The Role of NMDA and Non-NMDA Excitatory Amino Acid
... and Willis, 199 I a,b, Dougherty et al., 1992). Recordings from STT cells were made within 750 pm from the nearest edge of the microdialysis fiber and were generally much closer than this. Variation in the distance of the recording sites from the fiber did not result in any apparent differences in t ...
... and Willis, 199 I a,b, Dougherty et al., 1992). Recordings from STT cells were made within 750 pm from the nearest edge of the microdialysis fiber and were generally much closer than this. Variation in the distance of the recording sites from the fiber did not result in any apparent differences in t ...
Brainstem (II)
... smaller anterior corticospinal tract that typically crosses in the spinal cord before terminating. ...
... smaller anterior corticospinal tract that typically crosses in the spinal cord before terminating. ...
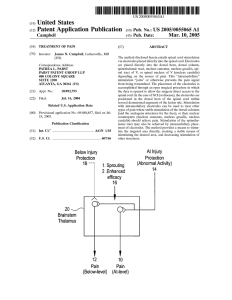
18 "1: 1_ Sprouting (Abnormiall1 Actrvlty)
... thalamus that have lost inputs from distal regions (as a result of the SCI) recruit inputs from the abnormal dorsal horn cells near the SCI. Thus, the inputs from this spinal cord ...
... thalamus that have lost inputs from distal regions (as a result of the SCI) recruit inputs from the abnormal dorsal horn cells near the SCI. Thus, the inputs from this spinal cord ...
Glossary
... Otolaryngologist (ENT Physician)*: Physician specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the ear nose and throat, including diseases of related structures of the head and neck. Otoscope*: A speculumlike instrument for visual examination of the external auditory meatus, external audito ...
... Otolaryngologist (ENT Physician)*: Physician specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the ear nose and throat, including diseases of related structures of the head and neck. Otoscope*: A speculumlike instrument for visual examination of the external auditory meatus, external audito ...
The Organization of Behavioral Repertoire in Motor Cortex
... representation. The method was then relatively neglected in the motor system until our stimulation studies in monkeys suggested a possible mapping of complex movements in the precentral gyrus (Cooke & Graziano 2004a; Graziano et al. 2002a, 2003, 2004, 2005). We found that short stimulation trains ev ...
... representation. The method was then relatively neglected in the motor system until our stimulation studies in monkeys suggested a possible mapping of complex movements in the precentral gyrus (Cooke & Graziano 2004a; Graziano et al. 2002a, 2003, 2004, 2005). We found that short stimulation trains ev ...
Selective visual attention and perceptual coherence
... attention are initiated by a transient control signal that ‘nudges’ the visual system from one coherent state to another. Conscious visual experience starts with the image thrown by the scene upon the retina, where local computations immediately begin to transform the representation of stimuli accor ...
... attention are initiated by a transient control signal that ‘nudges’ the visual system from one coherent state to another. Conscious visual experience starts with the image thrown by the scene upon the retina, where local computations immediately begin to transform the representation of stimuli accor ...
Brainstem (II)
... smaller anterior corticospinal tract that typically crosses in the spinal cord before terminating. ...
... smaller anterior corticospinal tract that typically crosses in the spinal cord before terminating. ...
Evaluation of ventral root reimplantation as a treatment of
... and the muscular effectors might be a limiting factor for anatomical and functional restoration, a factor that is less significant in small animals such as rats, 2/ in the experimental models, roots are generally avulsed just before reimplantation. Thus, this procedure does not take into account the ...
... and the muscular effectors might be a limiting factor for anatomical and functional restoration, a factor that is less significant in small animals such as rats, 2/ in the experimental models, roots are generally avulsed just before reimplantation. Thus, this procedure does not take into account the ...
Ch 48 49 Notes - Dublin City Schools
... • Action potential is the technical name for a nerve signal. ...
... • Action potential is the technical name for a nerve signal. ...
Auditory physiology chapter
... The negative sign here simply means that the signal will be 30 dB weaker on the fluid side of the boundary. Consequently, if the airborne sound wave were to directly drive a simple membrane covering the oval window, a 30 dB loss in signal intensity would occur at the air-fluid boundary. This is not ...
... The negative sign here simply means that the signal will be 30 dB weaker on the fluid side of the boundary. Consequently, if the airborne sound wave were to directly drive a simple membrane covering the oval window, a 30 dB loss in signal intensity would occur at the air-fluid boundary. This is not ...
Electrical Interactions via the Extracellular Potential Near Cell Bodies
... ephaptic interactions in healthy systems without such unusual properties. Several studies have shown significant effects of field potentials in response to electrical stimulation, when many neurons are simultaneously active (Dalkara et al., 1986; Turner and Richardson, 1991), but so far no interacti ...
... ephaptic interactions in healthy systems without such unusual properties. Several studies have shown significant effects of field potentials in response to electrical stimulation, when many neurons are simultaneously active (Dalkara et al., 1986; Turner and Richardson, 1991), but so far no interacti ...
aud
... The negative sign here simply means that the signal will be 30 dB weaker on the fluid side of the boundary. Consequently, if the airborne sound wave were to directly drive a simple membrane covering the oval window, a 30 dB loss in signal intensity would occur at the air-fluid boundary. This is not ...
... The negative sign here simply means that the signal will be 30 dB weaker on the fluid side of the boundary. Consequently, if the airborne sound wave were to directly drive a simple membrane covering the oval window, a 30 dB loss in signal intensity would occur at the air-fluid boundary. This is not ...
The functional role of GABA and glycine in monaural and binaural
... t Zoologisches Institut der Universit/it Miinchen, Luisenstr. 14, W 8000 M/inchen 2, FRG 2 Institut fiir Zoologie der Universitfit Regensburg, Universit/itsstr. 31, W 8400 Regensburg, FRG ...
... t Zoologisches Institut der Universit/it Miinchen, Luisenstr. 14, W 8000 M/inchen 2, FRG 2 Institut fiir Zoologie der Universitfit Regensburg, Universit/itsstr. 31, W 8400 Regensburg, FRG ...
Word doc - Center for Neural Science
... CF stimuli, narrow frequency receptive fields (reflected in narrow threshold-tuning functions and response areas), and a topographic arrangement of CF representations (Doron et al. 2002; Merzenich et al. 1975; Phillips et al. 1985b; Sally and Kelly 1988). Similar features are found throughout the le ...
... CF stimuli, narrow frequency receptive fields (reflected in narrow threshold-tuning functions and response areas), and a topographic arrangement of CF representations (Doron et al. 2002; Merzenich et al. 1975; Phillips et al. 1985b; Sally and Kelly 1988). Similar features are found throughout the le ...
Human Reflexes Introductory Reading and
... Reflex testing is an important diagnostic tool for assessing the condition of the nervous system. Distorted, exaggerated, or reflexes that are absent may indicate degeneration or pathology of portions of the nervous system, often before other signs are apparent. If the spinal cord is damaged, then r ...
... Reflex testing is an important diagnostic tool for assessing the condition of the nervous system. Distorted, exaggerated, or reflexes that are absent may indicate degeneration or pathology of portions of the nervous system, often before other signs are apparent. If the spinal cord is damaged, then r ...
Chapter 14:The Brain and Cranial Nerves
... • The human brain is complex • Brain function is associated with life • This chapter is a study of brain and cranial nerves directly connected to it • Will provide insight into brain circuitry and function ...
... • The human brain is complex • Brain function is associated with life • This chapter is a study of brain and cranial nerves directly connected to it • Will provide insight into brain circuitry and function ...
- Stem-cell and Brain Research Institute
... monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Some of the results from these injections have already been reported in another article (Falchier et al., 2002). Central area 17 injections were in the cortex subserving 0º–2º in the lower visual field (M85RHDY and M85RHFsB). Injections aimed at the peripheral represen ...
... monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Some of the results from these injections have already been reported in another article (Falchier et al., 2002). Central area 17 injections were in the cortex subserving 0º–2º in the lower visual field (M85RHDY and M85RHFsB). Injections aimed at the peripheral represen ...
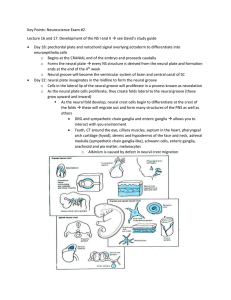
Key Points: Neuroscience Exam #2 Lecture 16 and 17: Development of
... o Clinical: testing reflexes can determine level of the lesion (hyper or hypo-reflexive) Muscle spindles give info about length of muscle and GTO give info about the tension on the muscle o provide continuous, subconscious feedback to the spinal cord, cerebellum, and cortex o they also play a role i ...
... o Clinical: testing reflexes can determine level of the lesion (hyper or hypo-reflexive) Muscle spindles give info about length of muscle and GTO give info about the tension on the muscle o provide continuous, subconscious feedback to the spinal cord, cerebellum, and cortex o they also play a role i ...
Organization of the primary somatosensory cortex and wing
... the Big Brown Bat. The existence of orderly representations of the sensory surface in somatosensory cortex and other brain regions has long been known. Earliest observations of correspondence between peripheral tactile stimulation and cortical excitation were reported during the late 1930s and early ...
... the Big Brown Bat. The existence of orderly representations of the sensory surface in somatosensory cortex and other brain regions has long been known. Earliest observations of correspondence between peripheral tactile stimulation and cortical excitation were reported during the late 1930s and early ...
Functional Neuroanatomy for Posture and Gait Control
... POSTURE-GAIT CONTROL Figure 1 illustrates our recent understanding of basic signal flows involved in motor control. Sensory signals arising from external stimuli and/or internal visceral information have various functions. For example, they are to be utilized for cognitive processing such as product ...
... POSTURE-GAIT CONTROL Figure 1 illustrates our recent understanding of basic signal flows involved in motor control. Sensory signals arising from external stimuli and/or internal visceral information have various functions. For example, they are to be utilized for cognitive processing such as product ...
Experiencing Sensation and Perception
... frequencies of sound. Organization in the somatosensory information is going to be even more important. The huge area of the skin makes it imperative that the brain, among other pieces of information to track, must know where the sensory information is coming from. In this section, two levels of org ...
... frequencies of sound. Organization in the somatosensory information is going to be even more important. The huge area of the skin makes it imperative that the brain, among other pieces of information to track, must know where the sensory information is coming from. In this section, two levels of org ...
Descending Pathways in Motor Control
... Each of the descending pathways involved in motor control has a number of anatomical, molecular, pharmacological, and neuroinformatic characteristics. They are differentially involved in motor control, a process that results from operations involving the entire motor network rather than from the bra ...
... Each of the descending pathways involved in motor control has a number of anatomical, molecular, pharmacological, and neuroinformatic characteristics. They are differentially involved in motor control, a process that results from operations involving the entire motor network rather than from the bra ...
1-Student`s Refexes
... The extent of the response in a reflex depends on the intensity of the stimulus. The more intense the stimulus is, the greater is the spread of activity in the spinal cord, involving and recruiting more and more other motor neurons . when the sole of the foot is stimulated by a weak painful stimulus ...
... The extent of the response in a reflex depends on the intensity of the stimulus. The more intense the stimulus is, the greater is the spread of activity in the spinal cord, involving and recruiting more and more other motor neurons . when the sole of the foot is stimulated by a weak painful stimulus ...
the manuscript as pdf
... awareness of self and environment. The fluctuations suggest that their limited functional capacities might be augmented if their highest functional performance level was stabilized. In some cases MCS patients fluctuate quite widely, revealing marked residual cerebral function including capacities fo ...
... awareness of self and environment. The fluctuations suggest that their limited functional capacities might be augmented if their highest functional performance level was stabilized. In some cases MCS patients fluctuate quite widely, revealing marked residual cerebral function including capacities fo ...