Spinal cord worksheet
... 5.The system that promotes the fight-or-flight response______________ 6.The system that stimulates the digestive and urinary tracts________________ 7.A complete pathway through the nervous system from stimulus to response____________________ ...
... 5.The system that promotes the fight-or-flight response______________ 6.The system that stimulates the digestive and urinary tracts________________ 7.A complete pathway through the nervous system from stimulus to response____________________ ...
Unit: Regulation Notes
... receptor (recognizes the stimulus), goes to the 2) sensory neuron (sends signal to brain), to the 3) interneuron (routes the impulse to the correct part of the brain), to the 4) motor neuron (alerts the muscle), and then to the 5) effector (the muscle or gland) Ex. Touching hot stove ...
... receptor (recognizes the stimulus), goes to the 2) sensory neuron (sends signal to brain), to the 3) interneuron (routes the impulse to the correct part of the brain), to the 4) motor neuron (alerts the muscle), and then to the 5) effector (the muscle or gland) Ex. Touching hot stove ...
456 ss 96 final - People Server at UNCW
... 56. “Phineas Gage” suffered damage to: a) the frontal lobe b) the temporal lobes c) the brain stem d) the hippocampus 57. The “locked in syndrome” may result from extensive damage to the: a) brainstem b) frontal lobes c) hippocampus d) spinal cord 58. Ischemic strokes occur due to: a) hemorrhage b) ...
... 56. “Phineas Gage” suffered damage to: a) the frontal lobe b) the temporal lobes c) the brain stem d) the hippocampus 57. The “locked in syndrome” may result from extensive damage to the: a) brainstem b) frontal lobes c) hippocampus d) spinal cord 58. Ischemic strokes occur due to: a) hemorrhage b) ...
Nervous System
... various body parts is proportional to how sensitive that part of the body is. ...
... various body parts is proportional to how sensitive that part of the body is. ...
Nervous System
... Uses hormones that travel through the bloodstream. Takes longer to get there but lasts a long time ...
... Uses hormones that travel through the bloodstream. Takes longer to get there but lasts a long time ...
آلفا با دامنهي زياد
... the scalp, electrical activity must involve thousands of neurons acting synchronously. The neocortex has a high density of neurons, which ...
... the scalp, electrical activity must involve thousands of neurons acting synchronously. The neocortex has a high density of neurons, which ...
Membrane potential
... • Most organs are continually receiving both sympathetic and parasympathetic stimulation • For example, sympathetic nerves signal heart to speed up, and parasympathetic stimulate it to slow down • Which dominates depends on situation ...
... • Most organs are continually receiving both sympathetic and parasympathetic stimulation • For example, sympathetic nerves signal heart to speed up, and parasympathetic stimulate it to slow down • Which dominates depends on situation ...
LECTURE OUTLINE
... The spinal cord and the brain make up the central nervous system (CNS). The Spinal Cord The spinal cord extends from the base of the brain through a large opening in the skull and into the vertebral canal. Structure of the Spinal Cord The spinal nerves project from the cord between the vertebrae. Fl ...
... The spinal cord and the brain make up the central nervous system (CNS). The Spinal Cord The spinal cord extends from the base of the brain through a large opening in the skull and into the vertebral canal. Structure of the Spinal Cord The spinal nerves project from the cord between the vertebrae. Fl ...
110 ~W~U~~ ~~~\W(Q)(UJ~
... sensory neuron, at least one synapse in the spinal cord, and a motor neuron. Each sensory neuron stimulated by the stove sends an impulse up its axonlike dendritic process, into the posterior root of the spinal nerve, past the posterior root ganglion containing the cell body of that sensory neuron, ...
... sensory neuron, at least one synapse in the spinal cord, and a motor neuron. Each sensory neuron stimulated by the stove sends an impulse up its axonlike dendritic process, into the posterior root of the spinal nerve, past the posterior root ganglion containing the cell body of that sensory neuron, ...
PNS/Reflexes
... pain receptors are tonic and do not exhibit peripheral adaptation; but central adaptation can reduce the perception of pain (see below). IV. Adaptation - when you are exposed to a constant stimulus (ex, a scent), your perception of that stimulus can sometimes diminish over time. One of two things ca ...
... pain receptors are tonic and do not exhibit peripheral adaptation; but central adaptation can reduce the perception of pain (see below). IV. Adaptation - when you are exposed to a constant stimulus (ex, a scent), your perception of that stimulus can sometimes diminish over time. One of two things ca ...
Slide ()
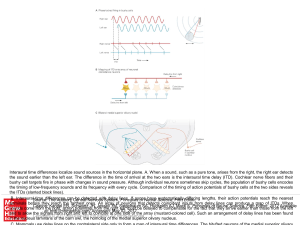
... Interaural time differences localize sound sources in the horizontal plane. A. When a sound, such as a pure tone, arises from the right, the right ear detects the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve ...
... Interaural time differences localize sound sources in the horizontal plane. A. When a sound, such as a pure tone, arises from the right, the right ear detects the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve ...
Unit Outline_Ch17 - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... The spinal cord and the brain make up the central nervous system (CNS). The Spinal Cord The spinal cord extends from the base of the brain through a large opening in the skull and into the vertebral canal. Structure of the Spinal Cord The spinal nerves project from the cord between the vertebrae. Fl ...
... The spinal cord and the brain make up the central nervous system (CNS). The Spinal Cord The spinal cord extends from the base of the brain through a large opening in the skull and into the vertebral canal. Structure of the Spinal Cord The spinal nerves project from the cord between the vertebrae. Fl ...
Neuron Function notes
... endoneurium – surrounds each nerve fiber Sensory nerve – only sensory fibers, afferent nerves , carry impulses to CNS Motor nerves – efferent, contain only motor fibers, carry impulse away from CNS Mixed nerves – have both sensory and motor nerve fibers Ganglia = clusters of neuron cell bodies Locat ...
... endoneurium – surrounds each nerve fiber Sensory nerve – only sensory fibers, afferent nerves , carry impulses to CNS Motor nerves – efferent, contain only motor fibers, carry impulse away from CNS Mixed nerves – have both sensory and motor nerve fibers Ganglia = clusters of neuron cell bodies Locat ...
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
... c. Awareness of these stimuli (sensation / perception) occurs in the brain 2. Classification by Stimulus Type a. Mechanoreceptors: Touch, pressure, vibration, stretch, & itch b. Thermoreceptors: Changes in temperature c. Photoreceptors: Light energy (e.g., retina) d. Chemoreceptors: Chemicals (e.g., ...
... c. Awareness of these stimuli (sensation / perception) occurs in the brain 2. Classification by Stimulus Type a. Mechanoreceptors: Touch, pressure, vibration, stretch, & itch b. Thermoreceptors: Changes in temperature c. Photoreceptors: Light energy (e.g., retina) d. Chemoreceptors: Chemicals (e.g., ...
The nervous system
... quadriceps muscle stretch. This information travels to the spinal cord. There, after one synapse in the spinal cord, the information is sent back out to the muscle making it contract and the knee ...
... quadriceps muscle stretch. This information travels to the spinal cord. There, after one synapse in the spinal cord, the information is sent back out to the muscle making it contract and the knee ...
Stimulus and response
... • E.1.1 Define the terms stimulus, response and reflex in the context of animal behaviour. • E.1.2 Explain the role of receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals to stimuli. • E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain w ...
... • E.1.1 Define the terms stimulus, response and reflex in the context of animal behaviour. • E.1.2 Explain the role of receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals to stimuli. • E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain w ...
Neurons - Seung Lab
... Neurons are excitatory or inhibitory (Dale’s Law) • Version 1: A neuron is either excitatory or inhibitory in its effects on other neurons. • Version 2: A neuron secretes a single neurotransmitter at its synapses. • There are exceptions to Dale’s Law. ...
... Neurons are excitatory or inhibitory (Dale’s Law) • Version 1: A neuron is either excitatory or inhibitory in its effects on other neurons. • Version 2: A neuron secretes a single neurotransmitter at its synapses. • There are exceptions to Dale’s Law. ...
chapter 8 lecture ppt
... • We are unaware of most sensory input • Sensory input is vital of our survival and normal functions ...
... • We are unaware of most sensory input • Sensory input is vital of our survival and normal functions ...
Regulation powerpoint File
... control and coordination of life functions and activities 2 systems involved: 1. nervous- electrical system, brain,spine and nerves found in multicellular organisms 2. endocrine- chemical system, hormones found in all organisms Nervous System: definitions: a. stimulus- change in the internal or ex ...
... control and coordination of life functions and activities 2 systems involved: 1. nervous- electrical system, brain,spine and nerves found in multicellular organisms 2. endocrine- chemical system, hormones found in all organisms Nervous System: definitions: a. stimulus- change in the internal or ex ...
answers - UCSD Cognitive Science
... Directional Specialization (in general, what are the differences between the front, mid, and back areas of the brain) a. Front: Motor b. Mid: Sensory c. Back: Visual Ventricles: A series of hollow, interconnected chambers that are filled with CSF. (lateral, third, fourth, choroid plexus creastes CSF ...
... Directional Specialization (in general, what are the differences between the front, mid, and back areas of the brain) a. Front: Motor b. Mid: Sensory c. Back: Visual Ventricles: A series of hollow, interconnected chambers that are filled with CSF. (lateral, third, fourth, choroid plexus creastes CSF ...
Nervous System
... Identify the two main parts of the Nervous System Describe the structure of a neuron and the function of each major part. Distinguish between sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Summarize the electrical and chemical conditions of resting potential. Outline the electrical and chemical c ...
... Identify the two main parts of the Nervous System Describe the structure of a neuron and the function of each major part. Distinguish between sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Summarize the electrical and chemical conditions of resting potential. Outline the electrical and chemical c ...
Chapter 48 p. 1040-1053
... hypothalamic nuclei: sexual and mating behaviors, fight-or-flight response, pleasure The Hypothalamus and Circadian Rhythms o biological clock: component of circadian rhythms o suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN): in mammal’s hypothalamus; acts as biological clock o external sues for circadian rhythms, ...
... hypothalamic nuclei: sexual and mating behaviors, fight-or-flight response, pleasure The Hypothalamus and Circadian Rhythms o biological clock: component of circadian rhythms o suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN): in mammal’s hypothalamus; acts as biological clock o external sues for circadian rhythms, ...
Document
... Telencephalon (endbrain) is located at the front of the forebrain. – called cerebrum in mammals mammals have brains particularly large relative to their body mass largely reflects enlargement of cerebrum center for correlation, association, and learning in mammals ...
... Telencephalon (endbrain) is located at the front of the forebrain. – called cerebrum in mammals mammals have brains particularly large relative to their body mass largely reflects enlargement of cerebrum center for correlation, association, and learning in mammals ...