experiment 10 - Faculty Web Pages
... where A, B, C, and D all exist as ions in solution. Will a reaction happen, and if so, what will be the products? Each of the positive ions could combine with the negative ion of the other compound, i.e. A+ and D¯ and C+ and B¯. The formation of a precipitate, the evolution of a gas, and a temperatu ...
... where A, B, C, and D all exist as ions in solution. Will a reaction happen, and if so, what will be the products? Each of the positive ions could combine with the negative ion of the other compound, i.e. A+ and D¯ and C+ and B¯. The formation of a precipitate, the evolution of a gas, and a temperatu ...
Copy of Acids, bases, salts answer key
... Arhhenius’ theory became quite popular and was widely accepted yet it had the following limitations: This theory was applicable only to aqueous solutions. Substances like Ammonia (NH3) do not contain hydroxide (OH) ion, even then its aqueous solution acts as a base. The theory could not explain ...
... Arhhenius’ theory became quite popular and was widely accepted yet it had the following limitations: This theory was applicable only to aqueous solutions. Substances like Ammonia (NH3) do not contain hydroxide (OH) ion, even then its aqueous solution acts as a base. The theory could not explain ...
Acids and Bases
... General rule: The conjugate base of a strong acid is a weak base. Similarly, the conjugate acid of a strong base is a weak acid. ...
... General rule: The conjugate base of a strong acid is a weak base. Similarly, the conjugate acid of a strong base is a weak acid. ...
ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS
... Atoms are indestructible – they retain their identity in reactions. Compounds are formed from a combination of elements in small whole number ratios. ...
... Atoms are indestructible – they retain their identity in reactions. Compounds are formed from a combination of elements in small whole number ratios. ...
KEY - Unit 10 - Practice Questions
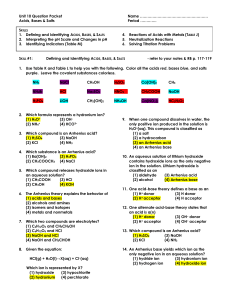
... 6. The Arrhenius theory explains the behavior of (1) acids and bases (2) alcohols and amines (3) isomers and isotopes (4) metals and nonmetals 7. Which two compounds are electrolytes? (1) C6H12O6 and CH3CH2OH (2) C6H12O6 and HCl (3) NaOH and HCl (4) NaOH and CH3CHOH 8. Given the equation: HCl(g) + H ...
... 6. The Arrhenius theory explains the behavior of (1) acids and bases (2) alcohols and amines (3) isomers and isotopes (4) metals and nonmetals 7. Which two compounds are electrolytes? (1) C6H12O6 and CH3CH2OH (2) C6H12O6 and HCl (3) NaOH and HCl (4) NaOH and CH3CHOH 8. Given the equation: HCl(g) + H ...
Recording Measurements
... 6. The Arrhenius theory explains the behavior of (1) acids and bases (2) alcohols and amines (3) isomers and isotopes (4) metals and nonmetals 7. Which two compounds are electrolytes? (1) C6H12O6 and CH3CH2OH (2) C6H12O6 and HCl (3) NaOH and HCl (4) NaOH and CH3CHOH 8. Given the equation: HCl(g) + H ...
... 6. The Arrhenius theory explains the behavior of (1) acids and bases (2) alcohols and amines (3) isomers and isotopes (4) metals and nonmetals 7. Which two compounds are electrolytes? (1) C6H12O6 and CH3CH2OH (2) C6H12O6 and HCl (3) NaOH and HCl (4) NaOH and CH3CHOH 8. Given the equation: HCl(g) + H ...
LN_atoms_etc
... Atoms are indestructible – they retain their identity in reactions. Compounds are formed from a combination of elements in small whole number ratios. ...
... Atoms are indestructible – they retain their identity in reactions. Compounds are formed from a combination of elements in small whole number ratios. ...
Practice Qs - Unit 10 Acid Base
... 6. The Arrhenius theory explains the behavior of (1) acids and bases (2) alcohols and amines (3) isomers and isotopes (4) metals and nonmetals 7. Which two compounds are electrolytes? (1) C6H12O6 and CH3CH2OH (2) C6H12O6 and HCl (3) NaOH and HCl (4) NaOH and CH3CHOH 8. Given the equation: HCl(g) + H ...
... 6. The Arrhenius theory explains the behavior of (1) acids and bases (2) alcohols and amines (3) isomers and isotopes (4) metals and nonmetals 7. Which two compounds are electrolytes? (1) C6H12O6 and CH3CH2OH (2) C6H12O6 and HCl (3) NaOH and HCl (4) NaOH and CH3CHOH 8. Given the equation: HCl(g) + H ...
American-Journal-of-Oil-and-Chemical-Technologies
... the negative charge of carboxylate groups compensates the positive charge induced by the metal centre and can mitigate the counter ion effect [3]. Furthermore, the flexibility of carboxylate groups is always efficient to form fascinating topologies. Besides supramolecular contacts, hydrogen bonding ...
... the negative charge of carboxylate groups compensates the positive charge induced by the metal centre and can mitigate the counter ion effect [3]. Furthermore, the flexibility of carboxylate groups is always efficient to form fascinating topologies. Besides supramolecular contacts, hydrogen bonding ...
Module 3 Exam Review 1. Organic chemistry is the study of which
... 25. Sucrose is split into glucose and fructose by the enzyme sucrase. This would be an example of a catabolic reaction known as _____. hydrolysis 26. A disaccharide consisting of two glucose molecules is _____. maltose 27. A phospholipid with a carbohydrate chain attached would be called a _____. gl ...
... 25. Sucrose is split into glucose and fructose by the enzyme sucrase. This would be an example of a catabolic reaction known as _____. hydrolysis 26. A disaccharide consisting of two glucose molecules is _____. maltose 27. A phospholipid with a carbohydrate chain attached would be called a _____. gl ...
AS Paper 1 Practice Paper 16 - A
... The equation for the reaction between magnesium carbonate and hydrochloric acid is given below. MgCO3 + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2O + CO2 When 75.0 cm3 of 0.500 mol dm–3 hydrochloric acid were added to 1.25 g of impure MgCO3 some acid was left unreacted. This unreacted acid required 21.6 cm3 of a 0.500 mol d ...
... The equation for the reaction between magnesium carbonate and hydrochloric acid is given below. MgCO3 + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2O + CO2 When 75.0 cm3 of 0.500 mol dm–3 hydrochloric acid were added to 1.25 g of impure MgCO3 some acid was left unreacted. This unreacted acid required 21.6 cm3 of a 0.500 mol d ...
Analytical Chemistry
... Equilibrium exists between the weak acid, water, H:O', and the anion of the weak acid. The equilibrium lies to the left hand side ofthe equation, indicating that not much H3O* is being produced. The fact that very little H3O* is being produced is the ...
... Equilibrium exists between the weak acid, water, H:O', and the anion of the weak acid. The equilibrium lies to the left hand side ofthe equation, indicating that not much H3O* is being produced. The fact that very little H3O* is being produced is the ...
Sections 6.4 - 6.5
... This reaction has a high activation energy, because the metal passivates itself with an oxide layer a few µm thick – a very common phenomenon with reactive metals. ...
... This reaction has a high activation energy, because the metal passivates itself with an oxide layer a few µm thick – a very common phenomenon with reactive metals. ...
Name
... 27. What is the solubility of sodium nitrate at 30oC? 28. A saturated solution of potassium nitrate is formed from 100 g of water. If the saturated solution is cooled from 80oC to 50oC, how many grams of precipitate are formed? ...
... 27. What is the solubility of sodium nitrate at 30oC? 28. A saturated solution of potassium nitrate is formed from 100 g of water. If the saturated solution is cooled from 80oC to 50oC, how many grams of precipitate are formed? ...
AP Chemistry Review Packet 1 CO2(g) + H2(g) « H2O(g) + CO(g
... An experiment is to be performed to determine the standard molar enthalpy of neutralization of a strong acid by a strong base. Standard school laboratory equipment and a supply of standardized 1.00-molar HCl and standardized 1.00-molar NaOH are available. (a) What equipment would be needed? (b) Wha ...
... An experiment is to be performed to determine the standard molar enthalpy of neutralization of a strong acid by a strong base. Standard school laboratory equipment and a supply of standardized 1.00-molar HCl and standardized 1.00-molar NaOH are available. (a) What equipment would be needed? (b) Wha ...
Chapter 8 Brønsted-Lowry Theory of Acids and Bases
... Write the chemical reaction for the following acids or bases in water. Identify the conjugate acid base pairs. 1. HF (a weak acid) 2. H2S (a weak acid) 3. HNO3 (a strong acid) 4. CH3NH2 (a weak base) Note: The degree of dissociation also defines weak and strong bases ...
... Write the chemical reaction for the following acids or bases in water. Identify the conjugate acid base pairs. 1. HF (a weak acid) 2. H2S (a weak acid) 3. HNO3 (a strong acid) 4. CH3NH2 (a weak base) Note: The degree of dissociation also defines weak and strong bases ...
worksheet Ka Kb buffers Ksp
... If NaCl is added to a 0.010 M solution of AgNO3 in water at 25ºC, at what [Cl ] does precipitation of AgCl begin? Ksp for AgCl = 1.8x10-10 ...
... If NaCl is added to a 0.010 M solution of AgNO3 in water at 25ºC, at what [Cl ] does precipitation of AgCl begin? Ksp for AgCl = 1.8x10-10 ...
Physical Chemistry (SCQF level 7)
... the effect of temperature changes Partition coefficients could be included as a specific example of an equilibrium constant. ...
... the effect of temperature changes Partition coefficients could be included as a specific example of an equilibrium constant. ...
m5zn_307118e6dc84400
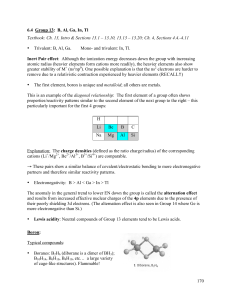
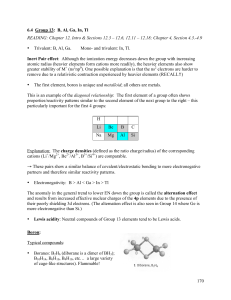
... 1. All cations are Lewis acids since they are able to accept electrons. (e.g., Cu2+, Fe2+ ) 2. An atom, ion, or molecule with an incomplete octet of electrons can act as an Lewis acid (e.g., BF3, AlF3). 3. Molecules that have multiple bonds between two atoms of different electronegativities (e.g., C ...
... 1. All cations are Lewis acids since they are able to accept electrons. (e.g., Cu2+, Fe2+ ) 2. An atom, ion, or molecule with an incomplete octet of electrons can act as an Lewis acid (e.g., BF3, AlF3). 3. Molecules that have multiple bonds between two atoms of different electronegativities (e.g., C ...