chapter 4
... cortex. Feature detectors in the primary visual cortex respond only when stimulation in their receptive field matches a particular pattern or orientation. Beyond the primary visual cortex, visual information flows along two pathways, the “what” pathway (or ventral stream) is involved in determining ...
... cortex. Feature detectors in the primary visual cortex respond only when stimulation in their receptive field matches a particular pattern or orientation. Beyond the primary visual cortex, visual information flows along two pathways, the “what” pathway (or ventral stream) is involved in determining ...
Reflex Arc.
... • Synapse is “The junction across which a nerve impulse passes from an axon terminal to a neuron, muscle cell or gland” • Two types of Synapses: o Excitatory o Inhibitory ...
... • Synapse is “The junction across which a nerve impulse passes from an axon terminal to a neuron, muscle cell or gland” • Two types of Synapses: o Excitatory o Inhibitory ...
Earthworm Action Potentials
... example, was used extensively for voltage clamp experiments. The role of these giant fibers, which conduct action potentials far faster than the small nerves, is to allow the animal to respond rapidly to threatening situations. Page 2 of 5 ...
... example, was used extensively for voltage clamp experiments. The role of these giant fibers, which conduct action potentials far faster than the small nerves, is to allow the animal to respond rapidly to threatening situations. Page 2 of 5 ...
Nervous System
... Cerebellum: receives information from the sensory systems, the spinal cord, and other parts of the brain and then regulates motor movements; coordinates voluntary movements such as posture, balance, coordination, and speech Brain stem: upper part is continuous with pons, medulla is lower half; medul ...
... Cerebellum: receives information from the sensory systems, the spinal cord, and other parts of the brain and then regulates motor movements; coordinates voluntary movements such as posture, balance, coordination, and speech Brain stem: upper part is continuous with pons, medulla is lower half; medul ...
the nervous system powerpoint
... controled by motor area Right hemisphere controls left side of body Left hemisphere controls right side Motor nerves cross sides in spinal cord ...
... controled by motor area Right hemisphere controls left side of body Left hemisphere controls right side Motor nerves cross sides in spinal cord ...
Vertebrate Zoology BIOL 322/Nervous System and Brain Complete
... - membrane is then repolarized; its resting potential is restored initially because K+ goes outside through the K+ channels; so you get a positive +++ charge outside again - then shortly after this, the Na+-K+ pump restores the ions to the correct side of the membrane (i.e., with Na+ outside, K+ ins ...
... - membrane is then repolarized; its resting potential is restored initially because K+ goes outside through the K+ channels; so you get a positive +++ charge outside again - then shortly after this, the Na+-K+ pump restores the ions to the correct side of the membrane (i.e., with Na+ outside, K+ ins ...
The Nervous System
... I. Propagation of action potentials • 1. concentration difference of ions on either side of membrane represents potential energy-kind of like of cocked gun • 2. stacked dominoes waiting to fall over • 3. one domino falling over initiates a wave of action potentials spreading out like the ripples in ...
... I. Propagation of action potentials • 1. concentration difference of ions on either side of membrane represents potential energy-kind of like of cocked gun • 2. stacked dominoes waiting to fall over • 3. one domino falling over initiates a wave of action potentials spreading out like the ripples in ...
Somatosensory system
... rate of muscle contraction, endings in parallel with muscle fibers 2. Golgi tendon organs – detect tension exerted by the muscle, ending in series with muscle fibers 3. Joint capsule receptors – detect flexion or extension of joints ...
... rate of muscle contraction, endings in parallel with muscle fibers 2. Golgi tendon organs – detect tension exerted by the muscle, ending in series with muscle fibers 3. Joint capsule receptors – detect flexion or extension of joints ...
Slide 1
... ► The mystery begins in the womb -- only four weeks into gestation the first brain cells, the neurons, are already forming at an astonishing rate: 250,000 every minute. ► Billions of neurons will form links with billions of other neurons and eventually there will be trillions and trillions of connec ...
... ► The mystery begins in the womb -- only four weeks into gestation the first brain cells, the neurons, are already forming at an astonishing rate: 250,000 every minute. ► Billions of neurons will form links with billions of other neurons and eventually there will be trillions and trillions of connec ...
Lecture_31_2014_noquiz
... typically containing thousands of neurons wrapped in connective tissue; carries impulses between the central nervous system and some other part of the body. ...
... typically containing thousands of neurons wrapped in connective tissue; carries impulses between the central nervous system and some other part of the body. ...
Nervous System ppt
... Parkinson's disease is a disorder of the brain that leads to shaking (tremors) and difficulty with walking, movement, and coordination. Caused by loss of dopamine producing cells in brain (substantia niagra) Dopamine helps control muscle movement by releasing inhibitory function of substantia nia ...
... Parkinson's disease is a disorder of the brain that leads to shaking (tremors) and difficulty with walking, movement, and coordination. Caused by loss of dopamine producing cells in brain (substantia niagra) Dopamine helps control muscle movement by releasing inhibitory function of substantia nia ...
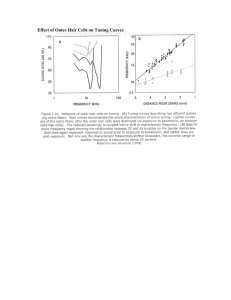
Effect of Outer Hair Cells on Tuning Curves
... component frequencies. The energy at each point in the frequency spectrum is indicated on a scale from low (blue) to high (red). The bottom panel shows the same audio signal after being processed to remove all information except the envelopes of four contiguous bands from 300 hertz to 5 kilohertz, w ...
... component frequencies. The energy at each point in the frequency spectrum is indicated on a scale from low (blue) to high (red). The bottom panel shows the same audio signal after being processed to remove all information except the envelopes of four contiguous bands from 300 hertz to 5 kilohertz, w ...
First-order neuron
... • 1 million upper motor neurons in cerebral cortex • 90% of fibers decussate(cross over) in the medulla – right side of brain controls left side muscles ...
... • 1 million upper motor neurons in cerebral cortex • 90% of fibers decussate(cross over) in the medulla – right side of brain controls left side muscles ...
nervous system outline PPT
... Autonomic Nervous System Carry impulses from the central nervous system to glands, various involuntary muscles, cardiac muscle, and membranes Stimulates organs, glands and senses by stimulating secretions of substances Divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions ...
... Autonomic Nervous System Carry impulses from the central nervous system to glands, various involuntary muscles, cardiac muscle, and membranes Stimulates organs, glands and senses by stimulating secretions of substances Divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions ...
Nervous System
... Use your knowledge of the timing of these gates to understand why there will be no response to a new stimulus during this phase of the action potential. ...
... Use your knowledge of the timing of these gates to understand why there will be no response to a new stimulus during this phase of the action potential. ...
Chapter 34
... Sensory Neuron: detects a stimulus at one or more receptor endings and relays information about it to other neurons Motor Neuron: delivers excitatory or inhibitory commands from other neurons to muscles or glands ...
... Sensory Neuron: detects a stimulus at one or more receptor endings and relays information about it to other neurons Motor Neuron: delivers excitatory or inhibitory commands from other neurons to muscles or glands ...
107B exam 1 test yourself
... **KNOW THIS** Overlay of egocentric maps – FOUR maps in Vision 1. retinotopic map (projects to layer ______ of V1) 2. ocular dominance columns (projects to layer ______ of V1) 3. orientation tuning map (projects to layer ______ of V1) 4. koniocellular input (to layers ______ of V1) Organized in hor ...
... **KNOW THIS** Overlay of egocentric maps – FOUR maps in Vision 1. retinotopic map (projects to layer ______ of V1) 2. ocular dominance columns (projects to layer ______ of V1) 3. orientation tuning map (projects to layer ______ of V1) 4. koniocellular input (to layers ______ of V1) Organized in hor ...
The Brain - cloudfront.net
... Thalamus – “the router” • Function: – Relays sensory, spatial sense and motor signals to cerebral cortex • Receives auditory, somatosensory and visual sensory signals, sorts data and relays it to proper area in brain ...
... Thalamus – “the router” • Function: – Relays sensory, spatial sense and motor signals to cerebral cortex • Receives auditory, somatosensory and visual sensory signals, sorts data and relays it to proper area in brain ...
Chapter 5: SENSATION - Charles Best Library
... The five million olfactory receptor cells recognize individual odor molecules, with some odors triggering a combination of receptors. An odor’s ability to spontaneously evoke memories is due to the close connections between brain areas that process smell and those involved in memory storage. ...
... The five million olfactory receptor cells recognize individual odor molecules, with some odors triggering a combination of receptors. An odor’s ability to spontaneously evoke memories is due to the close connections between brain areas that process smell and those involved in memory storage. ...
modality intensity duration location four attributes of a stimulus
... FIGURE 4 Center/surround organization of receptive fields is common in sensory systems. In this organization, a stimulus in the center of the receptive field produces one effect, usually excitation, whereas a stimulus in the surround area has the opposite effect, usually inhibition. (A) In the soma ...
... FIGURE 4 Center/surround organization of receptive fields is common in sensory systems. In this organization, a stimulus in the center of the receptive field produces one effect, usually excitation, whereas a stimulus in the surround area has the opposite effect, usually inhibition. (A) In the soma ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... Ependymal line the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord Astrocytes maintain the blood brain barrier (BBB), structural support, regulate ion content, and repair ...
... Ependymal line the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord Astrocytes maintain the blood brain barrier (BBB), structural support, regulate ion content, and repair ...