From visual field to V1
... --gating visual information flow, via different modes (oscillations and bursting/tonic firing) ...
... --gating visual information flow, via different modes (oscillations and bursting/tonic firing) ...
ANPS 019 Black 11-09
... -contains a map of all skeletal muscles -Pyramidal neurons (multipolar neurons that sends info down to body) in this gyrus that project via the internal capsule to synapse in the brainstem or spinal cord; they talk to the neurons that contact the muscles (they do NOT directly synapse on the muscles! ...
... -contains a map of all skeletal muscles -Pyramidal neurons (multipolar neurons that sends info down to body) in this gyrus that project via the internal capsule to synapse in the brainstem or spinal cord; they talk to the neurons that contact the muscles (they do NOT directly synapse on the muscles! ...
autonomic nervous system
... exit the CNS from the brain stem and sacral regions of the spinal cord • Parasympathetic ganglia lie within or very close to the effector organs that the postganglionic neurons innervate ...
... exit the CNS from the brain stem and sacral regions of the spinal cord • Parasympathetic ganglia lie within or very close to the effector organs that the postganglionic neurons innervate ...
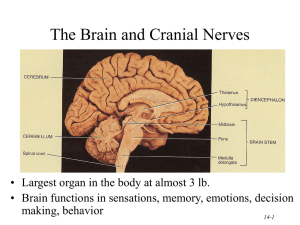
Sense Organs
... 3. CONCLUSION - Sensory input is essential to the integrity of personality and intellectual function. II. Classification of the senses. A. The Senses can be classified by their modality (form of the sensation) as either General (somatic and visceral) or Special. ...
... 3. CONCLUSION - Sensory input is essential to the integrity of personality and intellectual function. II. Classification of the senses. A. The Senses can be classified by their modality (form of the sensation) as either General (somatic and visceral) or Special. ...
14-1
... • Choroid plexus = capillaries covered by ependymal cells – 2 lateral ventricles, one within each cerebral hemisphere – 3rd ventricle – 4th ventricle ...
... • Choroid plexus = capillaries covered by ependymal cells – 2 lateral ventricles, one within each cerebral hemisphere – 3rd ventricle – 4th ventricle ...
Specialized Cells
... all the organs and are preset in skin, scalp, respiratory tract, and covers the human body. Skin ...
... all the organs and are preset in skin, scalp, respiratory tract, and covers the human body. Skin ...
Neural Axis Representing Target Range in the Auditory
... Range-sensitive neurons can be classified into two categories, tracking and range-tuned. The best delays (BD's) (8) of tracking neurons shorten and their delay-tuning curves become narrower as the bat changes the signal repetition rate and duration as it approaches a target. These neurons zero in on ...
... Range-sensitive neurons can be classified into two categories, tracking and range-tuned. The best delays (BD's) (8) of tracking neurons shorten and their delay-tuning curves become narrower as the bat changes the signal repetition rate and duration as it approaches a target. These neurons zero in on ...
Nature Versus Nurture
... connections as you might expect Remember that as you interact with others you change the structure of their nervous system and they change yours! § This also includes, yes….. removing and weakening synapses ...
... connections as you might expect Remember that as you interact with others you change the structure of their nervous system and they change yours! § This also includes, yes….. removing and weakening synapses ...
Time Zones
... 2. Name 2 things that can compromise neural communication (especially synaptic transmission): 3. Name the main function of the Myelin Sheath? 4. Name the 3 types of Neurons: 5. One word to describe all of a human’s cell nuclei (in regards to genetics)? 6. These long threads make a chromosome. Genes ...
... 2. Name 2 things that can compromise neural communication (especially synaptic transmission): 3. Name the main function of the Myelin Sheath? 4. Name the 3 types of Neurons: 5. One word to describe all of a human’s cell nuclei (in regards to genetics)? 6. These long threads make a chromosome. Genes ...
nervous system development and histology
... transmit information between neurons within the CNS; analyze inputs, • coordinate outputs are the most common type of neuron (20 billion)• are all multipolar• ...
... transmit information between neurons within the CNS; analyze inputs, • coordinate outputs are the most common type of neuron (20 billion)• are all multipolar• ...
The gustatory pathway - West Virginia University
... Arise from epithelial cells and are located on taste buds in the papillae of the tongue Detect different taste qualities each with a unique chemosensory mechanism Salty Sour Bitter Sweet Umami Innervated by the primary afferent fibers of cranial nerves VII, IX, and X ...
... Arise from epithelial cells and are located on taste buds in the papillae of the tongue Detect different taste qualities each with a unique chemosensory mechanism Salty Sour Bitter Sweet Umami Innervated by the primary afferent fibers of cranial nerves VII, IX, and X ...
ppt
... maggots eat the dead skin cells and bacteria. maggot therapy (also known as maggot debridement therapy (mdt), larval therapy, larva therapy, or larvae therapy) is the intentional introduction of live, disinfected maggots or fly larvae into non-healing skin or soft tissue wounds of a human or other a ...
... maggots eat the dead skin cells and bacteria. maggot therapy (also known as maggot debridement therapy (mdt), larval therapy, larva therapy, or larvae therapy) is the intentional introduction of live, disinfected maggots or fly larvae into non-healing skin or soft tissue wounds of a human or other a ...
Chp3 Weiten - Napa Valley College
... the power effects biology plays into our behavior. Much more complex than mere cause and effect, as ...
... the power effects biology plays into our behavior. Much more complex than mere cause and effect, as ...
Objective 1 | Explain why psychologists are concerned with human
... phrenology to scientific tests, but this early theory did help scientists to begin thinking about links among our biology, behavior, and mental processes. Pages: 53-54 Objective 2| Explain how viewing each person as a biopsychosocial system helps us understand human behavior, and discuss why researc ...
... phrenology to scientific tests, but this early theory did help scientists to begin thinking about links among our biology, behavior, and mental processes. Pages: 53-54 Objective 2| Explain how viewing each person as a biopsychosocial system helps us understand human behavior, and discuss why researc ...
Review Questions for Chapter 1: Studying the Nervous Systems of
... 1. Why do you have both rods and cones instead of just one type of photoreceptor? 2. Do you have more rods or cones in your retina? In your fovea? What accounts for the fact that your rods do not contribute to vision in daylight? 3. Draw a simplified diagram of the retina; label the five types of re ...
... 1. Why do you have both rods and cones instead of just one type of photoreceptor? 2. Do you have more rods or cones in your retina? In your fovea? What accounts for the fact that your rods do not contribute to vision in daylight? 3. Draw a simplified diagram of the retina; label the five types of re ...
Ch. 10 Outline
... A. One neuron sends impulses to several neurons B. Can amplify an impulse C. Impulse from a single neuron in CNS may be amplified to activate enough motor units needed for muscle contraction Outcomes to be Assessed 10.1: Introduction Describe the general functions of the nervous system. Identify ...
... A. One neuron sends impulses to several neurons B. Can amplify an impulse C. Impulse from a single neuron in CNS may be amplified to activate enough motor units needed for muscle contraction Outcomes to be Assessed 10.1: Introduction Describe the general functions of the nervous system. Identify ...
Notes Intro to Nervous System and Neurons
... Books says antagonistic, but they are more complimentary ...
... Books says antagonistic, but they are more complimentary ...
The Nervous System
... – causes partial depolarization bringing neuron closer to firing – one EPSP is probably too weak to trigger an action potential – EPSPs can be added together (summation) – results in firing of neuron ...
... – causes partial depolarization bringing neuron closer to firing – one EPSP is probably too weak to trigger an action potential – EPSPs can be added together (summation) – results in firing of neuron ...
Biology 4 Practice Exam Chapter 16 – Autonomic Nervous System 1
... b. may be excitatory or inhibitory c. are always inhibitory d. depend on the response of the membrane receptor e. b and d from above are correct 5. All of the following apply to preganglionic neurons of the ANS sympathetic division except a. their cell bodies are located between spinal segments T1 a ...
... b. may be excitatory or inhibitory c. are always inhibitory d. depend on the response of the membrane receptor e. b and d from above are correct 5. All of the following apply to preganglionic neurons of the ANS sympathetic division except a. their cell bodies are located between spinal segments T1 a ...
A View of Life
... – Motor neurons that convey impulses from the CNS to smooth muscle tissue, to cardiac tissue, and to glands. ...
... – Motor neurons that convey impulses from the CNS to smooth muscle tissue, to cardiac tissue, and to glands. ...
NMSI - 4 Central Nervous System
... Language and Speech • Studies of brain activity have mapped areas responsible for language and speech • Broca’s area in the frontal lobe is active when speech is generated • Wernicke’s area in the temporal lobe is active when speech is heard • These areas belong to a larger network of regions invol ...
... Language and Speech • Studies of brain activity have mapped areas responsible for language and speech • Broca’s area in the frontal lobe is active when speech is generated • Wernicke’s area in the temporal lobe is active when speech is heard • These areas belong to a larger network of regions invol ...
Central nervous system
... Language and Speech • Studies of brain activity have mapped areas responsible for language and speech • Broca’s area in the frontal lobe is active when speech is generated • Wernicke’s area in the temporal lobe is active when speech is heard • These areas belong to a larger network of regions invol ...
... Language and Speech • Studies of brain activity have mapped areas responsible for language and speech • Broca’s area in the frontal lobe is active when speech is generated • Wernicke’s area in the temporal lobe is active when speech is heard • These areas belong to a larger network of regions invol ...
Nervous tissues (NS)
... perineurium) binds groups of fibers together into fascicles. Yet another C.T. sheath (the epineurium) covers the whole nerve (including its several fascicles. Blood and lymph vessels are often located within the C.T. between fascicles of large nerves. Nerve fibers in tracts of the CNS are mostly mye ...
... perineurium) binds groups of fibers together into fascicles. Yet another C.T. sheath (the epineurium) covers the whole nerve (including its several fascicles. Blood and lymph vessels are often located within the C.T. between fascicles of large nerves. Nerve fibers in tracts of the CNS are mostly mye ...