1- WORD ORDER: English language follows a basic word order
... “How much money have you got?” “We haven’t got many matches”. “A lot of my friends like football”. 9- OTHER / OTHERS / ANOTHER: When OTHER is used as an adjective, it has no plural form. OTHERS is only used as a pronoun: “Where are the other photos?” “Some metals are magnetic and others aren’t”. ANO ...
... “How much money have you got?” “We haven’t got many matches”. “A lot of my friends like football”. 9- OTHER / OTHERS / ANOTHER: When OTHER is used as an adjective, it has no plural form. OTHERS is only used as a pronoun: “Where are the other photos?” “Some metals are magnetic and others aren’t”. ANO ...
Parts of Speech - Rocky View Schools
... Read some advertisements. What types of verbs are used most often: action? being? active? passive? Make a list of what you discover. ...
... Read some advertisements. What types of verbs are used most often: action? being? active? passive? Make a list of what you discover. ...
ENGLISH LANGUAGE – 2° YEAR A HISTORY OF THE ENGLISH
... • All new coinages and foreign borrowings were treated as weak (e.g. daunce(n) – daunced – daunced). • Gradually, formerly strong verbs started to develop weak forms. In such a transitory phase, boh variants may be found. • In Chaucer’s language, both strong and weak past participles can occur in tw ...
... • All new coinages and foreign borrowings were treated as weak (e.g. daunce(n) – daunced – daunced). • Gradually, formerly strong verbs started to develop weak forms. In such a transitory phase, boh variants may be found. • In Chaucer’s language, both strong and weak past participles can occur in tw ...
Verb Tense Exercises
... • The sopranos sang well, and they won first prize. The subject is third-person plural, and so is the pronoun “they,” which is the subject of the second independent clause. • The sopranos sang well. So first prize was awarded to them. “Them” is third-person plural and the object of a preposition. ...
... • The sopranos sang well, and they won first prize. The subject is third-person plural, and so is the pronoun “they,” which is the subject of the second independent clause. • The sopranos sang well. So first prize was awarded to them. “Them” is third-person plural and the object of a preposition. ...
Writing Practice – Simple Present Tense
... Directions: Write sentences with the verbs listed below. For each verb, make three sentences. For one sentence use the subject I. For the second sentence use one singular noun as the subject, such as my friend, my sister, my neighbor, this city, this college, or any other person, place, or thing you ...
... Directions: Write sentences with the verbs listed below. For each verb, make three sentences. For one sentence use the subject I. For the second sentence use one singular noun as the subject, such as my friend, my sister, my neighbor, this city, this college, or any other person, place, or thing you ...
Yr 8 and 9 Literacy - Set Three
... Frank (should have won) the race. ( Verb group with auxiliary verbs) Auxiliary verbs can be seen as ‘helping’ verbs. The basic forms are: be - 8 ways of using - be, am, is, are, was, were, being, been ...
... Frank (should have won) the race. ( Verb group with auxiliary verbs) Auxiliary verbs can be seen as ‘helping’ verbs. The basic forms are: be - 8 ways of using - be, am, is, are, was, were, being, been ...
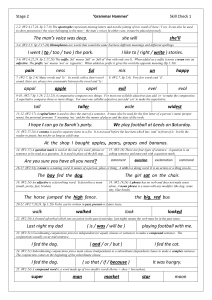
Stage 2 Check 1 – Answers
... 1-2. (W2:4,17,24. Sp 2:7-9) The apostrophe represents missing letters and not the joining of two words (I have / I’ve). It can also be used to show possession ( the voice belonging to the man – the man’s voice) In either case, it must be placed precisely. ...
... 1-2. (W2:4,17,24. Sp 2:7-9) The apostrophe represents missing letters and not the joining of two words (I have / I’ve). It can also be used to show possession ( the voice belonging to the man – the man’s voice) In either case, it must be placed precisely. ...
Diapositiva 1 - ercole patti
... In English most nouns make their plurals by simply adding –s to the end. •-es is added when the word ends with s, ...
... In English most nouns make their plurals by simply adding –s to the end. •-es is added when the word ends with s, ...
Greek I
... serves as the object of a preposition. Possessive – as the name implies, shows possession. The main words in English that change their forms according to the function they perform are pronouns, e.g. he, him, his. ...
... serves as the object of a preposition. Possessive – as the name implies, shows possession. The main words in English that change their forms according to the function they perform are pronouns, e.g. he, him, his. ...
Singular Plural
... MORPHOLOGICAL FEATURES Grammatical categories are composed of sets of morphological features. ...
... MORPHOLOGICAL FEATURES Grammatical categories are composed of sets of morphological features. ...
Used to describe a person doing something that involves himself or
... To use a reflexive verb, put the reflexive pronoun before the conjugated verb. EX. Cuando se levanto Marcos? You can also use them in the infinitive. Put the reflexive pronouns either: before the conjugated verb EX. No te debes preocupar. or attach it to the end of the infinitive EX. No debes procu ...
... To use a reflexive verb, put the reflexive pronoun before the conjugated verb. EX. Cuando se levanto Marcos? You can also use them in the infinitive. Put the reflexive pronouns either: before the conjugated verb EX. No te debes preocupar. or attach it to the end of the infinitive EX. No debes procu ...
Absolute Brush Stroke
... Mind racing, anxiety overtaking, the diver peered once more at the specimen. (E. Stralka) I glanced at my clock, digits glowing fluorescent blue in the inky darkness of my room. (J. Coppolo) Jaws cracking, tongue curling, the kitten yawned tiredly, awaking from her nap. (T. Tesmer) ...
... Mind racing, anxiety overtaking, the diver peered once more at the specimen. (E. Stralka) I glanced at my clock, digits glowing fluorescent blue in the inky darkness of my room. (J. Coppolo) Jaws cracking, tongue curling, the kitten yawned tiredly, awaking from her nap. (T. Tesmer) ...
Parts of Speech - Flagstaff High School
... * Connect ideas or join words, phrases, or clauses * Coordinating: Only conjunctions that can be used to join two complete sentences * For * And * Nor * But * Or * Yet * So ...
... * Connect ideas or join words, phrases, or clauses * Coordinating: Only conjunctions that can be used to join two complete sentences * For * And * Nor * But * Or * Yet * So ...
Chapter 2 Folder 1 – The Accusative Case In Chapter 1 you learned
... These are the verbs you have seen so far: Ambulo, ambulare, ambulavi Habito, habitare, habitavi Habeo, habere, habui Video, videre, vidi In the vocabulary list, verbs will be presented with their first three principal parts. Just as the second form given for nouns (genitive) told you the base and th ...
... These are the verbs you have seen so far: Ambulo, ambulare, ambulavi Habito, habitare, habitavi Habeo, habere, habui Video, videre, vidi In the vocabulary list, verbs will be presented with their first three principal parts. Just as the second form given for nouns (genitive) told you the base and th ...
Subject-Verb Study Sheet
... Three Step Process to Finding Subjects and Verbs 1. Look for any be, do, have, or others verb group words. 2. Look for any action words. (Key endings: -ed, -en, -ing) 3. Insert the verb into this question: Who or what (verb) ? ...
... Three Step Process to Finding Subjects and Verbs 1. Look for any be, do, have, or others verb group words. 2. Look for any action words. (Key endings: -ed, -en, -ing) 3. Insert the verb into this question: Who or what (verb) ? ...
RUSSIAN: ACCUSATIVE OR ACTIVE
... category of animacy (or activity) for the Russian morphosyntax and evokes immediately the idea of the active language type. Actually, two different approaches to the definition of this language type are found in literature. The first approach is purely syntactic (Kibrik 1992; Lazard 1998). The activ ...
... category of animacy (or activity) for the Russian morphosyntax and evokes immediately the idea of the active language type. Actually, two different approaches to the definition of this language type are found in literature. The first approach is purely syntactic (Kibrik 1992; Lazard 1998). The activ ...
NOUN - SchoolNotes
... Common prepositions include in, on, under, beside, below, to, at, by, like, of, over, since, and with. Prepositions are always found in prepositional phrases. A prepositional phrase is made up of a preposition and the noun or pronoun that comes after it, like “at the mall,” “under the table,” “with ...
... Common prepositions include in, on, under, beside, below, to, at, by, like, of, over, since, and with. Prepositions are always found in prepositional phrases. A prepositional phrase is made up of a preposition and the noun or pronoun that comes after it, like “at the mall,” “under the table,” “with ...
File
... bike), or a possessive pronoun may stand alone (the bike is mine). Unlike most nouns, possessive pronouns do not use an apostrophe to form the possessive. ...
... bike), or a possessive pronoun may stand alone (the bike is mine). Unlike most nouns, possessive pronouns do not use an apostrophe to form the possessive. ...
- ESL101.com
... sentences. We begin with a brief overview of common verb types but focus mostly on the various roles that auxiliary verbs (forms of BE, DO, HAVE, and MODALS) play in sentences and the ways they operate systematically with other sentence constituents. The second module focuses on nouns and other nomi ...
... sentences. We begin with a brief overview of common verb types but focus mostly on the various roles that auxiliary verbs (forms of BE, DO, HAVE, and MODALS) play in sentences and the ways they operate systematically with other sentence constituents. The second module focuses on nouns and other nomi ...
3.4 Transitive and Intransitive Verbs
... What is direct object, what type of verb? They bought her birthday present. They chose a watch with an orange band. She talks about her present all the time. The second hand sweeps around the numbers. The teacher watched the children at recess. She keeps the watch in its case. The numbers glow in th ...
... What is direct object, what type of verb? They bought her birthday present. They chose a watch with an orange band. She talks about her present all the time. The second hand sweeps around the numbers. The teacher watched the children at recess. She keeps the watch in its case. The numbers glow in th ...
Presentation
... with the second one. Be careful with inverted word order (verb comes first). Nouns of amount are generally singular. ...
... with the second one. Be careful with inverted word order (verb comes first). Nouns of amount are generally singular. ...
Parts of Speech Review (PowerPoint)
... sentence – there will always be at least one word between a reflexive pronoun and its antecedent. – Ex. Luke Skywalker made himself a lightsaber. ...
... sentence – there will always be at least one word between a reflexive pronoun and its antecedent. – Ex. Luke Skywalker made himself a lightsaber. ...
Unit 3 Lesson 1 (sec 4)
... Three of the principal parts of a verb are the present, the past, and the past participle. The past participle is the form of the verb that is used after have. In regular verbs, the past and present participle forms are identical. In irregular verbs, however, these forms may ...
... Three of the principal parts of a verb are the present, the past, and the past participle. The past participle is the form of the verb that is used after have. In regular verbs, the past and present participle forms are identical. In irregular verbs, however, these forms may ...
Noun: A noun is a person, place, thing, quality, or act
... English: Noun: A noun is a person, place, thing, quality, or act. Examples: pencil, girl, supermarket, happiness Verb: Verbs are action or existence words that tell what nouns do. Examples: to fly, to run, to be, jump, lived Adjective: An adjective describes a noun. Examples: hairy, crazy, wonderful ...
... English: Noun: A noun is a person, place, thing, quality, or act. Examples: pencil, girl, supermarket, happiness Verb: Verbs are action or existence words that tell what nouns do. Examples: to fly, to run, to be, jump, lived Adjective: An adjective describes a noun. Examples: hairy, crazy, wonderful ...
Grammar_virtual_teacher
... A main clause is a group of words which contain a verb and someone Doing the action (it makes sense on its own): Ann went to the bank; A complex sentences are those that contain a subordinate clause as well as a main clause; He stayed at home because he was ill. A subordinate clause is is a less imp ...
... A main clause is a group of words which contain a verb and someone Doing the action (it makes sense on its own): Ann went to the bank; A complex sentences are those that contain a subordinate clause as well as a main clause; He stayed at home because he was ill. A subordinate clause is is a less imp ...
Inflection

In grammar, inflection or inflexion is the modification of a word to express different grammatical categories such as tense, mood, voice, aspect, person, number, gender and case. The inflection of verbs is also called conjugation, and the inflection of nouns, adjectives and pronouns is also called declension.An inflection expresses one or more grammatical categories with a prefix, suffix or infix, or another internal modification such as a vowel change. For example, the Latin verb ducam, meaning ""I will lead"", includes the suffix -am, expressing person (first), number (singular), and tense (future). The use of this suffix is an inflection. In contrast, in the English clause ""I will lead"", the word lead is not inflected for any of person, number, or tense; it is simply the bare form of a verb.The inflected form of a word often contains both a free morpheme (a unit of meaning which can stand by itself as a word), and a bound morpheme (a unit of meaning which cannot stand alone as a word). For example, the English word cars is a noun that is inflected for number, specifically to express the plural; the content morpheme car is unbound because it could stand alone as a word, while the suffix -s is bound because it cannot stand alone as a word. These two morphemes together form the inflected word cars.Words that are never subject to inflection are said to be invariant; for example, the English verb must is an invariant item: it never takes a suffix or changes form to signify a different grammatical category. Its categories can be determined only from its context.Requiring the inflections of more than one word in a sentence to be compatible according to the rules of the language is known as concord or agreement. For example, in ""the choir sings"", ""choir"" is a singular noun, so ""sing"" is constrained in the present tense to use the third person singular suffix ""s"".Languages that have some degree of inflection are synthetic languages. These can be highly inflected, such as Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, or weakly inflected, such as English. Languages that are so inflected that a sentence can consist of a single highly inflected word (such as many American Indian languages) are called polysynthetic languages. Languages in which each inflection conveys only a single grammatical category, such as Finnish, are known as agglutinative languages, while languages in which a single inflection can convey multiple grammatical roles (such as both nominative case and plural, as in Latin and German) are called fusional. Languages such as Mandarin Chinese that never use inflections are called analytic or isolating.