File
... - Simplest spinal reflex - Monosynaptic reflex - e.g knee jerk 1. Receptor muscle sense the action (e.g hammer on knee) 2. Message sent along afferent nerve axon to spinal cord 3. Afferent synapses with efferent of same muscles 4. Impulse in transmitted along efferent pathway 5. Motor unit contracts ...
... - Simplest spinal reflex - Monosynaptic reflex - e.g knee jerk 1. Receptor muscle sense the action (e.g hammer on knee) 2. Message sent along afferent nerve axon to spinal cord 3. Afferent synapses with efferent of same muscles 4. Impulse in transmitted along efferent pathway 5. Motor unit contracts ...
Sensory Physiology
... – Did you activate neurons with low as well as high threshold for activation? ...
... – Did you activate neurons with low as well as high threshold for activation? ...
The CNS - Mr. Lesiuk
... The Brain Stem The brain stem contains the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain. The medulla oblongata and pons have centers for vital functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and vasoconstriction. The medulla also coordinates swallowing and some other automatic reactions (many reflex centers for h ...
... The Brain Stem The brain stem contains the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain. The medulla oblongata and pons have centers for vital functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and vasoconstriction. The medulla also coordinates swallowing and some other automatic reactions (many reflex centers for h ...
BASICS OF NEUROBIOLOGY Zsolt Liposits and Imre Kalló 2016
... The first lecture characterises the nervous tissue, in which neurons and glial cells exist in structural and functional symbioses. The second lecture demonstrates the unique morphology and the excitability of neurons and some basic networks established by them. The third lecture explains how informa ...
... The first lecture characterises the nervous tissue, in which neurons and glial cells exist in structural and functional symbioses. The second lecture demonstrates the unique morphology and the excitability of neurons and some basic networks established by them. The third lecture explains how informa ...
physio unit 9 [4-20
... Decrease signal transmission when input intensity is too great They travel backwards from cortex to thalamus, medulla, and spinal cord Amplifying Divergence Example Characteristic of corticospinal pathway, which controls skeletal muscles Divergence into multiple tracts Occurs in information transmit ...
... Decrease signal transmission when input intensity is too great They travel backwards from cortex to thalamus, medulla, and spinal cord Amplifying Divergence Example Characteristic of corticospinal pathway, which controls skeletal muscles Divergence into multiple tracts Occurs in information transmit ...
Chapter 9 Nervous
... Describe the neuron, the nerve impulse, and the synapse, and explain the components of a reflex arc Neuron - specialized cell that lies within the nervous system; conducts electrochemical signals along their length body - major portion of neuron axon - transmits signals to other structures (groups a ...
... Describe the neuron, the nerve impulse, and the synapse, and explain the components of a reflex arc Neuron - specialized cell that lies within the nervous system; conducts electrochemical signals along their length body - major portion of neuron axon - transmits signals to other structures (groups a ...
Nervous system lecture 1
... potentials at the axon hillock can bring about an action potential or inhibit the generation of the action potential. – Spatial: stimulation by many neurons at one time. – Temporal: increased numbers of impulses per minute. ...
... potentials at the axon hillock can bring about an action potential or inhibit the generation of the action potential. – Spatial: stimulation by many neurons at one time. – Temporal: increased numbers of impulses per minute. ...
PNS and CNS Nervous System Organization Peripheral Nervous
... • voluntary movement of skeletal muscle (motor cortex) • personality • higher intellectual processes – planning, decision making ...
... • voluntary movement of skeletal muscle (motor cortex) • personality • higher intellectual processes – planning, decision making ...
P215 - Basic Human Physiology
... • Precentral gyrus of the central fissue • Controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles • Somatotopic • More area dedicated to body regions movements requiring precise movements ...
... • Precentral gyrus of the central fissue • Controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles • Somatotopic • More area dedicated to body regions movements requiring precise movements ...
Heart
... Population response – summary response of neuronal population APs of thousands of neurons Evoked potentials – response of sensory pathway to the stimulus ...
... Population response – summary response of neuronal population APs of thousands of neurons Evoked potentials – response of sensory pathway to the stimulus ...
2016-2017_1stSemester_Exam2_180117_final
... Estimated number of synapses established by parallel fibers on a Purkinje cell Speed of fast anterograde transport ...
... Estimated number of synapses established by parallel fibers on a Purkinje cell Speed of fast anterograde transport ...
Clinical Research Center for Brain Sciences, Herzog Hospital
... An increase in resting theta power is not directly related to normal late-life ageing but more likely a result of late-life neurological diseases (Klimesch, 1999, Finnigan and Robertson, 2011). ...
... An increase in resting theta power is not directly related to normal late-life ageing but more likely a result of late-life neurological diseases (Klimesch, 1999, Finnigan and Robertson, 2011). ...
Overview Functions of the Nervous System
... and binds to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane • 5. Binding of neurotransmitter opens ion channels, resulting in graded potentials. • 6.Neurotransmitter effects are terminated. ...
... and binds to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane • 5. Binding of neurotransmitter opens ion channels, resulting in graded potentials. • 6.Neurotransmitter effects are terminated. ...
Biological Bases Of Behaviour Central Nervous System
... Consists of the primary motor cortex which is responsible for generating movement of body parts. Specific points are responsible for certain parts of the body (motor homunculus) The association area is involved in expressing emotional behaviour, personality and temperament Broca’s area (only in left ...
... Consists of the primary motor cortex which is responsible for generating movement of body parts. Specific points are responsible for certain parts of the body (motor homunculus) The association area is involved in expressing emotional behaviour, personality and temperament Broca’s area (only in left ...
chapt12-nervous system
... Language and speech are dependent upon Broca’s area (a motor speech area) and Wernicke’s area (a sensory speech area) that are in communication. Interestingly enough, these two areas are located only in the left hemisphere. ...
... Language and speech are dependent upon Broca’s area (a motor speech area) and Wernicke’s area (a sensory speech area) that are in communication. Interestingly enough, these two areas are located only in the left hemisphere. ...
Nervous System
... Why are spinal injuries that result in paralysis often permanent? Sensory and motor nerves can heal completely but it is slow. The spinal nerves can also grow but not well enough to repair significant damage. ...
... Why are spinal injuries that result in paralysis often permanent? Sensory and motor nerves can heal completely but it is slow. The spinal nerves can also grow but not well enough to repair significant damage. ...
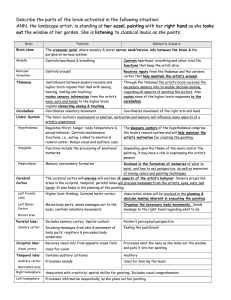
Describe the parts of the brain activated in the following situation
... higher brain regions that deal with seeing, hearing, tasting and touching; routes sensory information from the artist’s eyes, ears and hands to the higher brain regions connecting seeing & touching. ...
... higher brain regions that deal with seeing, hearing, tasting and touching; routes sensory information from the artist’s eyes, ears and hands to the higher brain regions connecting seeing & touching. ...
Anatomy and Physiology 121: The Nervous System General
... Impulses travel from dendrite on cell body through axon to presynaptic terminal Axons secrete neurotransmitter from synaptic vesicles in knobs on axon when receives an impulse When transmitter reaches postsynaptic neuron it triggers an synaptic potential Neurotransmitter Substances ~ 50 neur ...
... Impulses travel from dendrite on cell body through axon to presynaptic terminal Axons secrete neurotransmitter from synaptic vesicles in knobs on axon when receives an impulse When transmitter reaches postsynaptic neuron it triggers an synaptic potential Neurotransmitter Substances ~ 50 neur ...
Learning Objectives
... Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. ...
... Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. ...
Compound Action Potential, CAP
... When the strength of the stimulus is very low, we see no response from the nerve. This stimulus strength is subthreshold. If the strength is raised, a tiny response appears in the record and, as the strength is increased even more, the response grows to a maximum value; further increases in stimulus ...
... When the strength of the stimulus is very low, we see no response from the nerve. This stimulus strength is subthreshold. If the strength is raised, a tiny response appears in the record and, as the strength is increased even more, the response grows to a maximum value; further increases in stimulus ...
Tayler
... The brain uses neurotransmitters to tell your heart to beat, your lung to breathe, and your stomach to digest Once the neurotransmitter is picked up by receptors in the postsynaptic membrane, the molecule is internalized in the neuron and the impulse continues. This process of nerve cell communi ...
... The brain uses neurotransmitters to tell your heart to beat, your lung to breathe, and your stomach to digest Once the neurotransmitter is picked up by receptors in the postsynaptic membrane, the molecule is internalized in the neuron and the impulse continues. This process of nerve cell communi ...
Nervous Systems
... • Peripheral nervous system (PNS) – network of nerves extending into different parts of the body – carries sensory input to the CNS and motor output away from the CNS ...
... • Peripheral nervous system (PNS) – network of nerves extending into different parts of the body – carries sensory input to the CNS and motor output away from the CNS ...
The Reflex Arc
... C. Receptor – a specialized nerve tissue that is sensitive to a specific stimulus. 1. Receptors may be nerve endings in the skin which may be sensitive to temperature changes. 2. Receptors may be complex organs such as the eye or ear. Receptors are located in each sensory organ (eye, ear, tongue, s ...
... C. Receptor – a specialized nerve tissue that is sensitive to a specific stimulus. 1. Receptors may be nerve endings in the skin which may be sensitive to temperature changes. 2. Receptors may be complex organs such as the eye or ear. Receptors are located in each sensory organ (eye, ear, tongue, s ...
Information Processing SG
... Learning Target #3: I can describe the structure and function of nerves and neurons. ...
... Learning Target #3: I can describe the structure and function of nerves and neurons. ...