Sensory Nerves and Receptors
... All stimuli are transduced by the sensory receptors into nerve impulses in the afferent nerves. These impulses reach the brain acting as code signals specific for each sensation. The brain then deciphers these code signals and identifies the modality (type), the locality and the intensity of the sti ...
... All stimuli are transduced by the sensory receptors into nerve impulses in the afferent nerves. These impulses reach the brain acting as code signals specific for each sensation. The brain then deciphers these code signals and identifies the modality (type), the locality and the intensity of the sti ...
05First2yearsBiosocial
... • How do the risks from disease relate to the risks from immunization? • What is the difference between colostrum and milk? ...
... • How do the risks from disease relate to the risks from immunization? • What is the difference between colostrum and milk? ...
Final - Center for Neural Science
... Part II. Multiple Choice (1.5 points each). Write your name and fill in the circles using a #2 pencil on the accompanying scantron card. 1) In the study of perceptual processes, the term “transduction” is defined to be a) temporal patterning of nerve impulses. b) neural processing. c) the conversio ...
... Part II. Multiple Choice (1.5 points each). Write your name and fill in the circles using a #2 pencil on the accompanying scantron card. 1) In the study of perceptual processes, the term “transduction” is defined to be a) temporal patterning of nerve impulses. b) neural processing. c) the conversio ...
sensation - LackeyLand
... physical stimuli are translated into a psychological experience • As a school of thought, psychophysics was pioneered by Gustav Fechner (right) in 1860. • Fechner’s set out to “develop a method that relates matter to the mind, connecting the publicly observable world and a person’s privately experie ...
... physical stimuli are translated into a psychological experience • As a school of thought, psychophysics was pioneered by Gustav Fechner (right) in 1860. • Fechner’s set out to “develop a method that relates matter to the mind, connecting the publicly observable world and a person’s privately experie ...
Take the 10-item multiple choice quiz to check
... 2. The sensory root of a spinal nerve is also referred to as a. b. c. d. e. ...
... 2. The sensory root of a spinal nerve is also referred to as a. b. c. d. e. ...
7-4_DescendingPathways_HubaT
... In this picture you can see the 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Spinal nerves are grouped according to the place where they emerge from the spinal cord. Spinal nerves are responsible for carrying information between the central nervous system and other parts of the body. The spinal cord is the center of ...
... In this picture you can see the 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Spinal nerves are grouped according to the place where they emerge from the spinal cord. Spinal nerves are responsible for carrying information between the central nervous system and other parts of the body. The spinal cord is the center of ...
Chapters 13, and 14
... Vision is dependent on the eyes and the brain. About a third of the cerebral cortex takes part in processing visual information. Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye The eye has three layers. The outer layer, the sclera, can be seen as the white of the eye; it also becomes the transparent bulge in the ...
... Vision is dependent on the eyes and the brain. About a third of the cerebral cortex takes part in processing visual information. Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye The eye has three layers. The outer layer, the sclera, can be seen as the white of the eye; it also becomes the transparent bulge in the ...
File
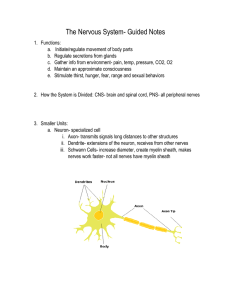
... What is the function of a neuron? They are highly specialized cells that transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. You will take a closer look at the neuron structure and its function during lecture. Prior to, make sure to read this section so you have a better unders ...
... What is the function of a neuron? They are highly specialized cells that transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. You will take a closer look at the neuron structure and its function during lecture. Prior to, make sure to read this section so you have a better unders ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier
... FIGURE 22.4 Center/surround organization of receptive fields is common in sensory systems. In this organization, a stimulus in the center of the receptive field produces one effect, usually excitation, whereas a stimulus in the surround area has the opposite effect, usually inhibition. (A) In the s ...
... FIGURE 22.4 Center/surround organization of receptive fields is common in sensory systems. In this organization, a stimulus in the center of the receptive field produces one effect, usually excitation, whereas a stimulus in the surround area has the opposite effect, usually inhibition. (A) In the s ...
nervous system power point
... receptors to CNS • via periphery • Interneurons (association) – connect motor to sensory neurons – lie within CNS • Motor (efferent) – multipolar,carry impulses from CNS to muscle and glands for reaction ...
... receptors to CNS • via periphery • Interneurons (association) – connect motor to sensory neurons – lie within CNS • Motor (efferent) – multipolar,carry impulses from CNS to muscle and glands for reaction ...
Nervous System Formative Study Guide File
... nerves leading to and from the CNS, often through junctions known as ganglia. 2. Using what you know about the processes of the central nervous system, describe the path an impulse would take that would make you move in response to a tap on the shoulder. The tap on the shoulder would be picked up by ...
... nerves leading to and from the CNS, often through junctions known as ganglia. 2. Using what you know about the processes of the central nervous system, describe the path an impulse would take that would make you move in response to a tap on the shoulder. The tap on the shoulder would be picked up by ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... • Forms floor of the 3rd ventricle • Maintains homeostasis by regulating hunger, sleep, thirst, body temperature and water balance. • Sex, pain , and pleasure centers are located here • Part of the limbic system • Called emotion visceral brain • Regulates the pituitary gland therefore it is the link ...
... • Forms floor of the 3rd ventricle • Maintains homeostasis by regulating hunger, sleep, thirst, body temperature and water balance. • Sex, pain , and pleasure centers are located here • Part of the limbic system • Called emotion visceral brain • Regulates the pituitary gland therefore it is the link ...
Nervous System
... be released by a single neuron and one neuron can have synapses with several different neurons (convergence and divergence), thus, a single neuron can have receptors for many different types of neurotransmitters. ...
... be released by a single neuron and one neuron can have synapses with several different neurons (convergence and divergence), thus, a single neuron can have receptors for many different types of neurotransmitters. ...
dynamics and functional connectivity in barrel network
... Abstract: Objective Cortical processing of somatosensory information is performed by a large population of neurons with complex dynamics and interactions in barrel cortex. Emerging evidences recently suggest that astrocytes receive surrounding synaptic inputs and participate in sensory information p ...
... Abstract: Objective Cortical processing of somatosensory information is performed by a large population of neurons with complex dynamics and interactions in barrel cortex. Emerging evidences recently suggest that astrocytes receive surrounding synaptic inputs and participate in sensory information p ...
Central Nervous System
... Myelinated neurons faster than unmyelinated Myelinated fibers conduct impulses from one Node of Ranvier to the next, a phenomenon called saltatory conduction. Speed of impulse conduction is proportional to the diameter of the axon a.Thick, myelinated motor axons conduct at 120 m/s b.Thin, unmyeli ...
... Myelinated neurons faster than unmyelinated Myelinated fibers conduct impulses from one Node of Ranvier to the next, a phenomenon called saltatory conduction. Speed of impulse conduction is proportional to the diameter of the axon a.Thick, myelinated motor axons conduct at 120 m/s b.Thin, unmyeli ...
Document
... impulses) • Magnitude estimation—intensity is coded in the frequency of impulses • Spatial discrimination—identifying the site or pattern of the stimulus (studied by the two-point discrimination test) ...
... impulses) • Magnitude estimation—intensity is coded in the frequency of impulses • Spatial discrimination—identifying the site or pattern of the stimulus (studied by the two-point discrimination test) ...
Nervous System Guided Notes
... Network of motor and sensory neurons in the GI tract and glands Influenced by parasympathetic and sympathetic systems **Functional without input from outside viscera Controls local events in GI tract ...
... Network of motor and sensory neurons in the GI tract and glands Influenced by parasympathetic and sympathetic systems **Functional without input from outside viscera Controls local events in GI tract ...
The Nervous System
... • Made up of bundles of myelinated long fibers of interneurons called tracts ...
... • Made up of bundles of myelinated long fibers of interneurons called tracts ...
CNS_notes
... Two pathways lead from peripheral sensory receptors (touch, temperature, pain, …) to cerebral cortex: spinothalamic and posterior (or dorsal) column pathways. For each pathway, know: where cell bodies/axons of 1st, 2nd, 3rd order neurons are/travel; what sensations are carried. Common features of bo ...
... Two pathways lead from peripheral sensory receptors (touch, temperature, pain, …) to cerebral cortex: spinothalamic and posterior (or dorsal) column pathways. For each pathway, know: where cell bodies/axons of 1st, 2nd, 3rd order neurons are/travel; what sensations are carried. Common features of bo ...
REGULATION
... 3. Impulse is received by effector that responds B. Structure of NEURON A cell specialized for the transmission of nerve impulses from place to place in the body. It is composed of: ...
... 3. Impulse is received by effector that responds B. Structure of NEURON A cell specialized for the transmission of nerve impulses from place to place in the body. It is composed of: ...
Outline10 Action Potl
... Functional types of neurons 1. sensory (afferent) neurons - input to CNS from sensory receptors; dendrites located at receptors, axons in nerves, cell bodies in ganglia outside the CNS 2. motor (efferent) neurons - output from CNS to effectors (muscles, glands) cell bodies and dendrites in the CNS, ...
... Functional types of neurons 1. sensory (afferent) neurons - input to CNS from sensory receptors; dendrites located at receptors, axons in nerves, cell bodies in ganglia outside the CNS 2. motor (efferent) neurons - output from CNS to effectors (muscles, glands) cell bodies and dendrites in the CNS, ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM - Welcome to the Health Science Program
... Visceral (organs within the ventral cavity) ...
... Visceral (organs within the ventral cavity) ...
The Nervous System
... • The peripheral nervous system lies outside the central nervous system, and is composed of nerves and ganglia. • Sensory fibers carry information to the CNS, and motor fibers carry information away from the CNS. • Ganglia are swellings associated with nerves that contain collections of cell bodies. ...
... • The peripheral nervous system lies outside the central nervous system, and is composed of nerves and ganglia. • Sensory fibers carry information to the CNS, and motor fibers carry information away from the CNS. • Ganglia are swellings associated with nerves that contain collections of cell bodies. ...