Chapter 13: Peripheral Nervous System and Reflexes
... Motor division includes somatic nervous system (motor neurons going to skeletal muscle cells) and autonomic nervous system, with motor neurons going to visceral or smooth muscle, either through the sympathetic division or the parasympathetic division. ...
... Motor division includes somatic nervous system (motor neurons going to skeletal muscle cells) and autonomic nervous system, with motor neurons going to visceral or smooth muscle, either through the sympathetic division or the parasympathetic division. ...
The Nervous System
... • Other senses similar Left Visual Corpus Right Visual Cortex Callosum Cortex ...
... • Other senses similar Left Visual Corpus Right Visual Cortex Callosum Cortex ...
Cortical Stimulation Mapping www.AssignmentPoint.com Cortical
... considerations for patient care that the anesthesiologist must take into account. Rather than simply ensuring that the patient is asleep, the doctor can follow what is called the asleep-awake-asleep technique. In this technique the patient is anesthetized using a general anesthesia during the openin ...
... considerations for patient care that the anesthesiologist must take into account. Rather than simply ensuring that the patient is asleep, the doctor can follow what is called the asleep-awake-asleep technique. In this technique the patient is anesthetized using a general anesthesia during the openin ...
Chapter 11 - Central Nervous System
... sensory areas to --• provide memory, reasoning, verbalization, judgment ...
... sensory areas to --• provide memory, reasoning, verbalization, judgment ...
Human Nervous System
... receptors to the spinal cord and brain motor nerves contain the long axons of motor neurons; transmit impulses from the central nervous system to the effectors ...
... receptors to the spinal cord and brain motor nerves contain the long axons of motor neurons; transmit impulses from the central nervous system to the effectors ...
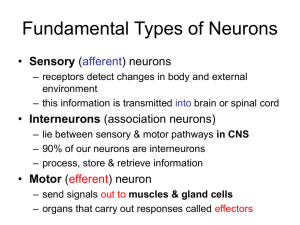
Fundamental Types of Neurons
... environment – this information is transmitted into brain or spinal cord ...
... environment – this information is transmitted into brain or spinal cord ...
2017 Nervous system Exam A and Key
... 42. During what phase of the “Nerve Impulse” are the sodium gates open and the potassium gates closed? A. B. C. D. ...
... 42. During what phase of the “Nerve Impulse” are the sodium gates open and the potassium gates closed? A. B. C. D. ...
PPt #2 Human Body Nervous system
... • A physically connected network of cells, tissues and organs that allow us to communicate with and react to the environment and perform life activities. ...
... • A physically connected network of cells, tissues and organs that allow us to communicate with and react to the environment and perform life activities. ...
Brainstem*s involvement in Motor process
... • Mediates motor (and sensation) control of the head, neck and face. • Influences parasympathetic reflexes • Contains ascending and descending pathways that carry motor (and sensory) information to other divisions of the central nervous system ...
... • Mediates motor (and sensation) control of the head, neck and face. • Influences parasympathetic reflexes • Contains ascending and descending pathways that carry motor (and sensory) information to other divisions of the central nervous system ...
Endocrine and nervous system
... 2. Dendrites: receives impulses to cell body (fingers) 3. Axon: carries impulses away from cell body (arm) 4. Axon Terminal: where impulses leave the neuron, contains chemical-filled vesicles (neurotransmitters) ...
... 2. Dendrites: receives impulses to cell body (fingers) 3. Axon: carries impulses away from cell body (arm) 4. Axon Terminal: where impulses leave the neuron, contains chemical-filled vesicles (neurotransmitters) ...
Vertebrate Zoology BIOL 322/Nervous System Ch 33 and Brain
... therefore, it takes longer for the impulse to be conducted ...
... therefore, it takes longer for the impulse to be conducted ...
Power Point Used in Lab
... Action potentials are tiny electric impulses produced by neurons. They are used for transmitting information away from the cell body and toward the axon terminals. When they reach the axon terminals, the action potentials cause the release of neurotransmitter from the terminals. ...
... Action potentials are tiny electric impulses produced by neurons. They are used for transmitting information away from the cell body and toward the axon terminals. When they reach the axon terminals, the action potentials cause the release of neurotransmitter from the terminals. ...
1 NOTES – CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System – LECTURE
... a. Afferent division 1) transmits impulses from sensory organs to the CNS 2) Afferent fibers/neurons – nerve fibers that transmit action potentials from the periphery to the CNS b. Efferent (motor) division 1) transmits impulses from the CNS to effectors a) effectors include muscles or glands 2) Eff ...
... a. Afferent division 1) transmits impulses from sensory organs to the CNS 2) Afferent fibers/neurons – nerve fibers that transmit action potentials from the periphery to the CNS b. Efferent (motor) division 1) transmits impulses from the CNS to effectors a) effectors include muscles or glands 2) Eff ...
NEURONS
... A REFLEX is an __________________________ response to a stimulus in which the brain is NOT directly involved! You are born with certain reflexes! A reflex happens so _____________ that you ...
... A REFLEX is an __________________________ response to a stimulus in which the brain is NOT directly involved! You are born with certain reflexes! A reflex happens so _____________ that you ...
Peripheral NS: Sensory processing & receptors
... • Stimulus detection: requires multiple impulses • Magnitude estimation: intensity coded by frequency of APs & number of neurons active ...
... • Stimulus detection: requires multiple impulses • Magnitude estimation: intensity coded by frequency of APs & number of neurons active ...
Classes #9-11: Differentiation of the brain vesicles
... class sessions 9-11. The first 46 questions are for review, and can be answered from earlier lectures. Many of these questions are answered in the readings as well. 1. The forebrain probably expanded in evolution initially because of the importance of _________________________________. 2. Give an ex ...
... class sessions 9-11. The first 46 questions are for review, and can be answered from earlier lectures. Many of these questions are answered in the readings as well. 1. The forebrain probably expanded in evolution initially because of the importance of _________________________________. 2. Give an ex ...
lesson 6
... 1) synthesized and released by neurons 2) released at the nerve terminal in a 'chemically identifiable' form 3) the chemical should reproduce the activity of the presynaptic neuron 4) can be blocked by competitive antagonist based on concentration 5) active mechanisms to stop the function of the neu ...
... 1) synthesized and released by neurons 2) released at the nerve terminal in a 'chemically identifiable' form 3) the chemical should reproduce the activity of the presynaptic neuron 4) can be blocked by competitive antagonist based on concentration 5) active mechanisms to stop the function of the neu ...
chapter 4 note sheet
... – Rods: black and white/low light vision – Cones: color and daylight vision • Adaptation: becoming more or less sensitive to light as needed ...
... – Rods: black and white/low light vision – Cones: color and daylight vision • Adaptation: becoming more or less sensitive to light as needed ...
The Nervous System Worksheet
... i) ………………… neurones transmit messages from sense receptors like the eye or ………………. to the brain or spinal cord. ii) Relay neurones relay messages from one side of the ………………… to the other. They also connect sensory neurones to motor neurones. iii) Motor neurones transmit messages from the brain and ...
... i) ………………… neurones transmit messages from sense receptors like the eye or ………………. to the brain or spinal cord. ii) Relay neurones relay messages from one side of the ………………… to the other. They also connect sensory neurones to motor neurones. iii) Motor neurones transmit messages from the brain and ...
20-NervousSystem
... “Nicotine receptors” normally served to bind acetylcholine Brain adjusts to prolonged exposure to nicotine by 1. Making fewer nicotine receptors 2. Altering the pattern of activation of nicotine receptors Addiction occurs because the brain compensates for the nicotineinduced changes by mak ...
... “Nicotine receptors” normally served to bind acetylcholine Brain adjusts to prolonged exposure to nicotine by 1. Making fewer nicotine receptors 2. Altering the pattern of activation of nicotine receptors Addiction occurs because the brain compensates for the nicotineinduced changes by mak ...
Sensory Processes - Department of Psychology | University of Toronto
... – Pattern of action potential sent to the brain that preserves the quantity and quality of a stimulus. ...
... – Pattern of action potential sent to the brain that preserves the quantity and quality of a stimulus. ...
Each of these case histories involves damaged areas of the brain
... Each of these case histories involves damaged areas of the brain and/or cerebral cortex. If the cortex cannot communicate with other brain areas or other cortical areas we are unable to perceive or interpret much of our surroundings. So, while most of these answers do not mention the cerebral cortex ...
... Each of these case histories involves damaged areas of the brain and/or cerebral cortex. If the cortex cannot communicate with other brain areas or other cortical areas we are unable to perceive or interpret much of our surroundings. So, while most of these answers do not mention the cerebral cortex ...
Neuroscience 5a – Touch and Proprioception
... Some free nerve endings Slow adapting receptors: these are generally receptors that are associated with pressure. They constantly fire action potentials and change in frequency depending on the strength of the stimulus. These include: Merkle’s Corpuscle – touch Ruffini Corpuscle – pressure Rec ...
... Some free nerve endings Slow adapting receptors: these are generally receptors that are associated with pressure. They constantly fire action potentials and change in frequency depending on the strength of the stimulus. These include: Merkle’s Corpuscle – touch Ruffini Corpuscle – pressure Rec ...