Nervous System - University of Nevada, Las Vegas
... The neural tube becomes the CNS There is a three-phase process of differentiation: – Proliferation of cells needed for development – Migration – cells become amitotic and move externally ...
... The neural tube becomes the CNS There is a three-phase process of differentiation: – Proliferation of cells needed for development – Migration – cells become amitotic and move externally ...
NervousSystem3
... pale with this stain, providing contrast. The large grey area dorsally is made up of a felt-work of fibers and neuron cell bodies, the reticular formation. From Gray’s Anatomy, 18th US edition; 1920. The figure was taken from Wikipedia. ...
... pale with this stain, providing contrast. The large grey area dorsally is made up of a felt-work of fibers and neuron cell bodies, the reticular formation. From Gray’s Anatomy, 18th US edition; 1920. The figure was taken from Wikipedia. ...
Exam Questions - NEVR2030 - Autumn 2012
... 1. Name one advantage and one disadvantage of lesion studies as a method for mapping brain functions. (2) 2. Spiral ganglion cells are bipolar cells that innervate peripheral sensory cells (hair cells in the inner ear) and send an axon into the 8th cranial nerve. In which ganglia do we find comp ...
... 1. Name one advantage and one disadvantage of lesion studies as a method for mapping brain functions. (2) 2. Spiral ganglion cells are bipolar cells that innervate peripheral sensory cells (hair cells in the inner ear) and send an axon into the 8th cranial nerve. In which ganglia do we find comp ...
“Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
... In terms of sensory receptors, _____respond to variations in light, but ______respond to changes in temperature. ...
... In terms of sensory receptors, _____respond to variations in light, but ______respond to changes in temperature. ...
chapter – 21
... • When thorn picks the hand the stimulus is received by a receptor in the skin. • Receptor sets sensory impulse and is carried to spinal cord through afferent neurons. • From there it passes outwards through the motor neuron and reaches either a muscle or gland cell where response is felt. 3. Explai ...
... • When thorn picks the hand the stimulus is received by a receptor in the skin. • Receptor sets sensory impulse and is carried to spinal cord through afferent neurons. • From there it passes outwards through the motor neuron and reaches either a muscle or gland cell where response is felt. 3. Explai ...
study notes quiz 1
... (b) Autonomic Nervous System: (i) receives unconscious sensory input from internal organs (e.g., the acid content of stomach) (ii) unconcious control of movement and organs (e.g., heartbeat, breathing, reflexes) (iii) Controls itself – it is autonomic and will function without upper cognitive functi ...
... (b) Autonomic Nervous System: (i) receives unconscious sensory input from internal organs (e.g., the acid content of stomach) (ii) unconcious control of movement and organs (e.g., heartbeat, breathing, reflexes) (iii) Controls itself – it is autonomic and will function without upper cognitive functi ...
File
... in the nervous system that carries information from the various parts of the body to the brain. It’s like a large communication cable The spinal cord is also known as the reflex centre ...
... in the nervous system that carries information from the various parts of the body to the brain. It’s like a large communication cable The spinal cord is also known as the reflex centre ...
Neocortex Cell Types
... Dendritic spines may be the sites of synapses that are selectively modified as a result of learning. Most or all pyramidal cells have long axons that leave the cortex to reach either other cortical areas or to various subcortical sites. Therefore, pyramidal cells are the principal output neurons. ...
... Dendritic spines may be the sites of synapses that are selectively modified as a result of learning. Most or all pyramidal cells have long axons that leave the cortex to reach either other cortical areas or to various subcortical sites. Therefore, pyramidal cells are the principal output neurons. ...
Human Biology Human Body Systems Nervous System
... once in motion the ACTION POTENTIAL keeps the impulse moving along the axon to the SYNAPSE ...
... once in motion the ACTION POTENTIAL keeps the impulse moving along the axon to the SYNAPSE ...
Factual - Cengage
... projected onto the retina. The retina converts the light rays into nerve impulses, which then travel via the optic nerve to the optic chiasm. At the optic chiasm, the axons from the inside half of each eye cross over and project along two divergent pathways to the opposite cerebral hemisphere. ...
... projected onto the retina. The retina converts the light rays into nerve impulses, which then travel via the optic nerve to the optic chiasm. At the optic chiasm, the axons from the inside half of each eye cross over and project along two divergent pathways to the opposite cerebral hemisphere. ...
Auditory: Stimulus Auditory
... • Receptors: Mechanoreceptors & Free nerve endings • Transduction: Physical movement, change in temp., or chemicals released by tissue damage • Afferent Pathway: Dorsal column pathway for touch, anterolateral pathway for temp and pain • CNS Areas & Perceptions: Postcentral gyrus is the primary ...
... • Receptors: Mechanoreceptors & Free nerve endings • Transduction: Physical movement, change in temp., or chemicals released by tissue damage • Afferent Pathway: Dorsal column pathway for touch, anterolateral pathway for temp and pain • CNS Areas & Perceptions: Postcentral gyrus is the primary ...
Altman presentation - NeuronDevelopment.org
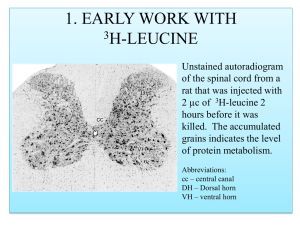
... • 3H-thymidine autoradiography is the ideal technique to study cell proliferation. • The nervous system contains many proliferating glial cells in mature animals. • To our surprise, we found evidence that the small granule cells (NEURONS) in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus are generated in the ...
... • 3H-thymidine autoradiography is the ideal technique to study cell proliferation. • The nervous system contains many proliferating glial cells in mature animals. • To our surprise, we found evidence that the small granule cells (NEURONS) in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus are generated in the ...
Neurons
... • Has two main parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • BOTH are composed of neurons, or nerve cells, that transmit messages to different parts of the body. • Neurons have three main parts: cell body (produces energy), dendrites (DELIVERS info to the cell body), and axo ...
... • Has two main parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • BOTH are composed of neurons, or nerve cells, that transmit messages to different parts of the body. • Neurons have three main parts: cell body (produces energy), dendrites (DELIVERS info to the cell body), and axo ...
The relationship between the activity of neurons recorded
... Accurate decoding of the neural activity in the primary motor cortex (M1) could be very useful for brain machine interface applications such as computer displays or prosthetic limbs. In this study we examined information coding in M1 neurons to elucidate the relationship between the activity of M1 n ...
... Accurate decoding of the neural activity in the primary motor cortex (M1) could be very useful for brain machine interface applications such as computer displays or prosthetic limbs. In this study we examined information coding in M1 neurons to elucidate the relationship between the activity of M1 n ...
Nervous System Objectives
... 10. Label a diagram of a synaptic region and tell where neurotransmitters are released, direction of impulse travel, ion flow, and fusion of the neurotransmitter occur. 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous syst ...
... 10. Label a diagram of a synaptic region and tell where neurotransmitters are released, direction of impulse travel, ion flow, and fusion of the neurotransmitter occur. 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous syst ...
November 13th Notes (Nervous System)
... Communication comes in the form of electrochemical messages relayed to and from the brain, or a series of chemical messengers carried in the blood. Through a series of adjustments, all systems of the body are regulated to maintain the ...
... Communication comes in the form of electrochemical messages relayed to and from the brain, or a series of chemical messengers carried in the blood. Through a series of adjustments, all systems of the body are regulated to maintain the ...
- Patuakhali Science and Technology University
... prey. Covering several ocelli on each side of the head seems to impair form vision, so the brain must be able to construct a coarse mosaic of nearby objects from the visual fields of adjacent ocelli. Extra-ocular Photoreception Some (perhaps most) insects respond to changes in light intensity even w ...
... prey. Covering several ocelli on each side of the head seems to impair form vision, so the brain must be able to construct a coarse mosaic of nearby objects from the visual fields of adjacent ocelli. Extra-ocular Photoreception Some (perhaps most) insects respond to changes in light intensity even w ...
Biology 13A
... b. may be excitatory or inhibitory c. are always inhibitory d. depend on the response of the membrane receptor e. b and d from above are correct 5. All of the following apply to preganglionic neurons of the ANS sympathetic division except a. their cell bodies are located between spinal segments T1 a ...
... b. may be excitatory or inhibitory c. are always inhibitory d. depend on the response of the membrane receptor e. b and d from above are correct 5. All of the following apply to preganglionic neurons of the ANS sympathetic division except a. their cell bodies are located between spinal segments T1 a ...
Human Physiology
... maintains homeostasis. Explain how the nervous sends messages and communicates with different parts of the body. Understand the impact of depressants and stimulants on brain chemistry and function. ...
... maintains homeostasis. Explain how the nervous sends messages and communicates with different parts of the body. Understand the impact of depressants and stimulants on brain chemistry and function. ...
Ch 10 Brain Damage & Neuroplasticity (pt2)
... Regrowth from proximal stump 2-3 days after axonal damage Does not necessarily mean that function will be returned ...
... Regrowth from proximal stump 2-3 days after axonal damage Does not necessarily mean that function will be returned ...
VISION John Gabrieli Melissa Troyer 9.00
... • A piano can only emit its own notes – it can’t sound like a clarinet. Similarly perceptions are evoked by the world, but they generate experiences limited by the neural structures of our brain. • Our percepts are evoked by nature; but they are personal and not a copy of nature. ...
... • A piano can only emit its own notes – it can’t sound like a clarinet. Similarly perceptions are evoked by the world, but they generate experiences limited by the neural structures of our brain. • Our percepts are evoked by nature; but they are personal and not a copy of nature. ...
Slide 1 - MisterSyracuse.com
... 15. Why is afterhyperpolarization, or undershoot, so very important to a neuron? ...
... 15. Why is afterhyperpolarization, or undershoot, so very important to a neuron? ...
LGN
... LGN interneurons make only local connections. There are more interneurons than relay neurons! LGN neurons get feedback connections from cortex. (The one-way connection from retina to rest of brain is unique in the visual system). LGN gets other inputs as well. For example: from brainstem and perigen ...
... LGN interneurons make only local connections. There are more interneurons than relay neurons! LGN neurons get feedback connections from cortex. (The one-way connection from retina to rest of brain is unique in the visual system). LGN gets other inputs as well. For example: from brainstem and perigen ...
Chapter 4 Outline
... d. Transmitters cross the synaptic cleft and briefly lock onto receptor sites on the receiving dendrites e. They can increase or decrease the likelihood that the receiving neuron will generate an action potential f. Receiving neuron averages the excitatory and inhibitory incoming messages to determi ...
... d. Transmitters cross the synaptic cleft and briefly lock onto receptor sites on the receiving dendrites e. They can increase or decrease the likelihood that the receiving neuron will generate an action potential f. Receiving neuron averages the excitatory and inhibitory incoming messages to determi ...