Slide ()
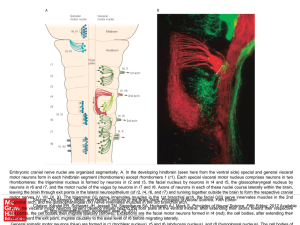
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
File
... The _________________________ is a long band of _____________________ which allows communication between the ______________________________________________. The _____________________ releases a hormone which _______________________________. Located deep inside the brain, the _______________________ ...
... The _________________________ is a long band of _____________________ which allows communication between the ______________________________________________. The _____________________ releases a hormone which _______________________________. Located deep inside the brain, the _______________________ ...
Chapter 2 - Safford Unified School
... A) The cerebral cortex is divided into four parts, with the occipital and parietal lobes in the right hemisphere and the frontal and temporal lobes in the left hemisphere. B) In general, each of the cerebral hemispheres controls feeling and movement on the opposite side of the body. C) The cerebral ...
... A) The cerebral cortex is divided into four parts, with the occipital and parietal lobes in the right hemisphere and the frontal and temporal lobes in the left hemisphere. B) In general, each of the cerebral hemispheres controls feeling and movement on the opposite side of the body. C) The cerebral ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... ANS that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. Parasympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that calms the body, conserving its ...
... ANS that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. Parasympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that calms the body, conserving its ...
Neurotransmitters
... period) before restoring itself to normal. Analogy: the absolute refractory period is like a gun. After you shoot it, you must reload it before you can shoot again. The charge dropping in the neuron is its way of reloading. ...
... period) before restoring itself to normal. Analogy: the absolute refractory period is like a gun. After you shoot it, you must reload it before you can shoot again. The charge dropping in the neuron is its way of reloading. ...
Meart: 1000 word catalogue essay:
... exhibition site) and others remote. In the gallery, a pen-wielding robotic appendage sends video images to and receives impulses from an in-vitro culture of rat neurons via the internet. The neurons are housed in Dr. Steve Potter’s neuro-science engineering laboratory at Georgia Institute of Technol ...
... exhibition site) and others remote. In the gallery, a pen-wielding robotic appendage sends video images to and receives impulses from an in-vitro culture of rat neurons via the internet. The neurons are housed in Dr. Steve Potter’s neuro-science engineering laboratory at Georgia Institute of Technol ...
The Cerebral Cortex
... Please complete the following which will allow you to compare and contrast the different parts of the brain. Rank each of the parts of the brain from 1-7 with 1 being the most important and 7 being the least. With each ranking, please provide a reason why you placed that section of the brain in that ...
... Please complete the following which will allow you to compare and contrast the different parts of the brain. Rank each of the parts of the brain from 1-7 with 1 being the most important and 7 being the least. With each ranking, please provide a reason why you placed that section of the brain in that ...
The left hemisphere
... These two types are never used, this is used on animals and not much in use today. However, humans can be used if they suffered from an injury. •Simulation method-electric and chemical simulation which allows researchers see what stimulation to different parts of the brain causes. This is in extensi ...
... These two types are never used, this is used on animals and not much in use today. However, humans can be used if they suffered from an injury. •Simulation method-electric and chemical simulation which allows researchers see what stimulation to different parts of the brain causes. This is in extensi ...
Flyer - Energy Kinesiology Association
... Emotional, short and long term stress effects on Glial Cell Neurotransmission Control of which neurons fire and their speed providing brain synchrony - the basis of Brain Integration ..... plus much more!! ...
... Emotional, short and long term stress effects on Glial Cell Neurotransmission Control of which neurons fire and their speed providing brain synchrony - the basis of Brain Integration ..... plus much more!! ...
nerve impulse
... Function: determined by the postsynaptic receptor; two major functional classifications are excitatory neurotransmitters and inhibitory neurotransmitters; can also be classified by whether the receptor directly opens a channel or uses a second messenger mechanism involving G proteins and intracell ...
... Function: determined by the postsynaptic receptor; two major functional classifications are excitatory neurotransmitters and inhibitory neurotransmitters; can also be classified by whether the receptor directly opens a channel or uses a second messenger mechanism involving G proteins and intracell ...
Nervous System
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...
Chapter 12: Nervous Tissue
... • Saltatory conduction (myelinated fibers) – depolarization only at nodes of Ranvier where there is a high density of voltage-gated ion channels – current carried by ions flows through extracellular fluid from node to node • Nerve impulse conduction in which the impulse jumps from node to node ...
... • Saltatory conduction (myelinated fibers) – depolarization only at nodes of Ranvier where there is a high density of voltage-gated ion channels – current carried by ions flows through extracellular fluid from node to node • Nerve impulse conduction in which the impulse jumps from node to node ...
lecture #6
... • each cell surrounds multiple unmyelinated PNS axons with a single layer of its plasma membrane • produces part of the myelin sheath surrounding an axon in the PNS • also contributes to regeneration of PNS axons ...
... • each cell surrounds multiple unmyelinated PNS axons with a single layer of its plasma membrane • produces part of the myelin sheath surrounding an axon in the PNS • also contributes to regeneration of PNS axons ...
The Biological Perspective - Shannon Deets Counseling LLC
... Antagonist for Norephinephrine • Norepinephrine is an excitatory neurotransmitter involved in arousal (wakefulness) • If a patient has excessive arousal and presents with difficulty sleeping and they are given an antagonist for norepinephrine what happens? ...
... Antagonist for Norephinephrine • Norepinephrine is an excitatory neurotransmitter involved in arousal (wakefulness) • If a patient has excessive arousal and presents with difficulty sleeping and they are given an antagonist for norepinephrine what happens? ...
The Nervous System
... How are motor neurons different from sensory neurons? How are neuroglial cells different from typical nerve cells? Name all four types of neuroglial cells and indicate the one that provides immune protection. What is the name of the small spaces that exist between the neurons? Can you give an exampl ...
... How are motor neurons different from sensory neurons? How are neuroglial cells different from typical nerve cells? Name all four types of neuroglial cells and indicate the one that provides immune protection. What is the name of the small spaces that exist between the neurons? Can you give an exampl ...
3a handout
... I. Work with the person sitting 3 people down from you (move to your left) to explain what happens in your nervous system in the following situations: a. You pull your hand away from a hot stove. ...
... I. Work with the person sitting 3 people down from you (move to your left) to explain what happens in your nervous system in the following situations: a. You pull your hand away from a hot stove. ...
Chapter Six
... physiology in man and other species. Cognitive neuroscience studies the structures and processes underlying cognitive function. What are the neural mechanisms for pattern recognition, attention, memory, and problem solving? ...
... physiology in man and other species. Cognitive neuroscience studies the structures and processes underlying cognitive function. What are the neural mechanisms for pattern recognition, attention, memory, and problem solving? ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 3.1 Typical morphology of projection
... FIGURE 3.4 Left, photomicrograph from one of the Cajal’s preparations of the “occipital pole” of an eighteen-day-old cat, showing the soma of a pyramidal cell (Py) and a neurogliaform cell (interneuron; Int) stained with the Golgi method. Right, the principal cellular types based on the works of Caj ...
... FIGURE 3.4 Left, photomicrograph from one of the Cajal’s preparations of the “occipital pole” of an eighteen-day-old cat, showing the soma of a pyramidal cell (Py) and a neurogliaform cell (interneuron; Int) stained with the Golgi method. Right, the principal cellular types based on the works of Caj ...
Chapter 04: The Action Potential
... Membrane Potential (potential difference across the plasma membrane) at which the net flow of an ion type = zero The number of ions moving into the cell = the number of ions moving out of the cell for a particular species of ion ...
... Membrane Potential (potential difference across the plasma membrane) at which the net flow of an ion type = zero The number of ions moving into the cell = the number of ions moving out of the cell for a particular species of ion ...
sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
... the pre synaptic membrane of the axon. (This involves Ca+2 ions). The Ca ions move into the bulb, causing the microtubules to constrict, pulling the synaptic vesicles towards the presynaptic membrane. These fuse to the membrane which then empty their contents (neurotransmitter substance) into the sy ...
... the pre synaptic membrane of the axon. (This involves Ca+2 ions). The Ca ions move into the bulb, causing the microtubules to constrict, pulling the synaptic vesicles towards the presynaptic membrane. These fuse to the membrane which then empty their contents (neurotransmitter substance) into the sy ...
Additional Nervous System Notes
... • Contain rhodopsin – visual pigment made up of protein (opsin) and retinal (made from vitamin A) – Light falling on rhodopsin causes reversible change in shape – called bleaching – This generates an action potential that is carried to visual cortex of brain via optic nerve • Groups of rods may pass ...
... • Contain rhodopsin – visual pigment made up of protein (opsin) and retinal (made from vitamin A) – Light falling on rhodopsin causes reversible change in shape – called bleaching – This generates an action potential that is carried to visual cortex of brain via optic nerve • Groups of rods may pass ...