Unit 2 - Monroe Community College
... ● perceptual asymmetries: left/right imbalances in the speed of visual or auditory processing - in normal people the input sent to one hemisphere is quickly shared with the other - but subtle differences can be detected by measuring how long it takes subjects to recognize different kinds of stimuli ...
... ● perceptual asymmetries: left/right imbalances in the speed of visual or auditory processing - in normal people the input sent to one hemisphere is quickly shared with the other - but subtle differences can be detected by measuring how long it takes subjects to recognize different kinds of stimuli ...
暨 南 大 学 考 试 试 卷
... D. Cerebral cortex 19) Presynaptic inhibition depends on B A. Reduced action potential amplitude B. Reduced transmitter release C. Increased postsynaptic potential D. IPSP produced in postsynaptic neuron 20) Synaptic innervation of a number of cells by one fiber is an example of A. Convergence B. Ch ...
... D. Cerebral cortex 19) Presynaptic inhibition depends on B A. Reduced action potential amplitude B. Reduced transmitter release C. Increased postsynaptic potential D. IPSP produced in postsynaptic neuron 20) Synaptic innervation of a number of cells by one fiber is an example of A. Convergence B. Ch ...
Nervous System Outline
... a receptor of information. Some neurons have numerous dendrites all branching out as receptors. c. Axon - The axon is the conducting end of the neuron. It transmits a message along its way. Some neurons can have very long axons, such as an axon traveling from your foot to your spinal cord. 2. Nerve ...
... a receptor of information. Some neurons have numerous dendrites all branching out as receptors. c. Axon - The axon is the conducting end of the neuron. It transmits a message along its way. Some neurons can have very long axons, such as an axon traveling from your foot to your spinal cord. 2. Nerve ...
Slide 1
... An efferent or motor neuron conducts impulses from CNS to PNS Voluntary Control – in somatic nervous system Involuntary control – in autonomic nervous system ...
... An efferent or motor neuron conducts impulses from CNS to PNS Voluntary Control – in somatic nervous system Involuntary control – in autonomic nervous system ...
Choose from list!
... Discuss the relationship between these 3 parts of an ACTION POTENTIAL. Ligand Acetylcholine Sodium Voltage gate ...
... Discuss the relationship between these 3 parts of an ACTION POTENTIAL. Ligand Acetylcholine Sodium Voltage gate ...
Neuroscience and Behavior - Bremerton School District
... brain’s connections to behavior and mind? 7: What are the functions of important lower-level brain structures? 8: What are the functions served by the various cerebral cortex regions? 9: To what extent can a damaged brain reorganize itself? ...
... brain’s connections to behavior and mind? 7: What are the functions of important lower-level brain structures? 8: What are the functions served by the various cerebral cortex regions? 9: To what extent can a damaged brain reorganize itself? ...
UNIT 2 REVIEW GUIDE *Be able to identify/label parts of the neuron
... involuntary movements and functions? ...
... involuntary movements and functions? ...
Functional Human Physiology for the Exercise and Sport Sciences
... The net effect of EPSPs and IPSPs on the post-synaptic membrane will determine if the net effect is excitatory or inhibitory. If the net effect is more excitatory than inhibitory, an action potential will be generated on the post-synaptic membrane and impulse transduction will occur The opposi ...
... The net effect of EPSPs and IPSPs on the post-synaptic membrane will determine if the net effect is excitatory or inhibitory. If the net effect is more excitatory than inhibitory, an action potential will be generated on the post-synaptic membrane and impulse transduction will occur The opposi ...
1. What type of joint do the capitulum of the humerus
... a) carry potentials towards neuron cell bodies b) carry potentials away from neruon cell bodies c) carry potentials up the axon in a retrograde fashion d) are only found on motor neurons e) are an urban legend 38. Action potentials usually begin at the (pick the best answer): a) dendrites b) cell bo ...
... a) carry potentials towards neuron cell bodies b) carry potentials away from neruon cell bodies c) carry potentials up the axon in a retrograde fashion d) are only found on motor neurons e) are an urban legend 38. Action potentials usually begin at the (pick the best answer): a) dendrites b) cell bo ...
Information Processing SG
... Learning Target #2: I can explain the location and function of brain parts. What are neurotransmitters? Describe three specific neurotransmitters and how they affect feelings and behavior. ...
... Learning Target #2: I can explain the location and function of brain parts. What are neurotransmitters? Describe three specific neurotransmitters and how they affect feelings and behavior. ...
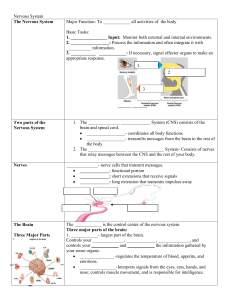
The Nervous System
... • To identify the basic structure of a neuron. • To explain the main components of the nervous system. • To compare and contrast the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • To differentiate between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. ...
... • To identify the basic structure of a neuron. • To explain the main components of the nervous system. • To compare and contrast the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • To differentiate between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. ...
Part 1: True/False
... 4. __ All neurotransmitters are synthesized in the soma and carried to the axon terminal through axoplasmic transport. 5. __ The two main families of neurotransmitter receptors are ligand-gated and neural-gated. 6. __ Postsynaptic responses mediated by G-protein coupled receptors are faster than tho ...
... 4. __ All neurotransmitters are synthesized in the soma and carried to the axon terminal through axoplasmic transport. 5. __ The two main families of neurotransmitter receptors are ligand-gated and neural-gated. 6. __ Postsynaptic responses mediated by G-protein coupled receptors are faster than tho ...
Unit – M Neuron, Impulse Generation, and Reflex Arc Structures and
... 3. Interneuron (associated neuron or Connector Neuron) -Relays message from sensory neuron to motor neuron. -Make up the brain and spinal cord. ...
... 3. Interneuron (associated neuron or Connector Neuron) -Relays message from sensory neuron to motor neuron. -Make up the brain and spinal cord. ...
Excitable Cells and Action Potentials
... signal to be regenerated in the membrane. Most cells in the body are not considered excitable, meaning that they cannot generate action potentials, since they lack Na+ channels. Axons are long projections of neurons, in which electrical impulses are created and also can travel away from the neuron’s ...
... signal to be regenerated in the membrane. Most cells in the body are not considered excitable, meaning that they cannot generate action potentials, since they lack Na+ channels. Axons are long projections of neurons, in which electrical impulses are created and also can travel away from the neuron’s ...
The Nervous System – Use notebook paper if
... Sketch a brain that shows the three main regions. Label and tell the primary functions of each region. ...
... Sketch a brain that shows the three main regions. Label and tell the primary functions of each region. ...
Nervous System - Effingham County Schools
... __________________-Disorder in which the myelin surrounding neurons deteriorate making it hard for signals to travel from one neuron to the next. __________________-Degeneration of nervous tissue that can cause memory loss, loss of verbal communication, and motor skills __________________-genetic di ...
... __________________-Disorder in which the myelin surrounding neurons deteriorate making it hard for signals to travel from one neuron to the next. __________________-Degeneration of nervous tissue that can cause memory loss, loss of verbal communication, and motor skills __________________-genetic di ...
The Human Brain
... Messages are sent through these neurons by incredibly quick electrical charges which are caused by incredibly quick chemical reactions. Different neurons can have different types of chemical transmitters which allow the messages to be passed from neuron to neuron. You may have heard of some of these ...
... Messages are sent through these neurons by incredibly quick electrical charges which are caused by incredibly quick chemical reactions. Different neurons can have different types of chemical transmitters which allow the messages to be passed from neuron to neuron. You may have heard of some of these ...
Chapter 8
... Figure 6-10 At the potassium equilibrium potential: buildup of positive charge in Compartment 1 produces an electrical potential that exactly offsets the K+ chemical concentration gradient. ...
... Figure 6-10 At the potassium equilibrium potential: buildup of positive charge in Compartment 1 produces an electrical potential that exactly offsets the K+ chemical concentration gradient. ...
Chapter 11
... h. axon depends upon the cell body for everything: organelles, proteins, and enzymes for synthesis of neurotransmitter i. anterograde transport - movement of material from cell body to synaptic knobs ii. retrograde transport - movement of material from synapse to cell body 3. myelin sheath - wrap of ...
... h. axon depends upon the cell body for everything: organelles, proteins, and enzymes for synthesis of neurotransmitter i. anterograde transport - movement of material from cell body to synaptic knobs ii. retrograde transport - movement of material from synapse to cell body 3. myelin sheath - wrap of ...
The Neuron - Austin Community College
... - The resting potential (when the cell is not firing) is a 70mV difference between the inside and the outside - the membrane is polarized -When gated ion channels open, ions diffuse across the membrane following their electrochemical gradients. - This movement of charge is an electrical current and ...
... - The resting potential (when the cell is not firing) is a 70mV difference between the inside and the outside - the membrane is polarized -When gated ion channels open, ions diffuse across the membrane following their electrochemical gradients. - This movement of charge is an electrical current and ...