Nervous Tissue NOTES
... Cell body- central unit of neuron. Contains nucleus, cytoplasm, etc. Axon- process that takes impulses away from the cell body. Neurons have at least 1 axon. ...
... Cell body- central unit of neuron. Contains nucleus, cytoplasm, etc. Axon- process that takes impulses away from the cell body. Neurons have at least 1 axon. ...
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
... The membrane potential of a nerve cell at rest is called its resting potential. It exists because of differences in the ionic composition of the extracellular and intracellular fluids across the plasma membrane. The concentration of Na+ is higher outside the cell, whereas the concentration of K+ ...
... The membrane potential of a nerve cell at rest is called its resting potential. It exists because of differences in the ionic composition of the extracellular and intracellular fluids across the plasma membrane. The concentration of Na+ is higher outside the cell, whereas the concentration of K+ ...
Biological Processes Neurons
... the PNS and send them to CNS. Motor neurons take signals from CNS and send them to the PNS. This is known as a reflex or a reflex arc ...
... the PNS and send them to CNS. Motor neurons take signals from CNS and send them to the PNS. This is known as a reflex or a reflex arc ...
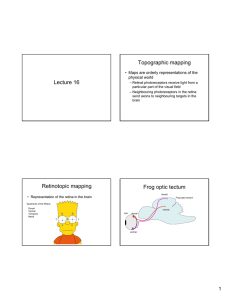
Lecture 16 Topographic mapping Retinotopic mapping Frog optic
... – D/V mapping by EphrinB • EphrinB mediates attractive cues with bidirectional signaling ...
... – D/V mapping by EphrinB • EphrinB mediates attractive cues with bidirectional signaling ...
The Nervous System
... and midbrain. – Medulla oblongata controls involuntary activities such as heart rate and breathing – Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. ...
... and midbrain. – Medulla oblongata controls involuntary activities such as heart rate and breathing – Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. ...
This Week in The Journal - Journal of Neuroscience
... neither high-frequency nor theta-burst stimulation induced LTP or LTD in interneurons that expressed cannabinoid receptors. ...
... neither high-frequency nor theta-burst stimulation induced LTP or LTD in interneurons that expressed cannabinoid receptors. ...
The Nervous System
... and midbrain. – Medulla oblongata controls involuntary activities such as heart rate and breathing – Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. ...
... and midbrain. – Medulla oblongata controls involuntary activities such as heart rate and breathing – Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. ...
Sensory Neuron Processing
... o Each sensory neuron responds primarily to only one particular type of stimulus This is called it’s normal – Example: photoreceptors, chemoreceptors The dendrite of the sensory neuron transduces (converts) the stimulus into changes in membrane potential. stimulus >>>>> increased permeability of ...
... o Each sensory neuron responds primarily to only one particular type of stimulus This is called it’s normal – Example: photoreceptors, chemoreceptors The dendrite of the sensory neuron transduces (converts) the stimulus into changes in membrane potential. stimulus >>>>> increased permeability of ...
Biosychology_Intro Reading
... branches: the sympathetic system regulates the flight-or-fight responses, while the parasympathetic system helps maintain normal body functions and conserves physical resources. The Brain The outermost part of the brain is known as the cerebral cortex. This portion of the brain is responsible for fu ...
... branches: the sympathetic system regulates the flight-or-fight responses, while the parasympathetic system helps maintain normal body functions and conserves physical resources. The Brain The outermost part of the brain is known as the cerebral cortex. This portion of the brain is responsible for fu ...
Neurology, Neurons, and EEG
... existence of our minds. Neurons are also found in the peripheral nervous system, but we will ignore these in this paper since we are addressing the neurons of the brain so as to be able to get a grasp of what an EEG is measuring. Neurons receive "information" from other neurons (input), they also se ...
... existence of our minds. Neurons are also found in the peripheral nervous system, but we will ignore these in this paper since we are addressing the neurons of the brain so as to be able to get a grasp of what an EEG is measuring. Neurons receive "information" from other neurons (input), they also se ...
Andrea Sookchan Jasmine Hodge Billy Chang
... space between two connected neurons. This is where the message is transmitted from one cell to another. Neurotransmitters travel along the axon to the terminal buttons of the first neuron and are released in the synaptic gap. They are received by the second neuron on its receptor sites on the dend ...
... space between two connected neurons. This is where the message is transmitted from one cell to another. Neurotransmitters travel along the axon to the terminal buttons of the first neuron and are released in the synaptic gap. They are received by the second neuron on its receptor sites on the dend ...
BrainMechanismsofUnconsciousInference2010
... The baseline firing rate of the neuron is thought to depend on a constant background input called its ‘bias’. When other neurons are active, their influences are combined with the bias to yield a quantity called the ‘net input’. The influence of a neuron j on another neuron i depends on the activati ...
... The baseline firing rate of the neuron is thought to depend on a constant background input called its ‘bias’. When other neurons are active, their influences are combined with the bias to yield a quantity called the ‘net input’. The influence of a neuron j on another neuron i depends on the activati ...
MBBC Junior Neuroscience E-Book v1
... controlling movement and in the planning and coordinating of behavior. GAMMA-AMINO BUTYRIC ACID (GABA) - An amino acid transmitter in the brain whose primary function is to inhibit the firing of nerve cells. GLIA - Specialized cells that nourish and support neurons. GLUTAMATE - An amino acid neurotr ...
... controlling movement and in the planning and coordinating of behavior. GAMMA-AMINO BUTYRIC ACID (GABA) - An amino acid transmitter in the brain whose primary function is to inhibit the firing of nerve cells. GLIA - Specialized cells that nourish and support neurons. GLUTAMATE - An amino acid neurotr ...
Intro-The neuron
... 1. A scientific discipline: • Which parts of the brain are involved in visual processing? • Memory impairments - which memories are most/least affected? • What types of language problems can occur? What can these tell us about language? -> relating function to anatomy ...
... 1. A scientific discipline: • Which parts of the brain are involved in visual processing? • Memory impairments - which memories are most/least affected? • What types of language problems can occur? What can these tell us about language? -> relating function to anatomy ...
Adult Cortical Plasticity
... Long-term potentiation (LTP) and Long-term depression (LTD) -- Persistent increase or decrease in synaptic response due to repetitive activity, found in hippocampus and cortex -- Brief high-frequency stimulation – LTP Prolonged low-frequency stimulation – LTD Mechanism: 1. Induction of either LTP or ...
... Long-term potentiation (LTP) and Long-term depression (LTD) -- Persistent increase or decrease in synaptic response due to repetitive activity, found in hippocampus and cortex -- Brief high-frequency stimulation – LTP Prolonged low-frequency stimulation – LTD Mechanism: 1. Induction of either LTP or ...
13.1- neurons
... Not all nerve cells that have a myelin sheath have a neurilemma. Nerves within the brain that contain myelinated fibres are called white matter because the myelinated axons are whitish in colour. ...
... Not all nerve cells that have a myelin sheath have a neurilemma. Nerves within the brain that contain myelinated fibres are called white matter because the myelinated axons are whitish in colour. ...
doc nervous system notes
... They insulate, increase speed of nerve impulse (Saltatory Conduction) and are vital to regeneration of peripheral nerve processes. The exposed outer portion of the Schwann cell is called neurolemma. The myelin sheaths do not touch each other and the neuron is exposed at the Nodes of Ranvier Neurons: ...
... They insulate, increase speed of nerve impulse (Saltatory Conduction) and are vital to regeneration of peripheral nerve processes. The exposed outer portion of the Schwann cell is called neurolemma. The myelin sheaths do not touch each other and the neuron is exposed at the Nodes of Ranvier Neurons: ...
Neurons - Manatee School for the Arts
... • Neurons vary in size, shape & function • Mature neurons do NOT divide • All neurons have: • A cell body is the main component of a neuron. It contains cytoplasm, a cell membrane, a nucleus, & organelles. • The ER of a cell body is called the chromatophilic substance or nissl bodies (perform protei ...
... • Neurons vary in size, shape & function • Mature neurons do NOT divide • All neurons have: • A cell body is the main component of a neuron. It contains cytoplasm, a cell membrane, a nucleus, & organelles. • The ER of a cell body is called the chromatophilic substance or nissl bodies (perform protei ...
sensation.
... Did you write “The cat was the rat”? If you did you were incorrect. The correct answer is: “The cat SAW the rat” ...
... Did you write “The cat was the rat”? If you did you were incorrect. The correct answer is: “The cat SAW the rat” ...
Motor control
... Cerebellar function • It is clear that the cerebellum is important for coordinated motor actions. Just how it accomplishes this is in dispute: – One theory argues the cerebellum regulates the timing of movements so that the can be ...
... Cerebellar function • It is clear that the cerebellum is important for coordinated motor actions. Just how it accomplishes this is in dispute: – One theory argues the cerebellum regulates the timing of movements so that the can be ...
chapter30_Sensory Perception(1
... • The fourth somatosensory sense is muscle sense, which relates to the positioning of body parts • Muscle spindles and mechanoreceptors near joints and tendons contribute to muscle sense; the more a muscle stretches, the more frequently receptors fire ...
... • The fourth somatosensory sense is muscle sense, which relates to the positioning of body parts • Muscle spindles and mechanoreceptors near joints and tendons contribute to muscle sense; the more a muscle stretches, the more frequently receptors fire ...
Right vestibular nucleus
... (“smooth”) and fast (“saccadic”) in the other 3. When you induce it by spinning yourself around…. ...
... (“smooth”) and fast (“saccadic”) in the other 3. When you induce it by spinning yourself around…. ...
Stimulus Response Time Lab
... Introduction: The human nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord (Central Nervous System, CNS) and the nerves which branch out from the CNS, the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS). Sensory neurons of the PNS carry information to the CNS. Signals from the brain are carried to motor neuron ...
... Introduction: The human nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord (Central Nervous System, CNS) and the nerves which branch out from the CNS, the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS). Sensory neurons of the PNS carry information to the CNS. Signals from the brain are carried to motor neuron ...
The nervous system
... Highly concentrated potassium ions inside nerve cells have tendency to diffuse outside the nerve cells Highly concentrated sodium ions outside the nerve cell tend to diffuse into the nerve cell As potassium diffuses out of the neuron, sodium diffuses into the neuron Positively charged ions move both ...
... Highly concentrated potassium ions inside nerve cells have tendency to diffuse outside the nerve cells Highly concentrated sodium ions outside the nerve cell tend to diffuse into the nerve cell As potassium diffuses out of the neuron, sodium diffuses into the neuron Positively charged ions move both ...