Multisensory Integration of Dynamic Faces and Voices
... tonotopic map representing high-to-low frequencies in the caudal-torostral direction. Such a map is identified as primary auditory cortex (A1). Lateral belt areas are collinear with tonotopic areas in the core region (Hackett, 2002). The lateral belt area adjacent to A1 is the “middle lateral belt a ...
... tonotopic map representing high-to-low frequencies in the caudal-torostral direction. Such a map is identified as primary auditory cortex (A1). Lateral belt areas are collinear with tonotopic areas in the core region (Hackett, 2002). The lateral belt area adjacent to A1 is the “middle lateral belt a ...
When the Sun Prickles Your Nose: An EEG Study Identifying
... [11]. Generally, the sneeze reflex has two phases: An initial spasmodic inspiratory phase followed by a nasal and oral expiratory phase (described in detail by [1,2,11]). It is concluded that the sneezing reflex might be modulated by voluntary cortical mechanisms. Furthermore, Songa & Cingi [2] repo ...
... [11]. Generally, the sneeze reflex has two phases: An initial spasmodic inspiratory phase followed by a nasal and oral expiratory phase (described in detail by [1,2,11]). It is concluded that the sneezing reflex might be modulated by voluntary cortical mechanisms. Furthermore, Songa & Cingi [2] repo ...
Chapter 14 - MDC Faculty Home Pages
... Signals for proprioception, touch, temperature, pressure, pain Somatosensory pathways carry signals from skin, muscles, joints Viscerosensory pathways carry signals from viscera Use a series of neurons to relay signal to brain o Primary (1st order) neuron has peripheral ending, cell body in posterio ...
... Signals for proprioception, touch, temperature, pressure, pain Somatosensory pathways carry signals from skin, muscles, joints Viscerosensory pathways carry signals from viscera Use a series of neurons to relay signal to brain o Primary (1st order) neuron has peripheral ending, cell body in posterio ...
Forward Prediction in the Posterior Parietal Cortex and Dynamic
... that pre-movement activity in the PPC is informative of the intercepting movement, it is, in principle, possible to decoded this activity and utilize it as a predictor of an upcoming movement destination. Based on the decoded endpoint position, a computer cursor or artificial limb could be moved by ...
... that pre-movement activity in the PPC is informative of the intercepting movement, it is, in principle, possible to decoded this activity and utilize it as a predictor of an upcoming movement destination. Based on the decoded endpoint position, a computer cursor or artificial limb could be moved by ...
Different Stimuli, Different Spatial Codes: A Visual Map and an
... bootstrap analysis shows that this difference is significant for the visual sensory examples and one of the two visual motor examples (the sigmoidal R2 was calculated for 100 iterations with 80% of data for each target location; if the full-data Gaussian R2 exceeded 95% of these subsampled sigmoidal ...
... bootstrap analysis shows that this difference is significant for the visual sensory examples and one of the two visual motor examples (the sigmoidal R2 was calculated for 100 iterations with 80% of data for each target location; if the full-data Gaussian R2 exceeded 95% of these subsampled sigmoidal ...
Electrical Activity of a Membrane Resting Potential
... of the brain using a voltmeter and electrodes on the skull ...
... of the brain using a voltmeter and electrodes on the skull ...
Visual adaptation: Neural, psychological and computational aspects
... adjusting neural filtering such that the filtered stimulus distribution remained unchanged. If such adjustments in filtering could be achieved then there would be no need for any adjustments at the nonlinear stage. Strictly speaking, this argument only applies to stimuli taken from a correlated Gaussia ...
... adjusting neural filtering such that the filtered stimulus distribution remained unchanged. If such adjustments in filtering could be achieved then there would be no need for any adjustments at the nonlinear stage. Strictly speaking, this argument only applies to stimuli taken from a correlated Gaussia ...
Postoperative Left Prefrontal Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic
... perception in neuropathic pain patients and in healthy adults using laboratory pain models. No studies have investigated the effects of prefrontal cortex stimulation using transcranial magnetic stimulation on postoperative pain. Methods: Twenty gastric bypass surgery patients were randomly assigned ...
... perception in neuropathic pain patients and in healthy adults using laboratory pain models. No studies have investigated the effects of prefrontal cortex stimulation using transcranial magnetic stimulation on postoperative pain. Methods: Twenty gastric bypass surgery patients were randomly assigned ...
Neurochemical excitation of propriospinal neurons facilitates
... spinal cord. During electrical stimulation of the brain stem, propriospinal transmission alone, independent of long direct projections, was sufficient to activate locomotor-like activity in 27% of in vitro rat preparations (Cowley et al. 2008). Thus regeneration of propriospinal connections and arti ...
... spinal cord. During electrical stimulation of the brain stem, propriospinal transmission alone, independent of long direct projections, was sufficient to activate locomotor-like activity in 27% of in vitro rat preparations (Cowley et al. 2008). Thus regeneration of propriospinal connections and arti ...
Anatomofunctional organization of the ventral primary motor and
... Functional data were then matched with the cytoarchitectonic parcellation of the recorded region. The results demonstrated the existence of a dorso-ventral functional border, encompassing the anatomical boundary between areas F4 and F1, and a rostro-caudal anatomo-functional border between areas F5 ...
... Functional data were then matched with the cytoarchitectonic parcellation of the recorded region. The results demonstrated the existence of a dorso-ventral functional border, encompassing the anatomical boundary between areas F4 and F1, and a rostro-caudal anatomo-functional border between areas F5 ...
A multi-level account of selective attention
... interrupt the sequence of events between sensory input and motor output. First, the sensory neurons that encode external stimuli are noisy. As a result, an identical stimulus will evoke a slightly different response pattern each time it is presented, and this instability can place limits on the amou ...
... interrupt the sequence of events between sensory input and motor output. First, the sensory neurons that encode external stimuli are noisy. As a result, an identical stimulus will evoke a slightly different response pattern each time it is presented, and this instability can place limits on the amou ...
An Extended Model for Stimulus Onset Asynchrony (SOA) in Stroop
... Experiments on Stimulus Onset Asynchrony (SOA) investigated the time course of the Stoop effect [9] [11]. For example, Glaser and Glaser [11] presented words and colors with a set of target-first and distractor-first SOAs (Fig. 1b and c). In their configuration, the words were presented in white on ...
... Experiments on Stimulus Onset Asynchrony (SOA) investigated the time course of the Stoop effect [9] [11]. For example, Glaser and Glaser [11] presented words and colors with a set of target-first and distractor-first SOAs (Fig. 1b and c). In their configuration, the words were presented in white on ...
download file
... (1–48 kHz) at 16 intensities (1–75 dB SPL) to determine the characteristic frequency of each site. Tones had 5 ms cosine-squared ramps and their total duration was 25 ms. Additional stimuli were randomly interleaved and presented at 20 repeats per recording site. Broad band noise was presented in tr ...
... (1–48 kHz) at 16 intensities (1–75 dB SPL) to determine the characteristic frequency of each site. Tones had 5 ms cosine-squared ramps and their total duration was 25 ms. Additional stimuli were randomly interleaved and presented at 20 repeats per recording site. Broad band noise was presented in tr ...
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation: A Neuroscientific Probe of
... Additionally, spTMS or short trains of TMS during real-time EEG or other brain imaging methods can be used to activate a given cortical region and assess the distributed effects on the basis of transsynaptic corticocortical and corticosubcortical effects. Although this approach has yet to be applied ...
... Additionally, spTMS or short trains of TMS during real-time EEG or other brain imaging methods can be used to activate a given cortical region and assess the distributed effects on the basis of transsynaptic corticocortical and corticosubcortical effects. Although this approach has yet to be applied ...
Examples of well-written lab reports, by section
... Simple reflexes occur when single synapses are present between sensory axons and motor neurons. All three nerve cell types involved, sensory, intermediate, and motor, are confined to the spinal cord. As the brain is not necessary to perform these involuntary tasks, it only determines the reflex has ...
... Simple reflexes occur when single synapses are present between sensory axons and motor neurons. All three nerve cell types involved, sensory, intermediate, and motor, are confined to the spinal cord. As the brain is not necessary to perform these involuntary tasks, it only determines the reflex has ...
Pontine Gustatory Activity Is Altered by Electrical Stimulation in the
... were recorded from 51 single PBN neurons during application of sucrose, NaCl, NaCl mixed with amiloride, citric acid, and QHCl with or without concurrent electrical stimulation in the ipsilateral central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA). Based on the sapid stimulus that evoked the greatest discharge, 3 ...
... were recorded from 51 single PBN neurons during application of sucrose, NaCl, NaCl mixed with amiloride, citric acid, and QHCl with or without concurrent electrical stimulation in the ipsilateral central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA). Based on the sapid stimulus that evoked the greatest discharge, 3 ...
neural mechanisms for detecting and remembering novel events
... Most investigators studying the effects of stimulus repetition frame their results in terms of the effects of repetition, rather than the effects of novelty. However, investigations of field potentials recorded from the human medial temporal lobes during performance of verbal memory tasks indicate t ...
... Most investigators studying the effects of stimulus repetition frame their results in terms of the effects of repetition, rather than the effects of novelty. However, investigations of field potentials recorded from the human medial temporal lobes during performance of verbal memory tasks indicate t ...
01-Spinal Reflexes Student`s Copy
... Stimulation of each afferent separately causes discharge of some neurons but only facilitates some nearby neurons (excites them but not enough to discharge). Those facilitated neurons are said to lie in the subliminal fringe zone of those discharging. ...
... Stimulation of each afferent separately causes discharge of some neurons but only facilitates some nearby neurons (excites them but not enough to discharge). Those facilitated neurons are said to lie in the subliminal fringe zone of those discharging. ...
Corticofugal modulation of frequency processing in bat auditory
... Auditory signals are transmitted from the inner ear through the brainstem to the higher auditory regions of the brain. Neurons throughout the auditory system are tuned to stimulus frequency, and in many auditory regions are arranged in topographical maps with respect to their preferred frequency. Th ...
... Auditory signals are transmitted from the inner ear through the brainstem to the higher auditory regions of the brain. Neurons throughout the auditory system are tuned to stimulus frequency, and in many auditory regions are arranged in topographical maps with respect to their preferred frequency. Th ...
Sensory Pathways
... • Arriving stimulus reaches cortical neurons via labeled line • Takes many forms (modalities) • Physical force (such as pressure) ...
... • Arriving stimulus reaches cortical neurons via labeled line • Takes many forms (modalities) • Physical force (such as pressure) ...
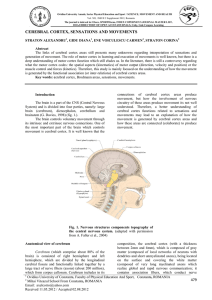
cerebral cortex, sensations and movements
... Fig. 6. Topography of motor and sensory areas located in anterior paracentral and, respectively, posterior paracentral gyri (medial section view of the left side of the left hemisphere). Anterior paracentral gyrus (primary somatomotor cortex) - lower extremity area consists of thigh and calf areas ( ...
... Fig. 6. Topography of motor and sensory areas located in anterior paracentral and, respectively, posterior paracentral gyri (medial section view of the left side of the left hemisphere). Anterior paracentral gyrus (primary somatomotor cortex) - lower extremity area consists of thigh and calf areas ( ...