Review Package
... 5. Ionic Compounds (Textbook p. 139-146; 148-149) Terminology (ion, cation, anion, ionic charge/combining capacity, valence electron, stable octet, polyatomic ion, binary compound, ternary compound, ionic bond) Draw Bohr-Rutherford diagrams/Lewis Dot structures to show the formation of ionic com ...
... 5. Ionic Compounds (Textbook p. 139-146; 148-149) Terminology (ion, cation, anion, ionic charge/combining capacity, valence electron, stable octet, polyatomic ion, binary compound, ternary compound, ionic bond) Draw Bohr-Rutherford diagrams/Lewis Dot structures to show the formation of ionic com ...
F Practice Test #2 Solutions
... Each of the following multiple choice questions are worth 4 points. Your answers need to be filled in on the Scantron provided. Note: Your Scantrons will not be returned to you, therefore, for your records, you may want to mark your answers on this sheet. On the Scantron you need to fill in your per ...
... Each of the following multiple choice questions are worth 4 points. Your answers need to be filled in on the Scantron provided. Note: Your Scantrons will not be returned to you, therefore, for your records, you may want to mark your answers on this sheet. On the Scantron you need to fill in your per ...
YU-ISSN 0352-5139
... Belgrade, Yugoslavia (Received 12 May 2000) By the application of the Log k pair linearity rule and the Proportionality rule to the previously published log k values for 27 compounds, obtained on diol-silica columns with acetonitrile, methanol and tetrahydrofuran as modifiers, the existence of commo ...
... Belgrade, Yugoslavia (Received 12 May 2000) By the application of the Log k pair linearity rule and the Proportionality rule to the previously published log k values for 27 compounds, obtained on diol-silica columns with acetonitrile, methanol and tetrahydrofuran as modifiers, the existence of commo ...
2C - Edexcel
... (b) The equation for the reaction between hydrogen and chlorine is H2 + Cl2 o 2HCl Different names are used for the product, depending on its state symbol. (i) What are the names used for HCl(g) and HCl(aq)? ...
... (b) The equation for the reaction between hydrogen and chlorine is H2 + Cl2 o 2HCl Different names are used for the product, depending on its state symbol. (i) What are the names used for HCl(g) and HCl(aq)? ...
The "pH Factor"
... Why Should I Be Concerned About My pH Levels? Since most of the body is water-based (making up 50-60% of our total body weight), the pH level has profound effects on all body chemistry, health and disease. An imbalanced pH describes the pH level of the body when it becomes too acidic or too alkaline ...
... Why Should I Be Concerned About My pH Levels? Since most of the body is water-based (making up 50-60% of our total body weight), the pH level has profound effects on all body chemistry, health and disease. An imbalanced pH describes the pH level of the body when it becomes too acidic or too alkaline ...
x - A Level Tuition
... Heat evolved by neutralisation reaction = mc∆T = (vol. of FA1 or FA2 + vol of FA3) x c x ∆T = (50 + 25) x 4.2 x ∆T = 315∆T J ∆Hneutralisation = – 315∆T / amount of water formed = – 315∆T / 0.050 = – 6300∆T J mol-1 ...
... Heat evolved by neutralisation reaction = mc∆T = (vol. of FA1 or FA2 + vol of FA3) x c x ∆T = (50 + 25) x 4.2 x ∆T = 315∆T J ∆Hneutralisation = – 315∆T / amount of water formed = – 315∆T / 0.050 = – 6300∆T J mol-1 ...
Spring 2014 Chem 100 Organic Synthesis and Mechanism
... • Course Goals/Objectives This course is designed to help students build a solid knowledge base of common methods and applications in organic synthesis. Reaction mechanisms are emphasized g chemical reactivity y and p predicting g for understanding reaction outcomes. You are expected to read each a ...
... • Course Goals/Objectives This course is designed to help students build a solid knowledge base of common methods and applications in organic synthesis. Reaction mechanisms are emphasized g chemical reactivity y and p predicting g for understanding reaction outcomes. You are expected to read each a ...
Water
... The region of one pH down, and one pH up of the pKa is called the buffer region. This region is where the Henderson-Hasselbach log factor is in control. As you add more OH-, there less and less deviation from the flat line of pH. This is buffering, one pH until below and one pH until above, the curv ...
... The region of one pH down, and one pH up of the pKa is called the buffer region. This region is where the Henderson-Hasselbach log factor is in control. As you add more OH-, there less and less deviation from the flat line of pH. This is buffering, one pH until below and one pH until above, the curv ...
weak conjugate base
... Note the product of H3O and OH- in any aqueous is constant which means when [OH-] goes up the [H3O] must go down Acidic solution [H+] > [OH-] Basic solution [ H+] < [OH-] Neutral solution [H+] = [OH-] ...
... Note the product of H3O and OH- in any aqueous is constant which means when [OH-] goes up the [H3O] must go down Acidic solution [H+] > [OH-] Basic solution [ H+] < [OH-] Neutral solution [H+] = [OH-] ...
Chapter 12
... Atoms can lose or gains more than one electron. Examples: Mg2+, Fe3+, S2-, and N3A monatomic ion contains only one atom. Mg2+, Fe3+, S2-, Al3+. A polyatomic ion contains more than one atom. OH-, CN-, NH4+. Chemical Formulas are used to express the composition of molecules and ionic compounds in term ...
... Atoms can lose or gains more than one electron. Examples: Mg2+, Fe3+, S2-, and N3A monatomic ion contains only one atom. Mg2+, Fe3+, S2-, Al3+. A polyatomic ion contains more than one atom. OH-, CN-, NH4+. Chemical Formulas are used to express the composition of molecules and ionic compounds in term ...
Chemical Equation Reactions
... 2. Solid calcium reacts with oxygen gas. 3. Solutions of aluminum chloride & sodium carbonate are mixed. 4. Liquid magnesium bromide is decomposed at high temperature. 5. Solid nickel is reacted with aqueous magnesium sulfate. 6. Chlorine gas is reacted with aqueous potassium bromide. 7. Solid magne ...
... 2. Solid calcium reacts with oxygen gas. 3. Solutions of aluminum chloride & sodium carbonate are mixed. 4. Liquid magnesium bromide is decomposed at high temperature. 5. Solid nickel is reacted with aqueous magnesium sulfate. 6. Chlorine gas is reacted with aqueous potassium bromide. 7. Solid magne ...
Ch. 6 - Chemical Bonds I. Why Atoms Combine
... cation first. Change the anion’s ending to -ide. Write the names of polyatomic ions. ...
... cation first. Change the anion’s ending to -ide. Write the names of polyatomic ions. ...
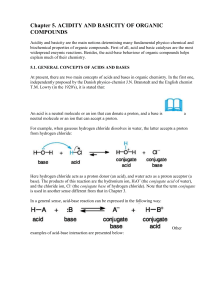
Chapter 5. ACIDITY AND BASICITY OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
... Here hydrogen chloride acts as a proton donor (an acid), and water acts as a proton acceptor (a base). The products of this reaction are the hydronium ion, H3O+ (the conjugate acid of water), and the chloride ion, Cl- (the conjugate base of hydrogen chloride). Note that the term conjugate is used in ...
... Here hydrogen chloride acts as a proton donor (an acid), and water acts as a proton acceptor (a base). The products of this reaction are the hydronium ion, H3O+ (the conjugate acid of water), and the chloride ion, Cl- (the conjugate base of hydrogen chloride). Note that the term conjugate is used in ...
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
... 50 ml of HCl solution has been titrated with 0.1524 M NaOH solution. At the end point, 33.32 ml of NaOH was used in the titration. What is the concentration of the HCl solution? ...
... 50 ml of HCl solution has been titrated with 0.1524 M NaOH solution. At the end point, 33.32 ml of NaOH was used in the titration. What is the concentration of the HCl solution? ...
Solutions, Solubility Rules, and Molarity File
... Solutions • Solutions are defined as homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances. • Aqueous solution – solution in which water is the dissolving medium • The solvent is present in greatest abundance. • All other substances are solutes; they are dissolved in the solvent. – Example: NaCl diss ...
... Solutions • Solutions are defined as homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances. • Aqueous solution – solution in which water is the dissolving medium • The solvent is present in greatest abundance. • All other substances are solutes; they are dissolved in the solvent. – Example: NaCl diss ...
Rate and Equilibrium
... the position of the equilibrium will shift in a direction that tends to reduce that change. Effect of concentration change on equilibrium: If the concentration of a substance involved in equilibrium is artificially increased, the reaction tends to adjust the composition so as to minimize the increas ...
... the position of the equilibrium will shift in a direction that tends to reduce that change. Effect of concentration change on equilibrium: If the concentration of a substance involved in equilibrium is artificially increased, the reaction tends to adjust the composition so as to minimize the increas ...
Nature of Acids and Bases
... ionization of water, which of the following is true? (1) The forward reaction forming ions from water is favored. (2) The concentration of ions in pure water is high. (3) The concentration of hydronium in pure water is higher than the concentration of hydroxide. (4) The concentration of ions in pure ...
... ionization of water, which of the following is true? (1) The forward reaction forming ions from water is favored. (2) The concentration of ions in pure water is high. (3) The concentration of hydronium in pure water is higher than the concentration of hydroxide. (4) The concentration of ions in pure ...
Tutorial 6 Writing Chemical Formulas for Molecular Compounds and
... • Ionic compounds form when metals transfer valence electrons to nonmetals forming cations and anions, respectively. The ratio of cations to anions is always expressed in the simplest whole number ratio k ...
... • Ionic compounds form when metals transfer valence electrons to nonmetals forming cations and anions, respectively. The ratio of cations to anions is always expressed in the simplest whole number ratio k ...
Multiple Choice Practice. A) P B) S C) Cl D) Li E) 1 F 1. Has the
... 67. CH3CSNH2 + H2O CH3CONH2 + H2S. The rate equation for this reaction in dilute acid solution is found to be rate = k[H3O+][CH3CSNH2] All of the following statements about the reaction are true EXCEPT A) Adding H2O increases the reaction rate B) Increasing the temperature increases the reaction r ...
... 67. CH3CSNH2 + H2O CH3CONH2 + H2S. The rate equation for this reaction in dilute acid solution is found to be rate = k[H3O+][CH3CSNH2] All of the following statements about the reaction are true EXCEPT A) Adding H2O increases the reaction rate B) Increasing the temperature increases the reaction r ...
Part I - American Chemical Society
... 43. Which experimental evidence most clearly supports the suggestion that electrons have wave properties? (A) diffraction ...
... 43. Which experimental evidence most clearly supports the suggestion that electrons have wave properties? (A) diffraction ...