CHAPTER 2 –OUTLINE I. Introduction: Neuroscience and Behavior
... a. Many axons are surrounded by a myelin sheath, a white, fatty covering that insulates axons from one another and increases the neuron’s communication speed. b. Nodes of Ranvier are small gaps in the myelin sheath. B. Communication Within the Neuron: The All-or-None Action Potential In general, mes ...
... a. Many axons are surrounded by a myelin sheath, a white, fatty covering that insulates axons from one another and increases the neuron’s communication speed. b. Nodes of Ranvier are small gaps in the myelin sheath. B. Communication Within the Neuron: The All-or-None Action Potential In general, mes ...
Summary of: Stevens, Alison P. "Learning Rewires the Brain
... areas became less active over time. Other areas of the brain linked with daydreaming and mind-wandering became more active as people became more familiar with a task. With extensive practice a person can perform a task thinking about other things or without think nothing at all. The brain is made up ...
... areas became less active over time. Other areas of the brain linked with daydreaming and mind-wandering became more active as people became more familiar with a task. With extensive practice a person can perform a task thinking about other things or without think nothing at all. The brain is made up ...
CHAPTER 13 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... controls cardiac muscle, smooth muscle and glands system is divided into sympathetic and ...
... controls cardiac muscle, smooth muscle and glands system is divided into sympathetic and ...
Neural Networks.Chap..
... Rule 2: Items to be categorized as separate classes should be given widely different representations in the network. (This is the exact opposite of Rule 1.) Rule 3: If a particular feature is important, then there should be a large number of neurons involved in the representation of that item. Rule ...
... Rule 2: Items to be categorized as separate classes should be given widely different representations in the network. (This is the exact opposite of Rule 1.) Rule 3: If a particular feature is important, then there should be a large number of neurons involved in the representation of that item. Rule ...
Terms being described
... 11. It’s another name for motor neurons because of their direction of conduction. 13. It’s another name for sensory neurons because of their direction of conduction. 15. It’s the ability of a potential change to spread along the axon that is analogous to the conduction of electricity by a wire. 17. ...
... 11. It’s another name for motor neurons because of their direction of conduction. 13. It’s another name for sensory neurons because of their direction of conduction. 15. It’s the ability of a potential change to spread along the axon that is analogous to the conduction of electricity by a wire. 17. ...
Neurons and the BOLD response
... significant electrical and magnetic fields, which can be detected fairly easily. That is how the EEG was discovered in 1929, simply by placing an electrode on the scalp and amplifying the electrical signal. ...
... significant electrical and magnetic fields, which can be detected fairly easily. That is how the EEG was discovered in 1929, simply by placing an electrode on the scalp and amplifying the electrical signal. ...
The Action Potential
... The depolarization phase of action potential is abrupt and very rapid: in takes place in less than one milisecond. Soon after reaching the maximum peak of depolarization ( which inverts the membrane potential to some +10 to+ 20 mV), it begins to return to normal, that is, towards its value at rest. ...
... The depolarization phase of action potential is abrupt and very rapid: in takes place in less than one milisecond. Soon after reaching the maximum peak of depolarization ( which inverts the membrane potential to some +10 to+ 20 mV), it begins to return to normal, that is, towards its value at rest. ...
Copy Notes
... at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position occipital lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; includes areas that receive information from the visual fields temporal lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly ab ...
... at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position occipital lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; includes areas that receive information from the visual fields temporal lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly ab ...
The Nervous System
... • General interpretative and speech centers (Wernicke’s area – receives info from all sensory association areas, integrates sensory to visual and auditory memories) • Language-based skills (speech center = Broca’s area) • Representational Hemisphere (usually right) • Spatial relationships • Logical ...
... • General interpretative and speech centers (Wernicke’s area – receives info from all sensory association areas, integrates sensory to visual and auditory memories) • Language-based skills (speech center = Broca’s area) • Representational Hemisphere (usually right) • Spatial relationships • Logical ...
Neuronal Cell Death Post Trauma
... We have demonstrated beyond any doubt that Ndfip1 is a valid intrinsic mechanism present in the brain for protecting neurons from death following injury. Normally, Ndfip1 is only protective in a small number of neurons following injury, due to an unknown reason. However, since all neurons express lo ...
... We have demonstrated beyond any doubt that Ndfip1 is a valid intrinsic mechanism present in the brain for protecting neurons from death following injury. Normally, Ndfip1 is only protective in a small number of neurons following injury, due to an unknown reason. However, since all neurons express lo ...
Artificial Intelligence Methods
... Artificial neurons simulate the four basic functions of natural neurons - Signals are passed between neurons over connection links - Each connection link has an associated weight which multiplies the signal transmitted ...
... Artificial neurons simulate the four basic functions of natural neurons - Signals are passed between neurons over connection links - Each connection link has an associated weight which multiplies the signal transmitted ...
nervous system study guide
... SOMATIC VS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM What does each do? Which is involuntary? ...
... SOMATIC VS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM What does each do? Which is involuntary? ...
PSYC 100 Chap. 2 - Traditional method: Observing electrical activity
... - Neuroscientist: investigators who conduct research on the brain or other part of nervous system > brain research often involves neuroscientist from different disciplines; anatomy, phyisio, bio, pharma - Usual method: electrical recordings, lesioning, electrical stimulation and brain-imaging (obser ...
... - Neuroscientist: investigators who conduct research on the brain or other part of nervous system > brain research often involves neuroscientist from different disciplines; anatomy, phyisio, bio, pharma - Usual method: electrical recordings, lesioning, electrical stimulation and brain-imaging (obser ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... A direct motor pathway (also called the pyramidal pathway) originates in the pyramidal cells of the primary motor cortex. This type of pathway is involved in the conscious control of movements. Midbrain nuclei initiate motor commands for the indirect motor pathways. They work at an unconscious level ...
... A direct motor pathway (also called the pyramidal pathway) originates in the pyramidal cells of the primary motor cortex. This type of pathway is involved in the conscious control of movements. Midbrain nuclei initiate motor commands for the indirect motor pathways. They work at an unconscious level ...
Chapter 12 Nervous System Cells
... several knobs being activated simultaneously and stimulating different locations on the postsynaptic membrane, producing an action potential – Temporal summation—when synaptic knobs stimulate a postsynaptic neuron in rapid succession, their effects can summate over a brief period of time to produce ...
... several knobs being activated simultaneously and stimulating different locations on the postsynaptic membrane, producing an action potential – Temporal summation—when synaptic knobs stimulate a postsynaptic neuron in rapid succession, their effects can summate over a brief period of time to produce ...
unit 3A-3B DA BRAIN - Madeira City Schools
... ANS that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. Parasympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that calms the body, conserving its ...
... ANS that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. Parasympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that calms the body, conserving its ...
BIOLOGY 12: U NIT M/N - C A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. What are the
... B. COMPLETION AND SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS 1. The peripheral nervous system may be divided into the _____________ and _______________ divisions. 2. A motor neuron has a ________ (long/short) axon and __________ (long/short) dendrites. 3. During depolarization of the nerve impulse, the _____________ i ...
... B. COMPLETION AND SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS 1. The peripheral nervous system may be divided into the _____________ and _______________ divisions. 2. A motor neuron has a ________ (long/short) axon and __________ (long/short) dendrites. 3. During depolarization of the nerve impulse, the _____________ i ...
Information Processing in the Central Nervous System
... from other neurons at synapses; leads to integrative activity in the dendrites and soma, where the neuron receives information from hundreds or even thousands of other neurons; and ends with transmissive activity associated with changes in their membrane potentials along long axons. A distinction is ...
... from other neurons at synapses; leads to integrative activity in the dendrites and soma, where the neuron receives information from hundreds or even thousands of other neurons; and ends with transmissive activity associated with changes in their membrane potentials along long axons. A distinction is ...
ch 3 the brain pp - Madeira City Schools
... ANS that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. Parasympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that calms the body, conserving its ...
... ANS that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. Parasympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that calms the body, conserving its ...
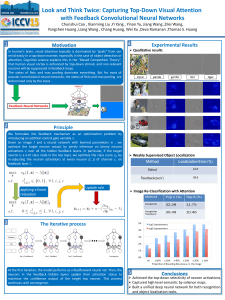
feedback-poster
... Chunshui Cao , Xianming Liu ,Yi Yang , Yinan Yu, Jiang Wang ,Zilei Wang, Yongzhen Huang ,Liang Wang , Chang Huang, Wei Xu ,Deva Ramanan ,Thomas S. Huang ...
... Chunshui Cao , Xianming Liu ,Yi Yang , Yinan Yu, Jiang Wang ,Zilei Wang, Yongzhen Huang ,Liang Wang , Chang Huang, Wei Xu ,Deva Ramanan ,Thomas S. Huang ...
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... provide energy, and dense areas of RER and ribosomes that produce neurotransmitters. These dense areas, called Nissl bodies, make neural tissues appear gray (the gray matter). - the cytoskeleton with neurofilaments and neurotubules (in place of microfilaments and microtubules) Bundles of neurofilam ...
... provide energy, and dense areas of RER and ribosomes that produce neurotransmitters. These dense areas, called Nissl bodies, make neural tissues appear gray (the gray matter). - the cytoskeleton with neurofilaments and neurotubules (in place of microfilaments and microtubules) Bundles of neurofilam ...
Nervous System
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...