The Nervous System crossword
... 3. The cells of the nervous system are called neurones. 4. What is the name of the membrane bound structure found in the body of the cell? [Nucleus] 6. The small space between two nerve cells is called the ...
... 3. The cells of the nervous system are called neurones. 4. What is the name of the membrane bound structure found in the body of the cell? [Nucleus] 6. The small space between two nerve cells is called the ...
Slide ()
... between different of theScience, motor map subject2012 to inhibition ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principlesparts of Neural FifthisEditon; Available mediated by local at: inhibitory interneurons, so that electrical stimulation of a whisker site evokes contractions ...
... between different of theScience, motor map subject2012 to inhibition ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principlesparts of Neural FifthisEditon; Available mediated by local at: inhibitory interneurons, so that electrical stimulation of a whisker site evokes contractions ...
Biology Option Review Section E
... Animal responses can be affected by natural selection in regards to higher rates of survival, as is the case with the Loggerhead turtles who are, after birth and successful survival until reproduction can occur, able to instinctively remember the beach they were born on, known as natal beaches, and ...
... Animal responses can be affected by natural selection in regards to higher rates of survival, as is the case with the Loggerhead turtles who are, after birth and successful survival until reproduction can occur, able to instinctively remember the beach they were born on, known as natal beaches, and ...
Lecture #19 - Suraj @ LUMS
... • As AcCh released across synapse, binds to muscle cell membrane. Causes depolarization of muscle cell membrane, which passes down muscle cell. Releases Ca ++ ions, which triggers muscle contraction. • If AcCh not removed, membrane remains depolarized, no more impulses. So must quickly get rid of Ac ...
... • As AcCh released across synapse, binds to muscle cell membrane. Causes depolarization of muscle cell membrane, which passes down muscle cell. Releases Ca ++ ions, which triggers muscle contraction. • If AcCh not removed, membrane remains depolarized, no more impulses. So must quickly get rid of Ac ...
1 - Sur Lab
... Action potentials can be elicited by stimulating pins close to the patched cell within an approximate radius determined by stimulus intensity. (F) Maximum effective range of stimulus as a function of stimulus intensity. (G) Spread of activation on a cortical slice bulk loaded with Oregon Green BAPTA ...
... Action potentials can be elicited by stimulating pins close to the patched cell within an approximate radius determined by stimulus intensity. (F) Maximum effective range of stimulus as a function of stimulus intensity. (G) Spread of activation on a cortical slice bulk loaded with Oregon Green BAPTA ...
The Nervous System
... electrical signals to communicate with other cells • An impulse is: an electrical signal travelling through a neuron • A nerve is: a bundle of neurons • Sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors (e.g. in skin) to the central nervous system (brain/spinal cord) • Motor neurons: carry impulses fro ...
... electrical signals to communicate with other cells • An impulse is: an electrical signal travelling through a neuron • A nerve is: a bundle of neurons • Sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors (e.g. in skin) to the central nervous system (brain/spinal cord) • Motor neurons: carry impulses fro ...
Chapter 6
... Physical site of the stimulated receptor Acuity - precision of stimulus location Greater receptive field size and overlap decreases acuity Lateral inhibition increases acuity Intensity Stronger stimuli result in higher frequency of receptor potentials leading to a higher frequency of action potentia ...
... Physical site of the stimulated receptor Acuity - precision of stimulus location Greater receptive field size and overlap decreases acuity Lateral inhibition increases acuity Intensity Stronger stimuli result in higher frequency of receptor potentials leading to a higher frequency of action potentia ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... The system is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. These divisions function automatically and usually in an involuntary manner, they innervate all internal organs, and utilize two motor neurons that synapse at a ganglion. Sympathetic Division The sympathetic division is especia ...
... The system is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. These divisions function automatically and usually in an involuntary manner, they innervate all internal organs, and utilize two motor neurons that synapse at a ganglion. Sympathetic Division The sympathetic division is especia ...
The Nervous System
... Cell body (soma) Has typical cell components used for cell maintenance Axon Transfers information to other neurons Axon terminal is where the synapse is located/ structure that passes an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron ...
... Cell body (soma) Has typical cell components used for cell maintenance Axon Transfers information to other neurons Axon terminal is where the synapse is located/ structure that passes an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron ...
study notes quiz 1
... 2) Cerebellum: “little brain” (a) responsible for coordinated movements (b) receives all sensory input except olfactory (c) connected to pons Mesencephalon: “mid-brain” – surrounds cerebral aqueduct 1) Tectum: “roof” (a) responsible for audiovisual reactions (contains inferior and superior colliculi ...
... 2) Cerebellum: “little brain” (a) responsible for coordinated movements (b) receives all sensory input except olfactory (c) connected to pons Mesencephalon: “mid-brain” – surrounds cerebral aqueduct 1) Tectum: “roof” (a) responsible for audiovisual reactions (contains inferior and superior colliculi ...
2. Nervous system anatomy
... • Pons (ventral brainstem) – Projects information from cortex to cerebellum – Role in sleep and arousal ...
... • Pons (ventral brainstem) – Projects information from cortex to cerebellum – Role in sleep and arousal ...
bio 342 human physiology
... a) The intensity of a stimulus is proportional to the size of the graded potential in the receptive membrane. b) The modality of a stimulus is encoded by which type or types of sensory receptors are activated. c) The intensity of a stimulus is encoded by the frequency of action potentials. d) Some a ...
... a) The intensity of a stimulus is proportional to the size of the graded potential in the receptive membrane. b) The modality of a stimulus is encoded by which type or types of sensory receptors are activated. c) The intensity of a stimulus is encoded by the frequency of action potentials. d) Some a ...
Central and Peripheral nervous systems
... Each hemisphere is divided into 4 lobes (named after the bone that they lie over ...
... Each hemisphere is divided into 4 lobes (named after the bone that they lie over ...
Brain Cell or Neuron
... axons and dendrites are surrounded by a white myelin sheath. brain nerves in the PNS take impulses to and from the brain (CNS). spinal nerves take impulses to and away from the spinal cord. We are not aware of most sensory input carried in the PNS. ...
... axons and dendrites are surrounded by a white myelin sheath. brain nerves in the PNS take impulses to and from the brain (CNS). spinal nerves take impulses to and away from the spinal cord. We are not aware of most sensory input carried in the PNS. ...
The Central Nervous System
... B. Most of the corticospinal fibers decussate in the pyramids of the medulla oblongata. C. Regions of the cerebral cortex, the basal nuclei, and the cerebellum, control movements indirectly by synapsing with other regions that give rise to descending extrapyramidal fiber tracts. D. The major extrapy ...
... B. Most of the corticospinal fibers decussate in the pyramids of the medulla oblongata. C. Regions of the cerebral cortex, the basal nuclei, and the cerebellum, control movements indirectly by synapsing with other regions that give rise to descending extrapyramidal fiber tracts. D. The major extrapy ...
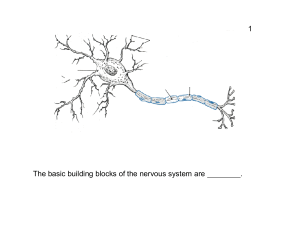
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
Chapter 14 - WordPress.com
... Posterior median sulcus- shallow groove on the dorsal surface Anterior median fissure- deep crease on the ventral surface Each region of the spinal cord contains tracts involved with that particular segment and those inferior to it Enlargements areas of coordination of incoming and outgoing ...
... Posterior median sulcus- shallow groove on the dorsal surface Anterior median fissure- deep crease on the ventral surface Each region of the spinal cord contains tracts involved with that particular segment and those inferior to it Enlargements areas of coordination of incoming and outgoing ...
Summary of Chapter 7
... • The nervous system receives, processes, stores and transmits information from both inside and outside the body (p. 203). • A neuron is a specialized nerve cell in the nervous system that receives and transmits messages (p. 203). ...
... • The nervous system receives, processes, stores and transmits information from both inside and outside the body (p. 203). • A neuron is a specialized nerve cell in the nervous system that receives and transmits messages (p. 203). ...
Review
... -Know the functions of the 4 lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal -White matter in the cerebrum consists of 3 types of neural tracts. What areas do they allow to communicate? -Gray matter is found in 3 places of the cerebrum. Which place has the most gray matter? Basal nuclei: where is it l ...
... -Know the functions of the 4 lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal -White matter in the cerebrum consists of 3 types of neural tracts. What areas do they allow to communicate? -Gray matter is found in 3 places of the cerebrum. Which place has the most gray matter? Basal nuclei: where is it l ...
spinal cord
... control and coordination of life functions and activities 2 systems involved: 1. nervous- electrical system, brain,spine and nerves found in multicellular organisms 2. endocrine- chemical system, hormones found in all organisms Nervous System: definitions: a. stimulus- change in the internal or ex ...
... control and coordination of life functions and activities 2 systems involved: 1. nervous- electrical system, brain,spine and nerves found in multicellular organisms 2. endocrine- chemical system, hormones found in all organisms Nervous System: definitions: a. stimulus- change in the internal or ex ...
Nervous System PPT
... – left = right side of body – right = left side of body • The right side of your brain perceives and controls the left side of your body • Left side of brain perceives and controls right side of your ...
... – left = right side of body – right = left side of body • The right side of your brain perceives and controls the left side of your body • Left side of brain perceives and controls right side of your ...