File
... POSSESSIVE PERSONAL PRONOUNS: my, mine, your, yours, his, her, hers, its, our, ours, their, theirs INDEFINITE PRONOUNS: Anybody, anyone, each, either, none, someone, somebody, both, everyone, no one, neither, many, few, several, one. INTERROGATIVE PRONOUNS: who, whom, what, which, whose DEMO ...
... POSSESSIVE PERSONAL PRONOUNS: my, mine, your, yours, his, her, hers, its, our, ours, their, theirs INDEFINITE PRONOUNS: Anybody, anyone, each, either, none, someone, somebody, both, everyone, no one, neither, many, few, several, one. INTERROGATIVE PRONOUNS: who, whom, what, which, whose DEMO ...
WALT – Describe what an auxiliary verb is and
... Compound Verbs Many verbs are made up of more than one word. These words are called COMPOUND VERBS Compound Verbs consist of: One or more helping (auxiliary) verbs ...
... Compound Verbs Many verbs are made up of more than one word. These words are called COMPOUND VERBS Compound Verbs consist of: One or more helping (auxiliary) verbs ...
PARTS OF SPEECH NOTES Eight Parts of Speech: Noun: Pronoun:
... personal pronoun (refers to a specific person/thing or shows possession) first person: I, me, my, mine, we, us our, ours second person: you, your, yours third person: he, him, his, she, her, hers, it , its, they, them, their, theirs reflexive pronoun (has self/selves in it): myself, yourself, himsel ...
... personal pronoun (refers to a specific person/thing or shows possession) first person: I, me, my, mine, we, us our, ours second person: you, your, yours third person: he, him, his, she, her, hers, it , its, they, them, their, theirs reflexive pronoun (has self/selves in it): myself, yourself, himsel ...
Parts of Speech
... Pronoun: a “replacement” noun, a word that serves as an ambassador for a noun. There are many different types of pronouns; the most common pronouns are “I”, “he”, or “she” (subject pronouns) and “me”, “him”, or “her” (object pronouns). Adjective: a word that modifies—describes or limits—a noun or pr ...
... Pronoun: a “replacement” noun, a word that serves as an ambassador for a noun. There are many different types of pronouns; the most common pronouns are “I”, “he”, or “she” (subject pronouns) and “me”, “him”, or “her” (object pronouns). Adjective: a word that modifies—describes or limits—a noun or pr ...
Parts of Speech Review
... Since Sherylee is such a klutz, she should have been eating a cake donut, which would not have stained her shirt. ...
... Since Sherylee is such a klutz, she should have been eating a cake donut, which would not have stained her shirt. ...
Coursework: Self Assessment
... I have used the present tense I have used a past tense I have used a future tense I have included at least 5 adjectives (also comparatives/superlatives if you can) I have included descriptions I have given my opinions, e.g. à mon avis, je pense/crois que I have used linking words, e.g. et, mais, cep ...
... I have used the present tense I have used a past tense I have used a future tense I have included at least 5 adjectives (also comparatives/superlatives if you can) I have included descriptions I have given my opinions, e.g. à mon avis, je pense/crois que I have used linking words, e.g. et, mais, cep ...
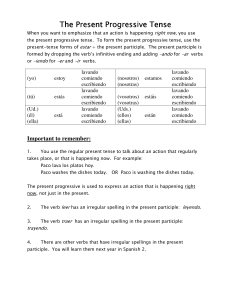
The Present Progressive Tense The Present
... When you want to emphasize that an action is happening right now, you use the present progressive tense. To form the present progressive tense, use the present-tense forms of estar + the present participle. The present participle is formed by dropping the verb’s infinitive ending and adding –ando fo ...
... When you want to emphasize that an action is happening right now, you use the present progressive tense. To form the present progressive tense, use the present-tense forms of estar + the present participle. The present participle is formed by dropping the verb’s infinitive ending and adding –ando fo ...
Glossary of grammatical terms for parents
... Exclamation mark Indicates an interjection/surprise/strong ...
... Exclamation mark Indicates an interjection/surprise/strong ...
Old Church Slavonic verbs
... English through history was very progressive and active - the whole revolution happened with it in the 15th and the 16th centuries, not only taking into consideration the Great Vowel Shift, but also the major grammar changes. The result was the Modern, or New, English, which has practically no decle ...
... English through history was very progressive and active - the whole revolution happened with it in the 15th and the 16th centuries, not only taking into consideration the Great Vowel Shift, but also the major grammar changes. The result was the Modern, or New, English, which has practically no decle ...
Verbals - Santa Ana College
... The stolen car was never located. (Stolen is a past participle form of the verb steal. It is functioning as an adjective modifying the noun car). *Note – the words accompanying the participle are part of a single grammatical unit known as a participial phrase. The whole phrase works together as one ...
... The stolen car was never located. (Stolen is a past participle form of the verb steal. It is functioning as an adjective modifying the noun car). *Note – the words accompanying the participle are part of a single grammatical unit known as a participial phrase. The whole phrase works together as one ...
Computational lexicography, morphology and syntax
... – The root domin- is combined with various endings (us, -um, -i, -o, etc.), which may also occur with other forms: equus, servus, etc. – English is relatively poor in inflectional variation: • most verbs have only -s, -ed and –ing available; – Romanian language is much richer. ...
... – The root domin- is combined with various endings (us, -um, -i, -o, etc.), which may also occur with other forms: equus, servus, etc. – English is relatively poor in inflectional variation: • most verbs have only -s, -ed and –ing available; – Romanian language is much richer. ...
Course 4
... – The root domin- is combined with various endings (us, -um, -i, -o, etc.), which may also occur with other forms: equus, servus, etc. – English is relatively poor in inflectional variation: • most verbs have only -s, -ed and –ing available; – Romanian language is much richer. ...
... – The root domin- is combined with various endings (us, -um, -i, -o, etc.), which may also occur with other forms: equus, servus, etc. – English is relatively poor in inflectional variation: • most verbs have only -s, -ed and –ing available; – Romanian language is much richer. ...
WORD CLASSES, SENTENCE STRUCTURE and TERMINOLOGY
... If you want to write proper English, you have to follow a rule called “subject-verb agreement.” – That means that if the subject is plural (ducks), then the verb needs to be plural (quack). If the subject is singular (duck) then the verb needs to be singular (quacks). – Notice that English verbs, un ...
... If you want to write proper English, you have to follow a rule called “subject-verb agreement.” – That means that if the subject is plural (ducks), then the verb needs to be plural (quack). If the subject is singular (duck) then the verb needs to be singular (quacks). – Notice that English verbs, un ...
Parts of Speech PowerPoint
... A preposition shows the relationship between a noun and another word in the sentence. A prepositional phrase starts with the preposition and ends with the next noun which is called the object of the preposition. Ex. Counting Crows is the coolest band in the ...
... A preposition shows the relationship between a noun and another word in the sentence. A prepositional phrase starts with the preposition and ends with the next noun which is called the object of the preposition. Ex. Counting Crows is the coolest band in the ...
Check 6 Answers - Tranmere Park Primary School
... 1-2. (W2:4,17,24. Sp 2:7-9) The apostrophe represents missing letters and not the joining of two words (I have / I’ve). It can also be used to show possession ( the voice belonging to the man – the man’s voice) In either case, it must be placed precisely. ...
... 1-2. (W2:4,17,24. Sp 2:7-9) The apostrophe represents missing letters and not the joining of two words (I have / I’ve). It can also be used to show possession ( the voice belonging to the man – the man’s voice) In either case, it must be placed precisely. ...
PDF
... This is another large class of words. Adjectives are words that are used to describe a noun or pronoun. They can become before or after a noun. e.g. the tall man or the man was tall. Adjectives can make comparisons e.g. the tall man, the taller man, the tallest ...
... This is another large class of words. Adjectives are words that are used to describe a noun or pronoun. They can become before or after a noun. e.g. the tall man or the man was tall. Adjectives can make comparisons e.g. the tall man, the taller man, the tallest ...
PARTS OF SPEECH
... Which one? this book these islands that child those rules How many? four oceans many rings few farmers both principals How much? More money no time enough salad little patience Forms of Adjectives – degrees of comparison Positive (1) Slow Healthy Strenuous ...
... Which one? this book these islands that child those rules How many? four oceans many rings few farmers both principals How much? More money no time enough salad little patience Forms of Adjectives – degrees of comparison Positive (1) Slow Healthy Strenuous ...
Step One Notes (Parts of Speech)
... shows relationship between a noun or pronoun and some other word in the sentence across, after, against, around, at, before, below, between, by, during, except, for, from, in, of, off, on, over, since, through, to, under, until, with, according to, because of, instead of, etc. We went to colle ...
... shows relationship between a noun or pronoun and some other word in the sentence across, after, against, around, at, before, below, between, by, during, except, for, from, in, of, off, on, over, since, through, to, under, until, with, according to, because of, instead of, etc. We went to colle ...
Document
... (possessive case from above) Singular or Plural Person: first, second, or third person Gender: masculine, feminine, or neuter reflexive or intensive = add -self or -selves reflexive - reflects an action back on the subject and is necessary to the meaning of the sentence intensive - emphasizes a noun ...
... (possessive case from above) Singular or Plural Person: first, second, or third person Gender: masculine, feminine, or neuter reflexive or intensive = add -self or -selves reflexive - reflects an action back on the subject and is necessary to the meaning of the sentence intensive - emphasizes a noun ...
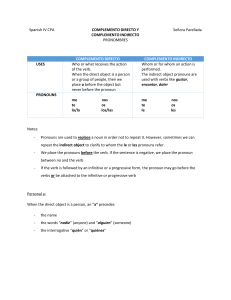
Repaso: C4G2 Verbs with reflexive pronouns and direct objects 1.
... 2. To form the past participles of regular verbs, drop the infinitive ending and add -ado (-AR), -ido (-ER & -IR). ex: hinchar -> hinchado: swollen torcer -> torcido: twisted, sprained herir -> herido: hurt cortar -> cortado: cut infectar-> infectado: infected quemar -> quemado: burned vendar -> ven ...
... 2. To form the past participles of regular verbs, drop the infinitive ending and add -ado (-AR), -ido (-ER & -IR). ex: hinchar -> hinchado: swollen torcer -> torcido: twisted, sprained herir -> herido: hurt cortar -> cortado: cut infectar-> infectado: infected quemar -> quemado: burned vendar -> ven ...
Inflection

In grammar, inflection or inflexion is the modification of a word to express different grammatical categories such as tense, mood, voice, aspect, person, number, gender and case. The inflection of verbs is also called conjugation, and the inflection of nouns, adjectives and pronouns is also called declension.An inflection expresses one or more grammatical categories with a prefix, suffix or infix, or another internal modification such as a vowel change. For example, the Latin verb ducam, meaning ""I will lead"", includes the suffix -am, expressing person (first), number (singular), and tense (future). The use of this suffix is an inflection. In contrast, in the English clause ""I will lead"", the word lead is not inflected for any of person, number, or tense; it is simply the bare form of a verb.The inflected form of a word often contains both a free morpheme (a unit of meaning which can stand by itself as a word), and a bound morpheme (a unit of meaning which cannot stand alone as a word). For example, the English word cars is a noun that is inflected for number, specifically to express the plural; the content morpheme car is unbound because it could stand alone as a word, while the suffix -s is bound because it cannot stand alone as a word. These two morphemes together form the inflected word cars.Words that are never subject to inflection are said to be invariant; for example, the English verb must is an invariant item: it never takes a suffix or changes form to signify a different grammatical category. Its categories can be determined only from its context.Requiring the inflections of more than one word in a sentence to be compatible according to the rules of the language is known as concord or agreement. For example, in ""the choir sings"", ""choir"" is a singular noun, so ""sing"" is constrained in the present tense to use the third person singular suffix ""s"".Languages that have some degree of inflection are synthetic languages. These can be highly inflected, such as Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, or weakly inflected, such as English. Languages that are so inflected that a sentence can consist of a single highly inflected word (such as many American Indian languages) are called polysynthetic languages. Languages in which each inflection conveys only a single grammatical category, such as Finnish, are known as agglutinative languages, while languages in which a single inflection can convey multiple grammatical roles (such as both nominative case and plural, as in Latin and German) are called fusional. Languages such as Mandarin Chinese that never use inflections are called analytic or isolating.