Neuron Teacher Key 5-17-16
... 13. What is a synapse? Identify where synapse junctions may occur in the body. A synapse is the junction where a neuron communicates with another cell across a ...
... 13. What is a synapse? Identify where synapse junctions may occur in the body. A synapse is the junction where a neuron communicates with another cell across a ...
Nervous System Part 1
... Bind neurons together and form framework for nervous tissue In fetus, guide migrating neurons to their destination If mature neuron is not in synaptic contact with another neuron it is covered by glial cells Prevents neurons from touching each other Gives precision to conduction pathways ...
... Bind neurons together and form framework for nervous tissue In fetus, guide migrating neurons to their destination If mature neuron is not in synaptic contact with another neuron it is covered by glial cells Prevents neurons from touching each other Gives precision to conduction pathways ...
MYELINATED AXON - Union County College Faculty Web Site
... Neurofilaments (arrows) are delicate fibers present throughout the cytoplasm of the cell body and extending in bundles into dendrites and axons. These bundles can extend from the cell body to the ends of cell processes. Neurofibrils are composed of microtubules formed from the protein tubulin and mi ...
... Neurofilaments (arrows) are delicate fibers present throughout the cytoplasm of the cell body and extending in bundles into dendrites and axons. These bundles can extend from the cell body to the ends of cell processes. Neurofibrils are composed of microtubules formed from the protein tubulin and mi ...
Chapter 2 Vocabulary
... computer-generated images that show brain structures more clearly. (p. 59) 30. The __________________ , the oldest and innermost region of the brain, is an extension of the spinal cord and is the central core of the brain; its structures direct automatic survival functions. (p. 61) 31. Located in t ...
... computer-generated images that show brain structures more clearly. (p. 59) 30. The __________________ , the oldest and innermost region of the brain, is an extension of the spinal cord and is the central core of the brain; its structures direct automatic survival functions. (p. 61) 31. Located in t ...
MBS 102-B
... 2. Please tick (√) correct one only. Cutting, overwriting or any other marking are not allowed. 3. For answering please use Ball- pen only. Q.1 ...
... 2. Please tick (√) correct one only. Cutting, overwriting or any other marking are not allowed. 3. For answering please use Ball- pen only. Q.1 ...
Nerve Cells - Dr Magrann
... There are five types of glial cells that we will cover: Oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells, astrocytes, and microglia. 1. OLIGODENDROCYTES (“few branches”). They are found in the CNS, are very large and complex cells. Ogliodendrocytes form MYELIN SHEATHS. This sheath is a covering around an axon to spe ...
... There are five types of glial cells that we will cover: Oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells, astrocytes, and microglia. 1. OLIGODENDROCYTES (“few branches”). They are found in the CNS, are very large and complex cells. Ogliodendrocytes form MYELIN SHEATHS. This sheath is a covering around an axon to spe ...
action potential
... doesn’t flush a little or a lot direction of impulse - the toilet only flushes one way, the impulse can’t come the other direction (you hope!) refractory period - after you flush the toilet, it won’t flush again for a certain period of time, even if you push the handle repeatedly threshold - you can ...
... doesn’t flush a little or a lot direction of impulse - the toilet only flushes one way, the impulse can’t come the other direction (you hope!) refractory period - after you flush the toilet, it won’t flush again for a certain period of time, even if you push the handle repeatedly threshold - you can ...
The Neuron
... named supporting cells. While the neurons are important for carrying the neural message, the supporting cells are important for insuring that the neurons carry out this process. In fact, without supporting cells communication among neurons would be impossible. There are many types of supporting cell ...
... named supporting cells. While the neurons are important for carrying the neural message, the supporting cells are important for insuring that the neurons carry out this process. In fact, without supporting cells communication among neurons would be impossible. There are many types of supporting cell ...
The History and Scope of Psychology Module 1
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...
Document
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...
Chapter2 - cfhssocialstudies
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...
... Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to o ...
The Nervous System - Marblehead High School
... Cell body - largest part containing the nucleus and cytoplasm Dendrites - branched extensions that carry impulses to the cell body Axon - long fiber ending at the terminals that carries impulses away from the cell body Myelin sheath - protective membrane surrounding the axon ...
... Cell body - largest part containing the nucleus and cytoplasm Dendrites - branched extensions that carry impulses to the cell body Axon - long fiber ending at the terminals that carries impulses away from the cell body Myelin sheath - protective membrane surrounding the axon ...
The History and Scope of Psychology Module 1
... enough stimulation, the gates open and lets some negative ions out and some positive ones in. – Then the whole cell fires, more gates open and more positive ions rush in – The electric charge of the ...
... enough stimulation, the gates open and lets some negative ions out and some positive ones in. – Then the whole cell fires, more gates open and more positive ions rush in – The electric charge of the ...
Nervous System
... stored in vesicles in the axon terminals. Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and diffuse through synaptic cleft neurotransmitters bind with receptors on postsynaptic membrane. ...
... stored in vesicles in the axon terminals. Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and diffuse through synaptic cleft neurotransmitters bind with receptors on postsynaptic membrane. ...
ppt - Le Moyne College
... • If you get a brain tumor, doctors can do two things: surgically remove the tissue and/or use radiation to kill cancer cells. Why can’t brain tumors be treated like other cancers by using chemotherapy? • Does a brain tumor really involve brain tissue? • What kind of cells form the largest number fo ...
... • If you get a brain tumor, doctors can do two things: surgically remove the tissue and/or use radiation to kill cancer cells. Why can’t brain tumors be treated like other cancers by using chemotherapy? • Does a brain tumor really involve brain tissue? • What kind of cells form the largest number fo ...
Unit 4 Test Nervous System
... 6. The direction an action potential (nerve impulse) travels is a. One direction: From dendrites to axon terminals b. One direction: From axon terminals to dendrites c. Two directions: Can travel up or down the neuron d. Any direction: Whichever direction the impulse is stronger ...
... 6. The direction an action potential (nerve impulse) travels is a. One direction: From dendrites to axon terminals b. One direction: From axon terminals to dendrites c. Two directions: Can travel up or down the neuron d. Any direction: Whichever direction the impulse is stronger ...
Test Question 1 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive
... AW: Blood flow increase follows the increased neural activity relatively slowly. Blood flow increase is not per definition spatially there “where the action is”. There is also a chance that activity dus not affect blood flow c) Why do researchers not always use more direct representations of the neu ...
... AW: Blood flow increase follows the increased neural activity relatively slowly. Blood flow increase is not per definition spatially there “where the action is”. There is also a chance that activity dus not affect blood flow c) Why do researchers not always use more direct representations of the neu ...
Template for poster presentations
... As shown in the above diagram, the signal acquisition module extracts electrical signals. This module then amplifies and digitizes these signals and sends them over to the signal processing module. In the first part of signal processing, specific signal features, which encode the users’ commands, ar ...
... As shown in the above diagram, the signal acquisition module extracts electrical signals. This module then amplifies and digitizes these signals and sends them over to the signal processing module. In the first part of signal processing, specific signal features, which encode the users’ commands, ar ...
Chapter 11 The Nervous System
... – When a nerve cell is stimulated, its plasma membrane increases its permeability to sodium ions. – Sodium ions rush in, causing depolarization down the membrane. – Depolarization is followed by repolarization. – The depolarization and repolarization of the neuron’s plasma membrane constitute a bioe ...
... – When a nerve cell is stimulated, its plasma membrane increases its permeability to sodium ions. – Sodium ions rush in, causing depolarization down the membrane. – Depolarization is followed by repolarization. – The depolarization and repolarization of the neuron’s plasma membrane constitute a bioe ...
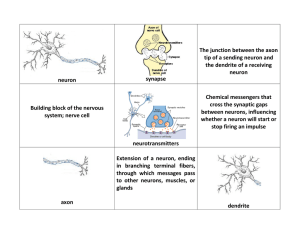
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending
... cross the synaptic gaps between neurons, influencing whether a neuron will start or stop firing an impulse ...
... cross the synaptic gaps between neurons, influencing whether a neuron will start or stop firing an impulse ...
Einstein`s Brain
... • E’s inferior parietal lobules are not divided by major cleft – Not seen in 191 controls! – Axons were connected in unusual ways • “might have allowed for his brilliance and his ability to put spatial representations into mathematical concepts” ...
... • E’s inferior parietal lobules are not divided by major cleft – Not seen in 191 controls! – Axons were connected in unusual ways • “might have allowed for his brilliance and his ability to put spatial representations into mathematical concepts” ...
einsteins-brain
... • E’s inferior parietal lobules are not divided by major cleft – Not seen in 191 controls! – Axons were connected in unusual ways • “might have allowed for his brilliance and his ability to put spatial representations into mathematical concepts” ...
... • E’s inferior parietal lobules are not divided by major cleft – Not seen in 191 controls! – Axons were connected in unusual ways • “might have allowed for his brilliance and his ability to put spatial representations into mathematical concepts” ...
amy-2a-2016-cryders-rmp-and-generation-of-action
... K+channels open with depolarization, but are so slow they only fully activate once AP peak is reached. Depolarization ends as the positive feedback loop breaks by these two processes. As less Na+ moves into the cell and more K+ moves out, the membrane potential (MP) becomes more negative. Moving clo ...
... K+channels open with depolarization, but are so slow they only fully activate once AP peak is reached. Depolarization ends as the positive feedback loop breaks by these two processes. As less Na+ moves into the cell and more K+ moves out, the membrane potential (MP) becomes more negative. Moving clo ...