High baseline activity in inferior temporal cortex
... Spontaneous firing is a ubiquitous property of neural activity in the brain. Recent literature suggests that this baseline activity plays a key role in perception. However, it is not known how the baseline activity contributes to neural coding and behavior. Here, by recording from the single neurons ...
... Spontaneous firing is a ubiquitous property of neural activity in the brain. Recent literature suggests that this baseline activity plays a key role in perception. However, it is not known how the baseline activity contributes to neural coding and behavior. Here, by recording from the single neurons ...
Spinal Cord
... the spinal cord. 3. CSF flows through the subarachnoid space. 4. CSF is absorbed into the dural venous sinuses via the ...
... the spinal cord. 3. CSF flows through the subarachnoid space. 4. CSF is absorbed into the dural venous sinuses via the ...
Handout: E-Brain Manual - Faculty Web Sites at the University of
... Systems Systems are collections of nuclei and tracts that provide a specific function; for example, motor, visual, or somatosensory systems. Systems are also named based on location. The limbic system [Latin; border] is involved in emotional regulation and includes several nuclei and structures tha ...
... Systems Systems are collections of nuclei and tracts that provide a specific function; for example, motor, visual, or somatosensory systems. Systems are also named based on location. The limbic system [Latin; border] is involved in emotional regulation and includes several nuclei and structures tha ...
physiological reviews
... of spiral ligament behind it. Smooth muscle cells are described in the walls of arterioles and in capillaries of the cochlea (except in the stria vascularis) and non-myelinated nerve fibers accompany the cochlear artery in the modiolus (216). Perilymph. The perilymph, which fills Scala tympani, Scal ...
... of spiral ligament behind it. Smooth muscle cells are described in the walls of arterioles and in capillaries of the cochlea (except in the stria vascularis) and non-myelinated nerve fibers accompany the cochlear artery in the modiolus (216). Perilymph. The perilymph, which fills Scala tympani, Scal ...
Negative BOLD in Sensory Cortices During
... Abstract People tend to close their eyes when trying to retrieve an event or a visual image from memory. However the brain mechanisms behind this phenomenon remain poorly understood. Recently, we showed that during visual mental imagery, auditory areas show a much more robust deactivation than durin ...
... Abstract People tend to close their eyes when trying to retrieve an event or a visual image from memory. However the brain mechanisms behind this phenomenon remain poorly understood. Recently, we showed that during visual mental imagery, auditory areas show a much more robust deactivation than durin ...
Efficacy of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in the
... Transcranial magnetic stimulation is the noninvasive technique to induce electrical currents in brain tissue via magnetic fields, proven to have therapeutic effects on depression. The magnetic coil located slightly above the scalp can either excite or inhibit cortical brain areas, depending on the s ...
... Transcranial magnetic stimulation is the noninvasive technique to induce electrical currents in brain tissue via magnetic fields, proven to have therapeutic effects on depression. The magnetic coil located slightly above the scalp can either excite or inhibit cortical brain areas, depending on the s ...
Neural correlates of attention in primate visual cortex
... Fig. 1. Time course of responses to two stimuli inside the receptive field. (a) The curves indicate the normalized instantaneous firing rate averaged across 64 cells from the middle-temporal area (MT) and the medial superior temporal area (MST). The x-axis plots the time (in ms) from the onset of th ...
... Fig. 1. Time course of responses to two stimuli inside the receptive field. (a) The curves indicate the normalized instantaneous firing rate averaged across 64 cells from the middle-temporal area (MT) and the medial superior temporal area (MST). The x-axis plots the time (in ms) from the onset of th ...
M555 Medical Neuroscience Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral
... LARGE Multipolar Neurons in the Anterior Horn location: one or more locations in anterior (ventral) horn of spinal cord gray matter present at all spinal cord levels, but ... particularly numerous at the level of the cervical and lumbar enlargements significance: innervate skeletal muscles axons of ...
... LARGE Multipolar Neurons in the Anterior Horn location: one or more locations in anterior (ventral) horn of spinal cord gray matter present at all spinal cord levels, but ... particularly numerous at the level of the cervical and lumbar enlargements significance: innervate skeletal muscles axons of ...
HSAN I - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... mutilations are more severe than in HSAN I: 1) begin earlier when patients cannot understand problem and cooperate. 2) hands are also seriously affected. loss of sweating over acral parts (but no postural hypotension). no prominent muscle weakness. nerve conduction studies - no sensory nerve ...
... mutilations are more severe than in HSAN I: 1) begin earlier when patients cannot understand problem and cooperate. 2) hands are also seriously affected. loss of sweating over acral parts (but no postural hypotension). no prominent muscle weakness. nerve conduction studies - no sensory nerve ...
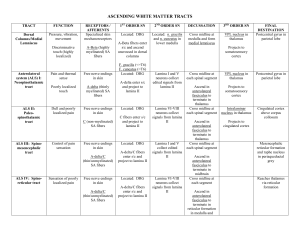
ASCENDING WHITE MATTER TRACTS
... where they cross again to reach CB via superior CB peduncle Ends up ipsilateral ...
... where they cross again to reach CB via superior CB peduncle Ends up ipsilateral ...
Alterations in Synaptic Strength Preceding Axon Withdrawal
... Small MEPPs are also associated with weaker inputs in multiply innervated cells. To determine whether changes in quantal efficacy could be explained by a reduction in the amount of acetylcholine molecules per vesicle, repetitive stimulation under the presence of hemicholinium-3 (depletes synaptic ve ...
... Small MEPPs are also associated with weaker inputs in multiply innervated cells. To determine whether changes in quantal efficacy could be explained by a reduction in the amount of acetylcholine molecules per vesicle, repetitive stimulation under the presence of hemicholinium-3 (depletes synaptic ve ...
Computational modeling of responses in human visual
... 50,000 neurons each. A subset of these neurons, as well as the local glial cells, respond to any given stimulus, and it is this population response that determines the voxel’s receptive field. Furthermore, pRF parameters will depend on the specific population of neurons stimulated by the pattern th ...
... 50,000 neurons each. A subset of these neurons, as well as the local glial cells, respond to any given stimulus, and it is this population response that determines the voxel’s receptive field. Furthermore, pRF parameters will depend on the specific population of neurons stimulated by the pattern th ...
Ultrastructure and Function of Cephalopod Chromatophores
... muscle fibers that represent separate cells. The pigment granules are contained within an elastic sacculus within the pigment cell. The sacculus is attached around the equator of the chromatophore to the cell membrane by zonal haptosomes. In turn, the cell membrane is attached to the radial muscle f ...
... muscle fibers that represent separate cells. The pigment granules are contained within an elastic sacculus within the pigment cell. The sacculus is attached around the equator of the chromatophore to the cell membrane by zonal haptosomes. In turn, the cell membrane is attached to the radial muscle f ...
Neurotic Overview
... k. Respirator brain: ICP > arterial P ischemia/brain death diffuse brain autolysis IF pt is kept alive by respirator l. Radiculopathy = damage to spinal root m. Plexopathy = damage to nerve plexus n. Causalgia = burning pain sensation ...
... k. Respirator brain: ICP > arterial P ischemia/brain death diffuse brain autolysis IF pt is kept alive by respirator l. Radiculopathy = damage to spinal root m. Plexopathy = damage to nerve plexus n. Causalgia = burning pain sensation ...
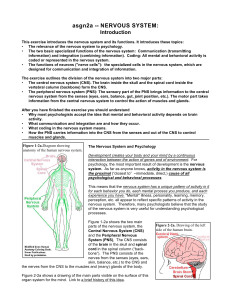
asgn2a -- NERVOUS SYSTEM - Indiana University Bloomington
... electrode in its hypothalamus. mental and behavioral function, as illustrated in Figure 4-2a. Link to the a website devoted to Phineas Gage. ! Electrical, chemical, and, recently, magnetic stimulation in different parts of the brain elicit (~trigger) different behavioral and mental reactions when de ...
... electrode in its hypothalamus. mental and behavioral function, as illustrated in Figure 4-2a. Link to the a website devoted to Phineas Gage. ! Electrical, chemical, and, recently, magnetic stimulation in different parts of the brain elicit (~trigger) different behavioral and mental reactions when de ...
Optical recording of electrical activity in intact neuronal networks
... neuroscience is how simple processes in neurons can generate cognitive functions and form complex memories like those experienced by humans and animals. In principle, if one were able to record from all the neurons in a network involved in a given behavior, it would be possible to reconstruct the r ...
... neuroscience is how simple processes in neurons can generate cognitive functions and form complex memories like those experienced by humans and animals. In principle, if one were able to record from all the neurons in a network involved in a given behavior, it would be possible to reconstruct the r ...
The Nervous System - Napa Valley College
... Many subtle forms of interaction, feedback, and regulation link higher centers with the various components of the brain stem. ...
... Many subtle forms of interaction, feedback, and regulation link higher centers with the various components of the brain stem. ...
Spinal Sensorimotor System: An Overview
... much involved in kinematical muscle actions, as suggested by the proximity of the skin receptors to the quadriceps muscle in Figure 9. That there is an interrelationship among muscle spindle receptors and joint receptors is perhaps obvious to you. Although most people do not commonly think of it as ...
... much involved in kinematical muscle actions, as suggested by the proximity of the skin receptors to the quadriceps muscle in Figure 9. That there is an interrelationship among muscle spindle receptors and joint receptors is perhaps obvious to you. Although most people do not commonly think of it as ...
The representation of Kanizsa illusory contours in the monkey
... be removed from stimuli, revealing how the change affects recognition and neural processing. An extreme reduction is the removal of the very stimulus, defining it with illusory lines. Perceived boundaries without physical differences between shape and background are called illusory (or subjective) c ...
... be removed from stimuli, revealing how the change affects recognition and neural processing. An extreme reduction is the removal of the very stimulus, defining it with illusory lines. Perceived boundaries without physical differences between shape and background are called illusory (or subjective) c ...
Lin J, 2013 - Tsien lab Website - University of California San Diego
... We used ReaChR expressed in the vibrissa motor cortex to drive spiking and vibrissa motion in awake mice when excited with red light through intact skull. Precise vibrissa movements were evoked by expressing ReaChR in the facial motor nucleus in the brainstem and illumination with red light through ...
... We used ReaChR expressed in the vibrissa motor cortex to drive spiking and vibrissa motion in awake mice when excited with red light through intact skull. Precise vibrissa movements were evoked by expressing ReaChR in the facial motor nucleus in the brainstem and illumination with red light through ...
Functional Organization of Ferret Auditory Cortex
... histograms for units recorded on neighbouring probe sites to ensure that responses on each recording site represented independent units. All data presented are from units whose spike counts following the stimulus were significantly different from the spike counts in windows of the same duration just ...
... histograms for units recorded on neighbouring probe sites to ensure that responses on each recording site represented independent units. All data presented are from units whose spike counts following the stimulus were significantly different from the spike counts in windows of the same duration just ...
ZAPORIZHZHIA STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
... Exploring a sensation, a doctor gets subjective information from a patient about his/her feelings that arise during irritation of the receptor apparatus. Therefore, it is necessary to adhere to certain conditions during the study. The study should be carried out in a quiet atmosphere, in a warm room ...
... Exploring a sensation, a doctor gets subjective information from a patient about his/her feelings that arise during irritation of the receptor apparatus. Therefore, it is necessary to adhere to certain conditions during the study. The study should be carried out in a quiet atmosphere, in a warm room ...
Spinal nerves, cervical, lumbar and sacral plexus
... • Higher centers of brain incorporate lower, reflexive motor patterns • Automatic reflexes: – can be activated by brain as needed – use few nerve impulses to control complex motor functions – walking, running, jumping ...
... • Higher centers of brain incorporate lower, reflexive motor patterns • Automatic reflexes: – can be activated by brain as needed – use few nerve impulses to control complex motor functions – walking, running, jumping ...
Multisensory Integration of Dynamic Faces and Voices
... tonotopic map representing high-to-low frequencies in the caudal-torostral direction. Such a map is identified as primary auditory cortex (A1). Lateral belt areas are collinear with tonotopic areas in the core region (Hackett, 2002). The lateral belt area adjacent to A1 is the “middle lateral belt a ...
... tonotopic map representing high-to-low frequencies in the caudal-torostral direction. Such a map is identified as primary auditory cortex (A1). Lateral belt areas are collinear with tonotopic areas in the core region (Hackett, 2002). The lateral belt area adjacent to A1 is the “middle lateral belt a ...