Slides Ch 2 - Department of Linguistics and English Language
... As rain from Hurricane Rita threatened to once again flood the city, the Army Corps of Engimeers was racing to patch New Orleans' fractured levee system while residents were forced to decide yet again whethel to stay or go. Forecasters said the storm that swiped Florida on Tuesday could strengthen t ...
... As rain from Hurricane Rita threatened to once again flood the city, the Army Corps of Engimeers was racing to patch New Orleans' fractured levee system while residents were forced to decide yet again whethel to stay or go. Forecasters said the storm that swiped Florida on Tuesday could strengthen t ...
Chapter 2
... • Sex differences; result rather than cause of behavioral differences – Nature or nurture ...
... • Sex differences; result rather than cause of behavioral differences – Nature or nurture ...
Nervous System
... Motor or Efferent Neurons conduct action portential from the CNS toward the muscle or gland. Interneurons or Association Neurons: conduct action potential from one neuron to another within the CNS. ...
... Motor or Efferent Neurons conduct action portential from the CNS toward the muscle or gland. Interneurons or Association Neurons: conduct action potential from one neuron to another within the CNS. ...
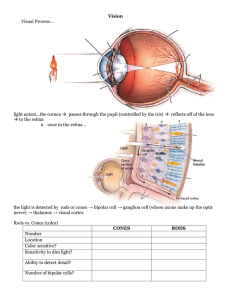
Vision Lecture Notes
... outer ear (pinna) → auditory canal → tympanic membrane (eardrum) → ossicles (bones) of the middle ear → oval window → cochlea → basilar membrane (hair cells) → auditory nerve → auditory cortex ...
... outer ear (pinna) → auditory canal → tympanic membrane (eardrum) → ossicles (bones) of the middle ear → oval window → cochlea → basilar membrane (hair cells) → auditory nerve → auditory cortex ...
Assignment 1 - Gordon State College
... 1. Communication in the nervous system takes place via _____________ or nerve cells. 2. The human brain is estimated to have (how many) _____________________neurons. 3. Cells that provide nutrition and support for neurons, remove waste products, and enhance the speed of communication are called ____ ...
... 1. Communication in the nervous system takes place via _____________ or nerve cells. 2. The human brain is estimated to have (how many) _____________________neurons. 3. Cells that provide nutrition and support for neurons, remove waste products, and enhance the speed of communication are called ____ ...
physiology_lec43_3_5_2011
... When center part is excited the lateral part is inhibited, that will prevent the lateral spread of light excitation on the retina. It is the same with cones (blue, red, green) one cone inhibit the others so that there will be contrast between these colors. ...
... When center part is excited the lateral part is inhibited, that will prevent the lateral spread of light excitation on the retina. It is the same with cones (blue, red, green) one cone inhibit the others so that there will be contrast between these colors. ...
Mind Is Matter
... 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with the synaptic cleft (synapse) from a diagram. Describe the function of each structure. Presynaptic membrane Postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter Vesicle Receptors and ion chan ...
... 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with the synaptic cleft (synapse) from a diagram. Describe the function of each structure. Presynaptic membrane Postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter Vesicle Receptors and ion chan ...
Therapeutic Cell Replacement - McLoon Lab
... IPSCs can be generated (possibly) from any differentiated cell type, but usually is done with skin cells. ...
... IPSCs can be generated (possibly) from any differentiated cell type, but usually is done with skin cells. ...
Powerpoint - Center Grove Community School
... • Mature neurons generally can’t divide • But new dendrites can grow • Provides room for more connections to other neurons • New connections are basis for learning ...
... • Mature neurons generally can’t divide • But new dendrites can grow • Provides room for more connections to other neurons • New connections are basis for learning ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Not all neurons are created equal. If neurons were created equal, there would be no paraplegics. Docs would just take a neuron from one part of our body and replace the broken neuron, but each neuron is unique. To gain a better understanding of how neurons work, click the following link: ...
... Not all neurons are created equal. If neurons were created equal, there would be no paraplegics. Docs would just take a neuron from one part of our body and replace the broken neuron, but each neuron is unique. To gain a better understanding of how neurons work, click the following link: ...
vision part VII_2
... Characters of colours: 1. Hue means the wave length e.g. red light (wavelength 723-647 nm), green light (575-492 nm), and blue light (492-450 nm). 2. Intensity or saturation means the purity of the colour i.e. it is pure or mixed with other colours 3. Brightness means the amount of light in the col ...
... Characters of colours: 1. Hue means the wave length e.g. red light (wavelength 723-647 nm), green light (575-492 nm), and blue light (492-450 nm). 2. Intensity or saturation means the purity of the colour i.e. it is pure or mixed with other colours 3. Brightness means the amount of light in the col ...
Nervous System notes
... - association (interneurons) – carry impulses from sensory neurons to motor neurons and are located in the brain and spinal cord only – makes up most neurons of humans II. Functions – A. Nerve Impulses – like tiny electrical currents that pass along neurons – these result from ion movement in and ou ...
... - association (interneurons) – carry impulses from sensory neurons to motor neurons and are located in the brain and spinal cord only – makes up most neurons of humans II. Functions – A. Nerve Impulses – like tiny electrical currents that pass along neurons – these result from ion movement in and ou ...
Nervous System Introduction
... • - cell winds around axon, inside its own layers, piling up layers of lipid/protein cell membranes • - one Schwann cell associates with and myelinates a segment of only one axon • - Schwann cell, myelin, axon are all surrounded by a basement membrane (covers whole unit) • - help to buffer excess ex ...
... • - cell winds around axon, inside its own layers, piling up layers of lipid/protein cell membranes • - one Schwann cell associates with and myelinates a segment of only one axon • - Schwann cell, myelin, axon are all surrounded by a basement membrane (covers whole unit) • - help to buffer excess ex ...
Neuro2
... Golgi network. These vesicles are transported down to synaptic terminals along microtubules (usually due to an influx of calcium from the extracellular space). The vesicles fuse w/ the membrane at “active zones” and release their drugs into the extracellular space. transportdockingprimingfusionr ...
... Golgi network. These vesicles are transported down to synaptic terminals along microtubules (usually due to an influx of calcium from the extracellular space). The vesicles fuse w/ the membrane at “active zones” and release their drugs into the extracellular space. transportdockingprimingfusionr ...
ganglion trigeminale – large light pseudounipolar neurons
... rich of cell’s organelles. One can observe hromatin along whole stretch of nuclear surface, finely dispersived in carioplasma. This picture determines light look of nucleus, which is the reason to name it hypohromic, characteristic for pseudounipolar neurons. Cytoplasma of larges light neurons is ri ...
... rich of cell’s organelles. One can observe hromatin along whole stretch of nuclear surface, finely dispersived in carioplasma. This picture determines light look of nucleus, which is the reason to name it hypohromic, characteristic for pseudounipolar neurons. Cytoplasma of larges light neurons is ri ...
M555 Medical Neuroscience
... gastrointestinal tract for newborns like J.G. This disorder involves the autonomic/enteric nervous systems and is one of the most common congenital anorectal malformations (1/5,500 births, four times more frequent in males). Neural crest may have failed to migrate toward the developing colon and rec ...
... gastrointestinal tract for newborns like J.G. This disorder involves the autonomic/enteric nervous systems and is one of the most common congenital anorectal malformations (1/5,500 births, four times more frequent in males). Neural crest may have failed to migrate toward the developing colon and rec ...
Morphogenesis
... The neural plate begins to fold, forming the neural groove. Closure to form the neural tube begins in the future midbrain region, and then extends cranially and caudally. Neural crest cells migrate away from the site of closure and later take numerous roles within the body, forming peripheral neuron ...
... The neural plate begins to fold, forming the neural groove. Closure to form the neural tube begins in the future midbrain region, and then extends cranially and caudally. Neural crest cells migrate away from the site of closure and later take numerous roles within the body, forming peripheral neuron ...
MyersExpPsych7e_IM_Module 03 garber edited
... How neurons communicate • Neurons communicate by means of an electrical signal called the Action Potential • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
... How neurons communicate • Neurons communicate by means of an electrical signal called the Action Potential • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
State Dependant Synaptic Plasticity in Purkinje Cells
... memory traces at the parallel fibers (pf) synapse. According to this theory, the climbing fibers (cf) control the learning process by inducing long-term depression (LTD) of the simultaneously activated pf synapses. In a recent study we showed that Purkinje cells (PCs), under in vivo conditions, disp ...
... memory traces at the parallel fibers (pf) synapse. According to this theory, the climbing fibers (cf) control the learning process by inducing long-term depression (LTD) of the simultaneously activated pf synapses. In a recent study we showed that Purkinje cells (PCs), under in vivo conditions, disp ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.