cell body
... Dendrites are highly branched, tapering processes which either end in specialized sensory receptors (as in primary sensory neurons) or form synapses with neighboring neurons from which they receive stimuli. In general, dendrites function as the major sites of information input into the neuron Ea ...
... Dendrites are highly branched, tapering processes which either end in specialized sensory receptors (as in primary sensory neurons) or form synapses with neighboring neurons from which they receive stimuli. In general, dendrites function as the major sites of information input into the neuron Ea ...
Neuro2
... 9) A neuropeptide is an amino acid chain released in large dense-core vesicles. Often, the neuropeptide acts as a modulator to the neurotransmitters or simply as a synaptic transmitter. 10) The activity of neurotransmitters and neuropeptides is terminated when they stimulate/destimulate (I totally j ...
... 9) A neuropeptide is an amino acid chain released in large dense-core vesicles. Often, the neuropeptide acts as a modulator to the neurotransmitters or simply as a synaptic transmitter. 10) The activity of neurotransmitters and neuropeptides is terminated when they stimulate/destimulate (I totally j ...
The nervous system
... Highly concentrated potassium ions inside nerve cells have tendency to diffuse outside the nerve cells Highly concentrated sodium ions outside the nerve cell tend to diffuse into the nerve cell As potassium diffuses out of the neuron, sodium diffuses into the neuron Positively charged ions move both ...
... Highly concentrated potassium ions inside nerve cells have tendency to diffuse outside the nerve cells Highly concentrated sodium ions outside the nerve cell tend to diffuse into the nerve cell As potassium diffuses out of the neuron, sodium diffuses into the neuron Positively charged ions move both ...
UNIT 4: Sensation and Perception I. Overview A. Sensation
... Frequency theory – explains the brain reads pitch by monitoring the frequency of neural impulses traveling up the auditory nerve b. ...
... Frequency theory – explains the brain reads pitch by monitoring the frequency of neural impulses traveling up the auditory nerve b. ...
“Brains on Beads” System Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Me
... surface-to-volume ratios of 5.9 and 12.5 μm-1 for neurons and astrocytes, respectively, from rat supraoptic media flow rate for beads only (open nucleus. Combined with the preexchange lifetimes measured herein, these ratios yield membrane circles) and a mixed neuron/astrocyte cell permeabilities of ...
... surface-to-volume ratios of 5.9 and 12.5 μm-1 for neurons and astrocytes, respectively, from rat supraoptic media flow rate for beads only (open nucleus. Combined with the preexchange lifetimes measured herein, these ratios yield membrane circles) and a mixed neuron/astrocyte cell permeabilities of ...
simple cell
... • small and stellate shape (spiny stellate or smooth stellate) • local interneurons (smooth) • either excitatory (spiny, with many dendritic spines, glutamate) or inhibitory (smooth, few spines, GABA) ...
... • small and stellate shape (spiny stellate or smooth stellate) • local interneurons (smooth) • either excitatory (spiny, with many dendritic spines, glutamate) or inhibitory (smooth, few spines, GABA) ...
Trigeminal Ganglion Cell
... Each neuron receives and combines multiple inputs to determine, whether to transmit an action potential to the next target in its network (Neuron, Muscle, Gland, or Organ). ...
... Each neuron receives and combines multiple inputs to determine, whether to transmit an action potential to the next target in its network (Neuron, Muscle, Gland, or Organ). ...
The Biological Basis of Behavior Why should Psychologists be
... outside the cell membrane make the neuron slightly more negative inside the cell than outside. When the neuron is stimulated sufficiently and reaches its “threshold of excitation,” the membrane becomes more porous, allowing the Na+ to rush inside the cell. That event causes a change in polarity call ...
... outside the cell membrane make the neuron slightly more negative inside the cell than outside. When the neuron is stimulated sufficiently and reaches its “threshold of excitation,” the membrane becomes more porous, allowing the Na+ to rush inside the cell. That event causes a change in polarity call ...
The Body and the Brain
... Really, sexual attraction is very chemical (or hormonal) because women have higher libido’s when they are ovulating because there is more estrogen in their body. ...
... Really, sexual attraction is very chemical (or hormonal) because women have higher libido’s when they are ovulating because there is more estrogen in their body. ...
EXAMPLE ONLINE ENTRANCE EXAMINATION Bio
... 2. The geometry of a water molecule is: a. Rectangular. b. Tetrahedral. c. Angular. d. Linear. ...
... 2. The geometry of a water molecule is: a. Rectangular. b. Tetrahedral. c. Angular. d. Linear. ...
PsychScich04
... • Ventral stream appears to be specialized for the perception and recognition of objects • Dorsal stream seems to be specialized for spatial perception (determining where an object is) • These two processing streams are therefore known as the “what” stream and the “where” stream ...
... • Ventral stream appears to be specialized for the perception and recognition of objects • Dorsal stream seems to be specialized for spatial perception (determining where an object is) • These two processing streams are therefore known as the “what” stream and the “where” stream ...
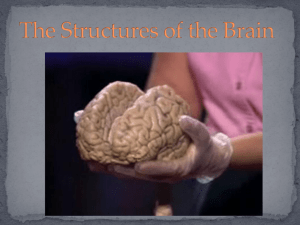
The Structures of the Brain
... almond-shaped neural clusters linked to the emotions of fear and anger. -Discriminates objects for ...
... almond-shaped neural clusters linked to the emotions of fear and anger. -Discriminates objects for ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... another etc. • Cannot go in reverse due to the refractory period (time during which membrane is returning to resting potential) • Travel faster in myelinated axons and in largerdiameter axons – Squid axons are big, so their response time is rapid! ...
... another etc. • Cannot go in reverse due to the refractory period (time during which membrane is returning to resting potential) • Travel faster in myelinated axons and in largerdiameter axons – Squid axons are big, so their response time is rapid! ...
CHAPTER 11 Nervous Tissue - Austin Community College
... Insulating layer around a nerve Formed by oligodendrocytes in CNS and Schwann cells in PNS Composed of a lipoprotein with phospholipids, glycolipids and cholesterol. Myelination is the process of myelin formation Myelin allows nerve conduction to be 150 x faster than nonmyelinated nerves. This occcu ...
... Insulating layer around a nerve Formed by oligodendrocytes in CNS and Schwann cells in PNS Composed of a lipoprotein with phospholipids, glycolipids and cholesterol. Myelination is the process of myelin formation Myelin allows nerve conduction to be 150 x faster than nonmyelinated nerves. This occcu ...
SompolinskyAug09
... describing a cellular process by which sensory neurons in the brain can automatically adjust their perceptual clocks and thus correct large temporal variations in the rate of sounds and speech that arrive from the environment. According to their findings, which were recently published in the PLoS Bi ...
... describing a cellular process by which sensory neurons in the brain can automatically adjust their perceptual clocks and thus correct large temporal variations in the rate of sounds and speech that arrive from the environment. According to their findings, which were recently published in the PLoS Bi ...
HUMAN ANATOMY
... • Axon – is the long (sometimes up to the 1 m or more) extension, which sends outgoing signals to the cells. ...
... • Axon – is the long (sometimes up to the 1 m or more) extension, which sends outgoing signals to the cells. ...
AP Psychology - Ms. Hofmann`s Website
... Peripheral Nervous system on this website. Read the two scenarios on the right that begin with, “It’s a nice sunny day…” Draw yourself in each of these situations and in the caption explain what is going on in your body. ...
... Peripheral Nervous system on this website. Read the two scenarios on the right that begin with, “It’s a nice sunny day…” Draw yourself in each of these situations and in the caption explain what is going on in your body. ...
Evolution and analysis of minimal neural circuits for klinotaxis in
... C. elegans performs a diverse set of orientation behaviors, including chemotaxis to tastants, odors, osmolarity, electrotaxis, thermotaxis, etc. Nearly all work on C. elegans chemotaxis was based on klinokinesis (biased random walk). Recently, Iino and colleagues have described a complementary strat ...
... C. elegans performs a diverse set of orientation behaviors, including chemotaxis to tastants, odors, osmolarity, electrotaxis, thermotaxis, etc. Nearly all work on C. elegans chemotaxis was based on klinokinesis (biased random walk). Recently, Iino and colleagues have described a complementary strat ...
Nervous System Student Notes File
... neurotransmitters which open K+ or Cl- gates causing hyperpolarization d) A single EPSP is rarely strong enough to trigger an action potential, although and additive effect, _______________________________, from several terminals can trigger a neuron to fire 1) __________________________________ is ...
... neurotransmitters which open K+ or Cl- gates causing hyperpolarization d) A single EPSP is rarely strong enough to trigger an action potential, although and additive effect, _______________________________, from several terminals can trigger a neuron to fire 1) __________________________________ is ...
lesson 6
... • Uneven concentrations of Na+ (outside) and K+ (inside) on either side of neuron membrane results in the inside of the neuron being 70 mV less positive than the outside ...
... • Uneven concentrations of Na+ (outside) and K+ (inside) on either side of neuron membrane results in the inside of the neuron being 70 mV less positive than the outside ...
File chapter 2 vocab pp
... of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions. ...
... of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions. ...
Gnostic cells in the 21st century
... “We perceive people, human faces, animals, small objects from nearby, large objects from afar (…). However, neither humans nor animal notice lines, edges, corners, “tongues”, or “rods,” which were the adequate stimuli for the units so far investigated.” “Having at our disposal the recent data derive ...
... “We perceive people, human faces, animals, small objects from nearby, large objects from afar (…). However, neither humans nor animal notice lines, edges, corners, “tongues”, or “rods,” which were the adequate stimuli for the units so far investigated.” “Having at our disposal the recent data derive ...
Human Nerve Chapter
... respond to changes in the external environment. In vertebrates, these functions are controlled by two organ systems that integrate and coordinate with each other, the nervous and the endocrine systems. Nervous systems perform these basic functions: Receiving sensory input from the internal and exter ...
... respond to changes in the external environment. In vertebrates, these functions are controlled by two organ systems that integrate and coordinate with each other, the nervous and the endocrine systems. Nervous systems perform these basic functions: Receiving sensory input from the internal and exter ...
Muscle/Nervous tissue - Nutley Public Schools
... • Main component of nervous system – Brain, spinal cord, nerves – Regulates and controls body functions ...
... • Main component of nervous system – Brain, spinal cord, nerves – Regulates and controls body functions ...