HTM Cortical Learning Algorithms
... computers, programmers create specific programs to solve specific problems. By contrast, HTMs are trained through exposure to a stream of sensory data. The HTM’s capabilities are determined largely by what it has been exposed to. ...
... computers, programmers create specific programs to solve specific problems. By contrast, HTMs are trained through exposure to a stream of sensory data. The HTM’s capabilities are determined largely by what it has been exposed to. ...
Mirror neurons and their clinical relevance
... Studies in which the properties of single neu rons were studied in a naturalistic context have been particularly important for establishing this new view on cortical motor organization.12 These studies showed that many neurons discharge when a motor act (e.g. grasping) is performed january 2009 vo ...
... Studies in which the properties of single neu rons were studied in a naturalistic context have been particularly important for establishing this new view on cortical motor organization.12 These studies showed that many neurons discharge when a motor act (e.g. grasping) is performed january 2009 vo ...
Diffuse optical imaging of brain activation
... axes parallel to the scalp in the adult human brain close to the skull (resolution degrades rapidly with increasing depth in the brain). However, current measurement strategies primarily utilize nonoverlapping geometric arrangements of sources and detectors, and thus spatial resolution is no better ...
... axes parallel to the scalp in the adult human brain close to the skull (resolution degrades rapidly with increasing depth in the brain). However, current measurement strategies primarily utilize nonoverlapping geometric arrangements of sources and detectors, and thus spatial resolution is no better ...
Human Biology I - Control and Development
... Eggs and sperm are gametes—haploid cells produced through meiosis. Eggs are large, because they are the result of unequal meiosis—during cell division, the future egg gets almost all of the cytoplasm and the other cells receive very little. These other cells quickly degenerate. Copyright © 2007 Pear ...
... Eggs and sperm are gametes—haploid cells produced through meiosis. Eggs are large, because they are the result of unequal meiosis—during cell division, the future egg gets almost all of the cytoplasm and the other cells receive very little. These other cells quickly degenerate. Copyright © 2007 Pear ...
Figure 1 - Journal of Neuroscience
... borders of the SC were roughly located by recording multiunit entrainment to a pulsed (1 or 4 Hz), red LED located in front of the monkey, or ⬃20 or ⬃40° to the side (contralateral to the IC under study). Although clear light responses were common, the precise mapping of visual receptive field cente ...
... borders of the SC were roughly located by recording multiunit entrainment to a pulsed (1 or 4 Hz), red LED located in front of the monkey, or ⬃20 or ⬃40° to the side (contralateral to the IC under study). Although clear light responses were common, the precise mapping of visual receptive field cente ...
Sprecher_2011_larval.. - Institute of Neuroinformatics
... located in the eye. Upon perception of light the PRs will send a signal to target neurons, which represent a first station of visual processing. Increasing complexity of visual processing stems from the number of distinct PR subtypes and their various types of target neurons that are contacted. The v ...
... located in the eye. Upon perception of light the PRs will send a signal to target neurons, which represent a first station of visual processing. Increasing complexity of visual processing stems from the number of distinct PR subtypes and their various types of target neurons that are contacted. The v ...
Word Definition 12 Cranial Nerve innervation of
... the posterior cingulate gyrus. These areas project to entorhinal cortex and to pre- and post-subiculum, and thereby to the hippocampus. Mitosis in the CNS that results in one post-mitotic cell and one cell that remains in the cell cycle. The post-mitotic cell migrates towards its final location. Man ...
... the posterior cingulate gyrus. These areas project to entorhinal cortex and to pre- and post-subiculum, and thereby to the hippocampus. Mitosis in the CNS that results in one post-mitotic cell and one cell that remains in the cell cycle. The post-mitotic cell migrates towards its final location. Man ...
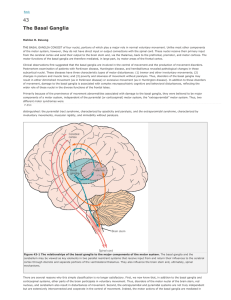
Basal Ganglia and Associated Pathways
... cells in the substantia nigra. Researchers attempted to recreate his drug synthesis reaction conditions and compared their findings against residues found in his laboratory glassware. The findings showed several synthetic impurities including MPTP. These findings were published in 1979. In 1982, six ...
... cells in the substantia nigra. Researchers attempted to recreate his drug synthesis reaction conditions and compared their findings against residues found in his laboratory glassware. The findings showed several synthetic impurities including MPTP. These findings were published in 1979. In 1982, six ...
Principles of Neural Science
... highly organized connections with virtually the entire cerebral cortex, as well as the hippocampus and amygdala. Finally, a wide range of motor and nonmotor behaviors have been correlated with activity in individual basal ganglia neurons in experimental animals and with metabolic activity in the bas ...
... highly organized connections with virtually the entire cerebral cortex, as well as the hippocampus and amygdala. Finally, a wide range of motor and nonmotor behaviors have been correlated with activity in individual basal ganglia neurons in experimental animals and with metabolic activity in the bas ...
The role of the Golgi apparatus in neuronal polarity
... endoplasmic reticulum. The middle portion of the Golgi is termed the medial Golgi. The trans-Golgi is the portion facing the plasma membrane. The transGolgi network is the final portion of the Golgi, which sends off vesicle buds targeting proteins to their final destination (Glick and Nakano, 2009). ...
... endoplasmic reticulum. The middle portion of the Golgi is termed the medial Golgi. The trans-Golgi is the portion facing the plasma membrane. The transGolgi network is the final portion of the Golgi, which sends off vesicle buds targeting proteins to their final destination (Glick and Nakano, 2009). ...
Contact guidance of CNS neurites on grooved quartz: influence of
... 100 W (rf) at 13.6 Mhz to give an etch rate of approximately 50 nm/minute. After removal of the remaining resist/chrome using acetone/chrome etch the substrates were blanket etched in CHF3 for 30 seconds using the parameters outlined above. Finally the mask plate was cut into 8 individual microscope ...
... 100 W (rf) at 13.6 Mhz to give an etch rate of approximately 50 nm/minute. After removal of the remaining resist/chrome using acetone/chrome etch the substrates were blanket etched in CHF3 for 30 seconds using the parameters outlined above. Finally the mask plate was cut into 8 individual microscope ...
Full Article - CIHR Research Group in Sensory
... superior colliculus (dSC) in covert orienting. Two monkeys were trained on a predictive cued-saccade task in which the cue predicted the target’s upcoming location with 80% validity. When the delay between cue and target onset was 250 ms, both monkeys showed faster responses to the uncued (Invalid) ...
... superior colliculus (dSC) in covert orienting. Two monkeys were trained on a predictive cued-saccade task in which the cue predicted the target’s upcoming location with 80% validity. When the delay between cue and target onset was 250 ms, both monkeys showed faster responses to the uncued (Invalid) ...
Ontogeny, Compartmentation, and Turnover of Spectrin lsoforms in
... knowledge of the assembly, organization, and metabolism of skeletal proteins is essential to understanding the molecular basis of neuronal form and function. While studies of neuronal structural proteins have long been directed at the microtubules, neurofilaments, and actin filaments (Wuerker and Ki ...
... knowledge of the assembly, organization, and metabolism of skeletal proteins is essential to understanding the molecular basis of neuronal form and function. While studies of neuronal structural proteins have long been directed at the microtubules, neurofilaments, and actin filaments (Wuerker and Ki ...
MAG, Nogo-A and NgR in Hippocampal Development and Regeneration TESIS DOCTORAL
... The question this thesis aims to address is, therefore, the role of myelin-associated inhibitors in the regeneration of cortical connections. The model we have used is the entorhino-hippocampal connection and the conceptual structure followed was i) characterizing the temporal expression of the prot ...
... The question this thesis aims to address is, therefore, the role of myelin-associated inhibitors in the regeneration of cortical connections. The model we have used is the entorhino-hippocampal connection and the conceptual structure followed was i) characterizing the temporal expression of the prot ...
Proceedings of 2014 BMI the Third International Conference on
... Juyang (John) Weng is a professor at the Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, the Cognitive Science Program, and the Neuroscience Program, Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michig ...
... Juyang (John) Weng is a professor at the Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, the Cognitive Science Program, and the Neuroscience Program, Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michig ...
Scents and Sensibility: A Molecular Logic of Olfactory Perception
... developed novel procedures that allowed DNA-mediated transformation of mammalian cells. Michael, even at this very early stage in his career, was conceptually and technically masterful and within a few years he devised procedures that permitted the introduction of virtually any gene into any cell in ...
... developed novel procedures that allowed DNA-mediated transformation of mammalian cells. Michael, even at this very early stage in his career, was conceptually and technically masterful and within a few years he devised procedures that permitted the introduction of virtually any gene into any cell in ...
Bayesian Computation in Recurrent Neural Circuits
... by a model computing the log-likelihood ratio of one target over the other (Carpenter & Williams, 1995). In another study, the saccadic response time distribution of monkeys could be predicted from the time taken by neural activity in area FEF to reach a fixed threshold (Hanes & Schall, 1996), sugges ...
... by a model computing the log-likelihood ratio of one target over the other (Carpenter & Williams, 1995). In another study, the saccadic response time distribution of monkeys could be predicted from the time taken by neural activity in area FEF to reach a fixed threshold (Hanes & Schall, 1996), sugges ...
The Basal Ganglia and Involuntary Movements
... tum to the GPi, leading to excessive inhibition of the GPi and excessive disinhibition of motor cortical areas. This would be reflected as enhanced facilitation and possibly expansion of the “center” of the present centersurround model (Figure 1). An alternative scheme, based on reduced dopamine D2 ...
... tum to the GPi, leading to excessive inhibition of the GPi and excessive disinhibition of motor cortical areas. This would be reflected as enhanced facilitation and possibly expansion of the “center” of the present centersurround model (Figure 1). An alternative scheme, based on reduced dopamine D2 ...
Synchronization of Fast (30-40 Hz)
... degree of resemblance and phase sign as well as the time-lags separating the waves. The autocorrelation function indicates the main period of the oscillation (at the abscissa of the first secondary peak) and the strength of the oscillation (as a function of the number of secondary peaks visible in t ...
... degree of resemblance and phase sign as well as the time-lags separating the waves. The autocorrelation function indicates the main period of the oscillation (at the abscissa of the first secondary peak) and the strength of the oscillation (as a function of the number of secondary peaks visible in t ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.