weiten6_PPT04
... that blue and yellow absorbed individually. The mixture is subtractive because more wavelengths are removed than by each paint alone. The yellow paint in the mixture absorbs the wavelengths associated with blue and the blue paint in the mixture absorbs the wavelengths associated with yellow. The onl ...
... that blue and yellow absorbed individually. The mixture is subtractive because more wavelengths are removed than by each paint alone. The yellow paint in the mixture absorbs the wavelengths associated with blue and the blue paint in the mixture absorbs the wavelengths associated with yellow. The onl ...
internal structure of spinal cord
... IN THE CENTER OF THE GREY MATTER, THE ORIGINAL CAVITY OF THE NEURAL TUBE, THE CANALIS CENTRALIS IS LOCATED. CRANIALLY, IT IS CONTINUOUS WITH THE 4TH CEREBRAL VENTRICLE THE POSTERIOR HORN IS ASSOCIATED WITH SENSORY INFORMATION PROCESSING. THE SENSORY MESSAGES ARE CONVEYED VIA THE DORSAL ROOT TO THE P ...
... IN THE CENTER OF THE GREY MATTER, THE ORIGINAL CAVITY OF THE NEURAL TUBE, THE CANALIS CENTRALIS IS LOCATED. CRANIALLY, IT IS CONTINUOUS WITH THE 4TH CEREBRAL VENTRICLE THE POSTERIOR HORN IS ASSOCIATED WITH SENSORY INFORMATION PROCESSING. THE SENSORY MESSAGES ARE CONVEYED VIA THE DORSAL ROOT TO THE P ...
Deciphering a neural code for vision
... to those derived from the average spatiotemporal transfer function of the eye measured in the laboratory (18, 26, 34). For each experiment we scaled two parameters to simulate illumination levels in the field. We trimmed one parameter, the mean bump rate, to match the estimated transduction noise an ...
... to those derived from the average spatiotemporal transfer function of the eye measured in the laboratory (18, 26, 34). For each experiment we scaled two parameters to simulate illumination levels in the field. We trimmed one parameter, the mean bump rate, to match the estimated transduction noise an ...
1 1 THE CEREBRAL CORTEX Parcellation of the cerebral cortex
... Apraxia. Apraxia is the inability to execute a normal volitional act, even though the motor system and mental status are relatively intact and the person is not paralyzed. The lesions affect cerebral areas around or distant from the primary motor area but do not involve it. The apraxias differ from ...
... Apraxia. Apraxia is the inability to execute a normal volitional act, even though the motor system and mental status are relatively intact and the person is not paralyzed. The lesions affect cerebral areas around or distant from the primary motor area but do not involve it. The apraxias differ from ...
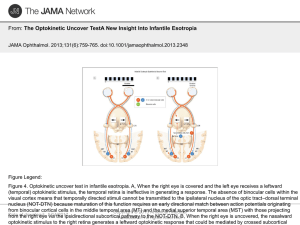
The Optokinetic Uncover TestA New Insight Into Infantile Esotropia
... JAMA Ophthalmol. 2013;131(6):759-765. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2013.2348 ...
... JAMA Ophthalmol. 2013;131(6):759-765. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2013.2348 ...
download file
... In the auditory system, receptive fields are described by tuning curves that quantify neural selectivity for tones over a limited range of frequency and intensity. Several investigators have demonstrated that these receptive fields can be altered by learning (Recanzone 2000; Scheich et al. 1997; Weinb ...
... In the auditory system, receptive fields are described by tuning curves that quantify neural selectivity for tones over a limited range of frequency and intensity. Several investigators have demonstrated that these receptive fields can be altered by learning (Recanzone 2000; Scheich et al. 1997; Weinb ...
cortex
... Apraxia. Apraxia is the inability to execute a normal volitional act, even though the motor system and mental status are relatively intact and the person is not paralyzed. The lesions affect cerebral areas around or distant from the primary motor area but do not involve it. The apraxias differ from ...
... Apraxia. Apraxia is the inability to execute a normal volitional act, even though the motor system and mental status are relatively intact and the person is not paralyzed. The lesions affect cerebral areas around or distant from the primary motor area but do not involve it. The apraxias differ from ...
Branched thalamic afferents - the Sherman Lab
... currently being generated at lower levels. An efference copy is an instruction for a movement and must be clearly distinguished from the movement itself. It is not a movement. Even if the axon that represents the efference copy innervates a ventral horn cell whose axon goes directly to a muscle, thi ...
... currently being generated at lower levels. An efference copy is an instruction for a movement and must be clearly distinguished from the movement itself. It is not a movement. Even if the axon that represents the efference copy innervates a ventral horn cell whose axon goes directly to a muscle, thi ...
Spontaneous plasticity in the injured spinal cord
... ing an absence of sensory and motor function below the level of injury) exhibit spared rims of white matter extending in continuity across the spinal cord lesion site.5 Further, it is notable that many patients with spinal cord injuries exhibit some recovery of function over weeks and months after i ...
... ing an absence of sensory and motor function below the level of injury) exhibit spared rims of white matter extending in continuity across the spinal cord lesion site.5 Further, it is notable that many patients with spinal cord injuries exhibit some recovery of function over weeks and months after i ...
The Brain and Cranial Nerves
... • 14-8 Identify the main components of the limbic system, and specify the locations and functions of each. • 14-9 Identify the major anatomical subdivisions and functions of the cerebrum, and discuss the origin and significance of the major types of brain waves seen in an electroencephalogram. • 14- ...
... • 14-8 Identify the main components of the limbic system, and specify the locations and functions of each. • 14-9 Identify the major anatomical subdivisions and functions of the cerebrum, and discuss the origin and significance of the major types of brain waves seen in an electroencephalogram. • 14- ...
Sensory signals during active versus passive movement
... velocity similarly during passive rotations of the head relative to the body and during passive rotations of the head and body together. Second, higher-order areas, such as parietoinsular vestibular cortex, that are involved in the perception of selfmotion [24] are known to send substantial projecti ...
... velocity similarly during passive rotations of the head relative to the body and during passive rotations of the head and body together. Second, higher-order areas, such as parietoinsular vestibular cortex, that are involved in the perception of selfmotion [24] are known to send substantial projecti ...
Giant Fibre Activation of Direct Flight Muscles in
... in amplitude had no effect on the voltage thresholds required to evoke muscle potentials and the latencies of the potentials. Thus, the amplitude changes do not alter the main conclusions presented in this report and no attempt was made to minimize muscle fibre contractions. Direct wing elevators ar ...
... in amplitude had no effect on the voltage thresholds required to evoke muscle potentials and the latencies of the potentials. Thus, the amplitude changes do not alter the main conclusions presented in this report and no attempt was made to minimize muscle fibre contractions. Direct wing elevators ar ...
Scale-Invariant Adaptation in Response to
... stimulus. (5) We believe that parallel coding is another mechanism which can resolve ambiguity—while one population of neurons may adapt to a stimulus, another may not, thus preserving the context of a stimulus. Our model organism is the weakly electric fish Apteronotus leptorhynchus. These fish emi ...
... stimulus. (5) We believe that parallel coding is another mechanism which can resolve ambiguity—while one population of neurons may adapt to a stimulus, another may not, thus preserving the context of a stimulus. Our model organism is the weakly electric fish Apteronotus leptorhynchus. These fish emi ...
Processing of complex stimuli and natural scenes in the visual cortex
... contextual effects, the authors came up with a different point of view: responses to combinations of orientations might be a more fundamental property than the response to a single orientation alone. One basis for this hypothesis is that even cells that do not seem to be orientation tuned when probe ...
... contextual effects, the authors came up with a different point of view: responses to combinations of orientations might be a more fundamental property than the response to a single orientation alone. One basis for this hypothesis is that even cells that do not seem to be orientation tuned when probe ...
Modulation of early cortical processing during divided attention to
... owing to the low temporal resolution of the methods employed, these studies are not suitable for investigating whether or not any cost involved in splitting the spotlight might impact on the precise temporal locus of attention, i.e. whether the modulation might occur during initial feedforward proce ...
... owing to the low temporal resolution of the methods employed, these studies are not suitable for investigating whether or not any cost involved in splitting the spotlight might impact on the precise temporal locus of attention, i.e. whether the modulation might occur during initial feedforward proce ...
No Binocular Rivalry in the LGN of Alert Macaque Monkeys
... Recordings were made from the dorsal LGN of two alert monkeys (a female Macaca nemestrina and a male M. fascicularis). Initial surgery implanted a stainless steel headpost, and also a scleral eye coil for monitoring eye position (Judge et al., 1980; Robinson, 1963). After the monkeys learned their t ...
... Recordings were made from the dorsal LGN of two alert monkeys (a female Macaca nemestrina and a male M. fascicularis). Initial surgery implanted a stainless steel headpost, and also a scleral eye coil for monitoring eye position (Judge et al., 1980; Robinson, 1963). After the monkeys learned their t ...
2. Parkinsons diseas and Movement Disorders. 1998
... Different areas of the cerebral cortex (neocortex) may be distinguished from one another by their histological features and neuroanatomical connections. Brodmann’s numbering scheme for cortical areas has been used for many years and will be introduced in this section. Projection areas. By following ...
... Different areas of the cerebral cortex (neocortex) may be distinguished from one another by their histological features and neuroanatomical connections. Brodmann’s numbering scheme for cortical areas has been used for many years and will be introduced in this section. Projection areas. By following ...
12 - William M. Clark, M.D
... Gray Matter • Dorsal horns—interneurons that receive somatic and visceral sensory input ...
... Gray Matter • Dorsal horns—interneurons that receive somatic and visceral sensory input ...
Cochlear Implant 1
... Thus, with damaged hair cells, the auditory system has no way of transforming acoustic pressure waves (sound) to neural impulses which in turn leads to hearing impairment. Hair cells damage might cause by diseases (e.g meningitis, Meniere’s). If large number of hair cells or auditory neurons through ...
... Thus, with damaged hair cells, the auditory system has no way of transforming acoustic pressure waves (sound) to neural impulses which in turn leads to hearing impairment. Hair cells damage might cause by diseases (e.g meningitis, Meniere’s). If large number of hair cells or auditory neurons through ...
Appendix S1 Relation of local short
... activities, where each of the activities has something common with the others within the class (one-class–to–one relation). Moreover, two classes of neurons’ activity do not overlap (otherwise the same configuration of firing neurons could give rise to two or more different short-term spectra). Thus ...
... activities, where each of the activities has something common with the others within the class (one-class–to–one relation). Moreover, two classes of neurons’ activity do not overlap (otherwise the same configuration of firing neurons could give rise to two or more different short-term spectra). Thus ...
The Red Nucleus: Past, Present, and Future
... the rubrospinal pathway appears to be ceding to the corticospinal tract as the primary motor pathway in bipeds – perhaps at least partially explaining the size decrease in RNm. In consideration of the RNp, Donkelaar [1] correlated levels of connectivity of the RN in terrestrial vertebrates to develo ...
... the rubrospinal pathway appears to be ceding to the corticospinal tract as the primary motor pathway in bipeds – perhaps at least partially explaining the size decrease in RNm. In consideration of the RNp, Donkelaar [1] correlated levels of connectivity of the RN in terrestrial vertebrates to develo ...
Plasticity in the developing brain: Implications for
... frontal regions lag behind those in visual areas, peaking at around early adolescence in the case of the frontal lobes. There is a general correlation between behavioral development and temporal periods of dynamic changes in synaptic number in specific cortical regions. For example, patching the eye ...
... frontal regions lag behind those in visual areas, peaking at around early adolescence in the case of the frontal lobes. There is a general correlation between behavioral development and temporal periods of dynamic changes in synaptic number in specific cortical regions. For example, patching the eye ...
Experience-dependent corticofugal adjustment
... confirm the shift in BF, i.e., the shift in the frequency map observed in the central nucleus of the IC by Yan and Suga (11), we delivered ASr in the same way as in that research. The BFs of single or multiple IC neurons were measured before and after 30-min delivery of ASr. (Step 2) To examine whet ...
... confirm the shift in BF, i.e., the shift in the frequency map observed in the central nucleus of the IC by Yan and Suga (11), we delivered ASr in the same way as in that research. The BFs of single or multiple IC neurons were measured before and after 30-min delivery of ASr. (Step 2) To examine whet ...
Spinal Cord
... the best choices because the extensive vertebral column injuries are not consistent with the typical presentation of any of these entities. ...
... the best choices because the extensive vertebral column injuries are not consistent with the typical presentation of any of these entities. ...