UNIT 4 – HOMEOSTASIS 8.1 – Human Body Systems and H
... The nervous system has two main divisions: central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). central nervous system: the body’s coordinating centre for mechanical and chemical actions; made up of the brain and spinal cord peripheral nervous system: all parts of the nervous system, ex ...
... The nervous system has two main divisions: central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). central nervous system: the body’s coordinating centre for mechanical and chemical actions; made up of the brain and spinal cord peripheral nervous system: all parts of the nervous system, ex ...
Malleable vs. Fixed Intelligence
... Neurons have three main parts: 1. The soma (a.k.a cell body) 2. The axon 3. The dendrites ...
... Neurons have three main parts: 1. The soma (a.k.a cell body) 2. The axon 3. The dendrites ...
Publisher Link - Synthetic Neurobiology Group
... second class of light-driven neural silencer, the light-driven outward proton pump, which could support extremely powerful neural silencing, an order of magnitude greater than that mediated by the original halorhodopsins, as exemplified by the molecule Arch from H. sodomense [3], which can result in ...
... second class of light-driven neural silencer, the light-driven outward proton pump, which could support extremely powerful neural silencing, an order of magnitude greater than that mediated by the original halorhodopsins, as exemplified by the molecule Arch from H. sodomense [3], which can result in ...
PowerLecture: Chapter 13
... dendrites; the cell body and the dendrites form the input zone for receiving information. Next comes the trigger zone, called the axon hillock in motor neurons and interneurons; the trigger zone leads to the axon, which is the neuron’s conducting zone. The axon’s endings are output zones where messa ...
... dendrites; the cell body and the dendrites form the input zone for receiving information. Next comes the trigger zone, called the axon hillock in motor neurons and interneurons; the trigger zone leads to the axon, which is the neuron’s conducting zone. The axon’s endings are output zones where messa ...
1 2 The Advent of Modern Neuroscience
... in a patient who could speak clearly. The brains of people who suffered from Wernicke’s aphasia revealed a lesion in an area now referred to as Wernicke’s area. In patients suffering from Wernicke’s aphasia, speech is fluent, but does not make any sense. He used his findings with those of Broca, Frits ...
... in a patient who could speak clearly. The brains of people who suffered from Wernicke’s aphasia revealed a lesion in an area now referred to as Wernicke’s area. In patients suffering from Wernicke’s aphasia, speech is fluent, but does not make any sense. He used his findings with those of Broca, Frits ...
m5zn_363798b57fd4c88
... Function of the spinal cord The main functions of the spinal cord are: 1. The spinal cord communicates through nerve fibers, its nervous pathways, with various parts of the brain and through spinal nerves with organs. The spinal cord contains two kinds of nervous pathway: ascending (sensory) and d ...
... Function of the spinal cord The main functions of the spinal cord are: 1. The spinal cord communicates through nerve fibers, its nervous pathways, with various parts of the brain and through spinal nerves with organs. The spinal cord contains two kinds of nervous pathway: ascending (sensory) and d ...
Lab 9 Nervous histology post lab answer key 2010
... terminal, nucleus of Schwann cell (neurilemma ok too), Schwann cell (myelin sheath ok), axon hillock, nucleus 2. Match the term with the description: a. b. c. ...
... terminal, nucleus of Schwann cell (neurilemma ok too), Schwann cell (myelin sheath ok), axon hillock, nucleus 2. Match the term with the description: a. b. c. ...
LABORATORY 9
... terminal, nucleus of Schwann cell (neurilemma ok too), Schwann cell (myelin sheath ok), axon hillock, nucleus 2. Match the term with the description: a. b. c. ...
... terminal, nucleus of Schwann cell (neurilemma ok too), Schwann cell (myelin sheath ok), axon hillock, nucleus 2. Match the term with the description: a. b. c. ...
Temporal Lobe
... o Definition: A brain abscess is a collection of immune cells, pus, and other material in the brain, usually from a bacterial or fungal infection. • Brain abscesses commonly occur when bacteria or fungi infect part of the brain. Swelling and irritation (inflammation) develops in response. Infected b ...
... o Definition: A brain abscess is a collection of immune cells, pus, and other material in the brain, usually from a bacterial or fungal infection. • Brain abscesses commonly occur when bacteria or fungi infect part of the brain. Swelling and irritation (inflammation) develops in response. Infected b ...
Biopsychology
... Steps • There are several steps that happen when the brain is sent a signal of pain. • We are going to go through each of these steps today. ...
... Steps • There are several steps that happen when the brain is sent a signal of pain. • We are going to go through each of these steps today. ...
13.1- neurons
... Somatic: responds to external environment voluntary control movement of skeletal muscle, bones, skin Autonomic: involuntary ‘automatic’ controls the internal body organs ◦ Sympathetic: typically functions in actions requiring quick responses ◦ Parasympathetic: functions with actions that do not requ ...
... Somatic: responds to external environment voluntary control movement of skeletal muscle, bones, skin Autonomic: involuntary ‘automatic’ controls the internal body organs ◦ Sympathetic: typically functions in actions requiring quick responses ◦ Parasympathetic: functions with actions that do not requ ...
Supplementary Figure Legends - Word file
... Supplementary Figure 1: Example responses to pure tones and harmonic complex tones from a pitchselective neuron (a, d) (Unit M36n-514) and a non-pitch-selective neuron (b, e) (Unit M2p-140). a. Pure tone frequency response from a pitch-selective neuron. b. Pure tone frequency response from a non-pit ...
... Supplementary Figure 1: Example responses to pure tones and harmonic complex tones from a pitchselective neuron (a, d) (Unit M36n-514) and a non-pitch-selective neuron (b, e) (Unit M2p-140). a. Pure tone frequency response from a pitch-selective neuron. b. Pure tone frequency response from a non-pit ...
Document
... Factors influencing rate of oxygen diffusion into cells Oxygen is lipophilic, so it can diffuse through the lipid phase. The cross-sectional area through which it can diffuse is huge Oxygen is a small molecule, so it can diffuse rapidly The diffusion path (across the thickness of cell membranes) is ...
... Factors influencing rate of oxygen diffusion into cells Oxygen is lipophilic, so it can diffuse through the lipid phase. The cross-sectional area through which it can diffuse is huge Oxygen is a small molecule, so it can diffuse rapidly The diffusion path (across the thickness of cell membranes) is ...
Neurons
... ● This is called the resting potential of the neuron. ● The negative charge is created because the cell membrane of the neuron is constantly pumping positive sodium ions out of the cell ● They do this using the sodium potassium pump which is a type of active transport (it requires energy because it ...
... ● This is called the resting potential of the neuron. ● The negative charge is created because the cell membrane of the neuron is constantly pumping positive sodium ions out of the cell ● They do this using the sodium potassium pump which is a type of active transport (it requires energy because it ...
Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... This is called the resting potential of the neuron. The negative charge is created because the cell membrane of the neuron is constantly pumping positive sodium ions out of the cell They do this using the sodium potassium pump which is a type of active transport (it requires energy because it ...
... This is called the resting potential of the neuron. The negative charge is created because the cell membrane of the neuron is constantly pumping positive sodium ions out of the cell They do this using the sodium potassium pump which is a type of active transport (it requires energy because it ...
The Nervous System
... which contains tiny hairs that wave back and forth. The motion of these hairs produce the nerve impulses that are sent to the brain ...
... which contains tiny hairs that wave back and forth. The motion of these hairs produce the nerve impulses that are sent to the brain ...
Outline for cognitive neuroscience Chapter 1 Introduction to Method
... Outline and page number Experimental methods in cognitive neuroscience 1. Animal experiment (P106-112): single cell recording, lesion, *genetic manipulation 2. *neurology 3. Converging methods A. cognitive deficits following brain damage(P124-126): single vs double dissociation B. TMS ...
... Outline and page number Experimental methods in cognitive neuroscience 1. Animal experiment (P106-112): single cell recording, lesion, *genetic manipulation 2. *neurology 3. Converging methods A. cognitive deficits following brain damage(P124-126): single vs double dissociation B. TMS ...
“Brains on Beads” System Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Me
... slice-selective spin echo pulse sequence. Water 1H MR signal from flowing extracellular media within the slice was suppressed by both time-of-flight effects and phase dispersion. For 1H MR measurement of the intracellular water exchange-modified longitudinal relaxation time (T1,obs), a slice-selecti ...
... slice-selective spin echo pulse sequence. Water 1H MR signal from flowing extracellular media within the slice was suppressed by both time-of-flight effects and phase dispersion. For 1H MR measurement of the intracellular water exchange-modified longitudinal relaxation time (T1,obs), a slice-selecti ...
Chapter 3 Practice Test
... Which part of your brain receives information that you are moving your legs? a. amygdala b. sensory cortex c. hypothalamus d. motor cortex e. Broca's area The capacity of one brain area to take over the functions of another damaged brain area is known as brain a. tomography. b. aphasia. c. phrenolog ...
... Which part of your brain receives information that you are moving your legs? a. amygdala b. sensory cortex c. hypothalamus d. motor cortex e. Broca's area The capacity of one brain area to take over the functions of another damaged brain area is known as brain a. tomography. b. aphasia. c. phrenolog ...
Nerve Tissue
... particles between one point and another • electrical current – a flow of charged particles from one point to another – in the body, currents are movement of ions, such as Na+ or K+ through gated channels in the plasma membrane – gated channels enable cells to turn electrical currents on and off ...
... particles between one point and another • electrical current – a flow of charged particles from one point to another – in the body, currents are movement of ions, such as Na+ or K+ through gated channels in the plasma membrane – gated channels enable cells to turn electrical currents on and off ...
LAB 10 NEURON and SPINAL CORD
... Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) is the most common means of collecting a specimen of cerebral spinal fluid. The spinal needle is inserted, usually between the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebrae. Once the needle is properly positioned in the subarachnoid space, pressures can be measured and fluid ...
... Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) is the most common means of collecting a specimen of cerebral spinal fluid. The spinal needle is inserted, usually between the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebrae. Once the needle is properly positioned in the subarachnoid space, pressures can be measured and fluid ...
File
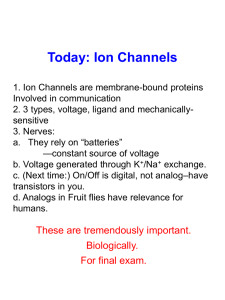
... 2. This changes that area of the cell to become more positive. 3. This affects the voltage-gated sodium channels nearby causing them to open. 4. This allows sodium to rush in, etc. ...
... 2. This changes that area of the cell to become more positive. 3. This affects the voltage-gated sodium channels nearby causing them to open. 4. This allows sodium to rush in, etc. ...