell, not a cell or a part of the cell • It depends largely on the synaptic inputs to the cell and to some degree the biophysical property of the cell itself ...
Primer
... arranged in columns 30–50 microns wide which run perpendicularly between the white matter and the pial surface (Figure 1d). The physiological investigations of Mountcastle, Hubel and Wiesel, beginning in the late 1950s, showed that neurons in the same column have similar physiological properties, an ...
... arranged in columns 30–50 microns wide which run perpendicularly between the white matter and the pial surface (Figure 1d). The physiological investigations of Mountcastle, Hubel and Wiesel, beginning in the late 1950s, showed that neurons in the same column have similar physiological properties, an ...
Skin Structure
... • Contains blood vessels that help regulate body temperature • All tissues are held together by fibres ...
... • Contains blood vessels that help regulate body temperature • All tissues are held together by fibres ...
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Sensory Physiology and the Thalamus
... • Motor efferents (from cortex to spinal cord) bypass thalamus ...
... • Motor efferents (from cortex to spinal cord) bypass thalamus ...
Synaptic Responses of Cortical Pyramidal Neurons to Light
... B, An extracellularrecordingof unit activity in the molecularlayerof the cortex(tap truce) revealsneuronsdischarging in response to a flashof light. The latencyof unit firing corresponds to the latencyof IPSPsrecordedintracellularlyin a nearbycorticalpyramidalneuron(lower truce). C, Schematicof the ...
... B, An extracellularrecordingof unit activity in the molecularlayerof the cortex(tap truce) revealsneuronsdischarging in response to a flashof light. The latencyof unit firing corresponds to the latencyof IPSPsrecordedintracellularlyin a nearbycorticalpyramidalneuron(lower truce). C, Schematicof the ...
Autonomic Nervous System Period 5 Jacquelene Hanein, Karina
... ex) knee jerk tests that a doctor gives ...
... ex) knee jerk tests that a doctor gives ...
HBNervous
... Amphetamines - activate Dopamine, Serotonin, and NE receptors (speed, crank) NE and Serotonin reuptake inhibitors - used to treat depression (Prozac) L-Dopa used to treat Parkinson's Disease The Brain is the master control center, directing output through the spinal cord and including homeostatic ce ...
... Amphetamines - activate Dopamine, Serotonin, and NE receptors (speed, crank) NE and Serotonin reuptake inhibitors - used to treat depression (Prozac) L-Dopa used to treat Parkinson's Disease The Brain is the master control center, directing output through the spinal cord and including homeostatic ce ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Coast Colleges Home Page
... Sensory Receptors Receptors are sensitive only to specific stimuli Free nerve endings (pain, temp, itch, tickle) Encapsulated nerve endings - Meissner’s & Pacinian corpuscles, Stretch receptors Complex, clusters of cells (sound, light, taste, balance) ...
... Sensory Receptors Receptors are sensitive only to specific stimuli Free nerve endings (pain, temp, itch, tickle) Encapsulated nerve endings - Meissner’s & Pacinian corpuscles, Stretch receptors Complex, clusters of cells (sound, light, taste, balance) ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... Sensory Receptors Receptors are sensitive only to specific stimuli Free nerve endings (pain, temp, itch, tickle) Encapsulated nerve endings - Meissner’s & Pacinian corpuscles, Stretch receptors Complex, clusters of cells (sound, light, taste, balance) ...
... Sensory Receptors Receptors are sensitive only to specific stimuli Free nerve endings (pain, temp, itch, tickle) Encapsulated nerve endings - Meissner’s & Pacinian corpuscles, Stretch receptors Complex, clusters of cells (sound, light, taste, balance) ...
the structure of the nervous system
... • It delivers sensory information to the CNS and carries motor commands to peripheral tissues and systems. • Bundles of axons, or nerve fibers, carry sensory information and motor commands in the PNS. • The PNS is divided into afferent and ...
... • It delivers sensory information to the CNS and carries motor commands to peripheral tissues and systems. • Bundles of axons, or nerve fibers, carry sensory information and motor commands in the PNS. • The PNS is divided into afferent and ...
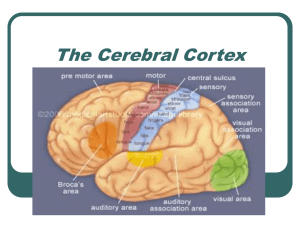
The Cerebral Cortex
... Sensory cortex (strip) lies within the parietal lobe & therefore this lobe’s association areas work with the sensory cortex to process sensory signals for accurate perception. The more sensitive the body region, the larger the sensory cortex devoted to it (lips, fingers…) ...
... Sensory cortex (strip) lies within the parietal lobe & therefore this lobe’s association areas work with the sensory cortex to process sensory signals for accurate perception. The more sensitive the body region, the larger the sensory cortex devoted to it (lips, fingers…) ...
Notes – Neurons and the nervous system
... How do we process and respond to information from the outside world? Sensory neurons, which are part of the PNS, detect changes in the world around us and then transmit that information to neurons in the CNS (brain and spinal cord), where the information gets processed and integrated with informa ...
... How do we process and respond to information from the outside world? Sensory neurons, which are part of the PNS, detect changes in the world around us and then transmit that information to neurons in the CNS (brain and spinal cord), where the information gets processed and integrated with informa ...
The Auditory Pathway: Transmission between Hair Cells and Eighth
... inferior colliculus (the nucleus of the lateral lemniscus is a synaptic way station for some of these fibers). Neurons in the ventral cochlear nucleus also provide collateral branches to both the ipsilateral and contralateral superior olivary nuclei. Third-order cells in the olivary nuclei, in turn, ...
... inferior colliculus (the nucleus of the lateral lemniscus is a synaptic way station for some of these fibers). Neurons in the ventral cochlear nucleus also provide collateral branches to both the ipsilateral and contralateral superior olivary nuclei. Third-order cells in the olivary nuclei, in turn, ...
Nervous Tissue
... – unipolar neurons = one process only(develops from a bipolar) • are always sensory neurons ...
... – unipolar neurons = one process only(develops from a bipolar) • are always sensory neurons ...
Orexin-A excites rat lateral vestibular nucleus neurons and improves
... Orexin is a newly discovered peptide which is synthesized exclusively within the lateral hypothalamic area and perifornical area. Lack of orexin neurons causes narcolepsy-cataplexy, which is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, premature transitions to REM sleep, and sudden skeletal muscle ...
... Orexin is a newly discovered peptide which is synthesized exclusively within the lateral hypothalamic area and perifornical area. Lack of orexin neurons causes narcolepsy-cataplexy, which is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, premature transitions to REM sleep, and sudden skeletal muscle ...