the spinal cord and spinal nerves
... The nervous system uses a series of electrochemical signals to receive information from the receptors of the body in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) regions and sends them to the central nervous system (CNS), the brain and spinal cord, to coordinate our actions. A new message is then sent to an ...
... The nervous system uses a series of electrochemical signals to receive information from the receptors of the body in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) regions and sends them to the central nervous system (CNS), the brain and spinal cord, to coordinate our actions. A new message is then sent to an ...
11-1 FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Sensory input
... 1) Sensory input can be at the conscious level, such as touch, taste, smell, sight, etc. 2) Sensory input can be at the unconscious level, such as blood pressure, blood oxygen levels, etc. B. The motor, or efferent, division carries action potentials FROM the CNS to effector organs and can be divide ...
... 1) Sensory input can be at the conscious level, such as touch, taste, smell, sight, etc. 2) Sensory input can be at the unconscious level, such as blood pressure, blood oxygen levels, etc. B. The motor, or efferent, division carries action potentials FROM the CNS to effector organs and can be divide ...
physiological plasticity in auditory cortex: rapid induction by learning
... various viewpoints--anatomical, biochemical and physiological. The topics most closely associated with neuroplasticity are (a) neural development, (b) recovery of function following pathology, (c) functional reorganization following sensory deprivation or peripheral manipulations, and (d) learning a ...
... various viewpoints--anatomical, biochemical and physiological. The topics most closely associated with neuroplasticity are (a) neural development, (b) recovery of function following pathology, (c) functional reorganization following sensory deprivation or peripheral manipulations, and (d) learning a ...
Responses to Odors Mapped in Snail Tentacle and Brain by [14C]
... label. In order to determine whether the small foci in the digits, which are variously placed, form a spatial pattern characteristic for each odor, all exposed tentacles were reconstructed in three dimensions by making drawings from selected sections. Comparisons between different stimulus condition ...
... label. In order to determine whether the small foci in the digits, which are variously placed, form a spatial pattern characteristic for each odor, all exposed tentacles were reconstructed in three dimensions by making drawings from selected sections. Comparisons between different stimulus condition ...
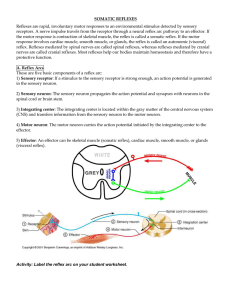
Reflex Activity/Lab
... These are five basic components of a reflex arc: 1) Sensory receptor: If a stimulus to the sensory receptor is strong enough, an action potential is generated in the sensory neuron. 2) Sensory neuron: The sensory neuron propagates the action potential and synapses with neurons in the spinal cord or ...
... These are five basic components of a reflex arc: 1) Sensory receptor: If a stimulus to the sensory receptor is strong enough, an action potential is generated in the sensory neuron. 2) Sensory neuron: The sensory neuron propagates the action potential and synapses with neurons in the spinal cord or ...
EXAMINATION OF NERVES OF LOWER LIMB
... OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture the students should know: •The sensory and motor nerve supplies of the different regions of lower limb •Examination of nerves of lower limb •Significance of lesions of different nerves of lower limb and what abnormality would appear in case of a lesion ...
... OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture the students should know: •The sensory and motor nerve supplies of the different regions of lower limb •Examination of nerves of lower limb •Significance of lesions of different nerves of lower limb and what abnormality would appear in case of a lesion ...
EXAMINATION OF NERVES OF LOWER LIMB
... OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture the students should know: •The sensory and motor nerve supplies of the different regions of lower limb •Examination of nerves of lower limb •Significance of lesions of different nerves of lower limb and what abnormality would appear in case of a lesion ...
... OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture the students should know: •The sensory and motor nerve supplies of the different regions of lower limb •Examination of nerves of lower limb •Significance of lesions of different nerves of lower limb and what abnormality would appear in case of a lesion ...
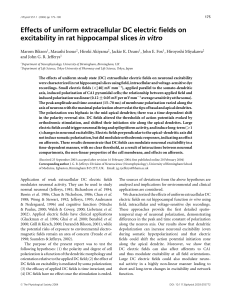
Effects of uniform extracellular DC electric fields on excitability in rat
... allowed to stabilize before applying the fields. Control responses were obtained before and after application of polarizing current. Orthodromic stimuli were applied >0.5 s after field application or termination. Unless otherwise stated, orthodromic stimulation intensity was adjusted to produce 30–7 ...
... allowed to stabilize before applying the fields. Control responses were obtained before and after application of polarizing current. Orthodromic stimuli were applied >0.5 s after field application or termination. Unless otherwise stated, orthodromic stimulation intensity was adjusted to produce 30–7 ...
View PDF - CiteSeerX
... oscilloscope, and stored on a digital tape recorder (Biologic DTR1800). The signal and stimulus traces were digitized (signal sample rate 4000 Hz, stimulus sample rate 500 Hz) and stored on a computer using a CED1401plus interface and Spike2 software (version 2.24, Cambridge Electronic Design, Cambr ...
... oscilloscope, and stored on a digital tape recorder (Biologic DTR1800). The signal and stimulus traces were digitized (signal sample rate 4000 Hz, stimulus sample rate 500 Hz) and stored on a computer using a CED1401plus interface and Spike2 software (version 2.24, Cambridge Electronic Design, Cambr ...
L13Spinal Cord Structure Functio13
... control movements of head in response to auditory, visual, and cutaneous stimulation ...
... control movements of head in response to auditory, visual, and cutaneous stimulation ...
Enhanced cholinergic suppression of previously strengthened synapses enables the formation of
... cognitive tasks, including encoding of verbal stimuli for subsequent retrieval (Atri et al., 2003; Ghonheim & Mewaldt, 1977), encoding of visual stimuli for subsequent recognition (Aigner & Mishkin, 1986; Sherman, Atri, Hasselmo, Stern, & Howard, 2003) and response to stimuli in a continuous perform ...
... cognitive tasks, including encoding of verbal stimuli for subsequent retrieval (Atri et al., 2003; Ghonheim & Mewaldt, 1977), encoding of visual stimuli for subsequent recognition (Aigner & Mishkin, 1986; Sherman, Atri, Hasselmo, Stern, & Howard, 2003) and response to stimuli in a continuous perform ...
Neural processes underlying conscious perception
... bold in V1 for undetected versus detected grating patches at threshold with a decrease of the P1 wave in ERP, which is an early component peaking at 100 ms post-stimulus. Similarly, Dehaene et al. showed that the P1 and N1 waves evoked by masked words were reduced as compared to unmasked words [14]. ...
... bold in V1 for undetected versus detected grating patches at threshold with a decrease of the P1 wave in ERP, which is an early component peaking at 100 ms post-stimulus. Similarly, Dehaene et al. showed that the P1 and N1 waves evoked by masked words were reduced as compared to unmasked words [14]. ...
Review The Neural Basis of Perceptual Learning
... orientation or the location of stimulus elements discussed above, the specificity of learning to more complex features requires a mechanism that is context dependent. This leads to the alternate possibilities that the learning involves higher order cortical areas that can encode more complex stimulu ...
... orientation or the location of stimulus elements discussed above, the specificity of learning to more complex features requires a mechanism that is context dependent. This leads to the alternate possibilities that the learning involves higher order cortical areas that can encode more complex stimulu ...
Synaptic Competition during the Reformation of a Neuromuscular Map
... C6 (ASI 5 1.03). Similar results were observed in sector III (data not shown). ...
... C6 (ASI 5 1.03). Similar results were observed in sector III (data not shown). ...
FORM A
... 40) Choose the INCORRECT statement concerning the brachial plexus. a) all nerves derived from the lateral cord contain contributions from C5, 6, 7 spinal nerve roots b) the ulnar nerve is derived from the medial cord c) nerves derived from the posterior cord innervate muscles which are mostly flexo ...
... 40) Choose the INCORRECT statement concerning the brachial plexus. a) all nerves derived from the lateral cord contain contributions from C5, 6, 7 spinal nerve roots b) the ulnar nerve is derived from the medial cord c) nerves derived from the posterior cord innervate muscles which are mostly flexo ...
Modulation of Sympathetic and Somatomotor Function by the
... The methods for all experiments were approved by the University of Chicago Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and conformed to the guidelines of National Institutes of Health and the International Association for the Study of Pain. Male Sprague-Dawley rats (250 – 450 g; n ⫽ 110; Charles Riv ...
... The methods for all experiments were approved by the University of Chicago Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and conformed to the guidelines of National Institutes of Health and the International Association for the Study of Pain. Male Sprague-Dawley rats (250 – 450 g; n ⫽ 110; Charles Riv ...
Properties of Single Neurons Responsive to Light Mechanical
... rod, on the end of which was attached a piece of acetate plastic, 0.3 mm wide x 5.0 or 7.5 mm long, was used. These “edge” stimuli were applied normal to the skin surface, both parallel and perpendicular to the long axis of the digit on which the RF was located. Cylindrical stimuli were also applied ...
... rod, on the end of which was attached a piece of acetate plastic, 0.3 mm wide x 5.0 or 7.5 mm long, was used. These “edge” stimuli were applied normal to the skin surface, both parallel and perpendicular to the long axis of the digit on which the RF was located. Cylindrical stimuli were also applied ...
tracts - Anatomický ústav 1. LF UK
... Spinal cord is supplied by spinal arteries coming from the branches of the subclavian artery and the descending aorta (aa. intercostales posteriores , aa . lumbales , a iliolumbalis , aa . sacrales laterales). They enter into the spinal canal through the foramen intervertebralia . Another source in ...
... Spinal cord is supplied by spinal arteries coming from the branches of the subclavian artery and the descending aorta (aa. intercostales posteriores , aa . lumbales , a iliolumbalis , aa . sacrales laterales). They enter into the spinal canal through the foramen intervertebralia . Another source in ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... (Department of Pediatric Medicine, NRS Medical college/ The West Bengal University of Health Sciences, India) ...
... (Department of Pediatric Medicine, NRS Medical college/ The West Bengal University of Health Sciences, India) ...
Modulation of brain activity by electrical stimulation and external
... method to this day. But because its positive effects decline over time and it can cause some serious side effect, some patients need to resort to other treatment methods. High frequency electrical stimulation of components of the basal ganglia or thalamus, called deep brain stimulation, has become i ...
... method to this day. But because its positive effects decline over time and it can cause some serious side effect, some patients need to resort to other treatment methods. High frequency electrical stimulation of components of the basal ganglia or thalamus, called deep brain stimulation, has become i ...
Limitations of Neural Map Topography for Decoding Spatial
... are equivalent to step functions in our one-dimensional model. To generate responses for decoding, we presented each stimulus to the model 50 times, for a total of 150 presentations. The response ri of each tectal cell to each presentation of each stimulus was recorded. Decoding was performed as des ...
... are equivalent to step functions in our one-dimensional model. To generate responses for decoding, we presented each stimulus to the model 50 times, for a total of 150 presentations. The response ri of each tectal cell to each presentation of each stimulus was recorded. Decoding was performed as des ...
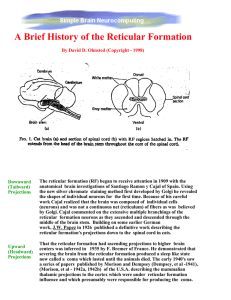
A Brief History of the Reticular Formation
... states that whenever the motivation is the same, a defined set of stimuli will always release a specific motor response. Lorentz was the first to propose this concept in a 1935 German paper but not until 1948 and 1951 did Tinbergen introduce this concept to the English speaking world. The region of ...
... states that whenever the motivation is the same, a defined set of stimuli will always release a specific motor response. Lorentz was the first to propose this concept in a 1935 German paper but not until 1948 and 1951 did Tinbergen introduce this concept to the English speaking world. The region of ...
Chapter 13 *Lecture PowerPoint The Spinal Cord,
... • Ascending tracts—carry sensory information up the spinal cord • Descending tracts—carry motor information down the spinal cord – All nerve fibers in a given tract have a similar origin, destination, and function • Decussation—as the fibers pass up or down the brainstem and spinal cord they cross o ...
... • Ascending tracts—carry sensory information up the spinal cord • Descending tracts—carry motor information down the spinal cord – All nerve fibers in a given tract have a similar origin, destination, and function • Decussation—as the fibers pass up or down the brainstem and spinal cord they cross o ...
Multisensory anatomical pathways - Centre de Recherche Cerveau
... projections when it comes to interactions between sensory modalities. This would support the hypothesis according to which the anatomical pattern of the cortico-cortical connections that involve the polysensory areas of the frontal lobe depend on the intrinsic architecture of areas linked together i ...
... projections when it comes to interactions between sensory modalities. This would support the hypothesis according to which the anatomical pattern of the cortico-cortical connections that involve the polysensory areas of the frontal lobe depend on the intrinsic architecture of areas linked together i ...
Section 1: Anatomy of the sensorimotor system
... There is currently controversy over exactly how many cortical motor areas exist. This is further confounded by disagreement over what criteria should be used to define a motor area. Proposed criteria include requirements that a motor area has projections to spinal motor neurons and a full representa ...
... There is currently controversy over exactly how many cortical motor areas exist. This is further confounded by disagreement over what criteria should be used to define a motor area. Proposed criteria include requirements that a motor area has projections to spinal motor neurons and a full representa ...


![Responses to Odors Mapped in Snail Tentacle and Brain by [14C]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017009313_1-932f7069dbfdd3fd3915bbe942d02b0f-300x300.png)