Molar Heat of Reaction
... An acid-base neutralization is a chemical reaction in which an acid reacts with a base to form a salt and water Acid + Base → Salt + Water ...
... An acid-base neutralization is a chemical reaction in which an acid reacts with a base to form a salt and water Acid + Base → Salt + Water ...
Soluble salts
... to ‘hydracids’ (e.g. HCl) lacking oxygen. More strictly, the term oxoacid designates a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of one or more hydrogen ions. H2SO4 ...
... to ‘hydracids’ (e.g. HCl) lacking oxygen. More strictly, the term oxoacid designates a compound which contains oxygen, at least one other element, and at least one hydrogen bound to oxygen, and which produces a conjugate base by loss of one or more hydrogen ions. H2SO4 ...
Question 1. Phosgene was used during the World War - IQ
... possible the existence of a molecule Li2, as the molecule H2 exists. (a) Using your understanding on chemical bond, show if it is possible the existence of the molecule Li2. (b) Describe an experiment by which you could verify if such a molecule can exist or not. Question 6. (a) The dissociation ene ...
... possible the existence of a molecule Li2, as the molecule H2 exists. (a) Using your understanding on chemical bond, show if it is possible the existence of the molecule Li2. (b) Describe an experiment by which you could verify if such a molecule can exist or not. Question 6. (a) The dissociation ene ...
Document
... Oxidation Number or State The charge the atom would have in a compound if electrons were completely transferred. Electron Book Keeping Method. 1. Free elements in their standard state have an oxidation number of zero. ...
... Oxidation Number or State The charge the atom would have in a compound if electrons were completely transferred. Electron Book Keeping Method. 1. Free elements in their standard state have an oxidation number of zero. ...
Intermediate 1 Chemistry - Deans Community High School
... Covalent Compounds • Covalent bonds only appear in non-metal compounds like water (H2O) and Carbon dioxide(CO2) • The compounds are also known as molecules and the covalent bonds are very strong between the non-metal atoms. • Between all the molecules there is weak forces holding them together. ...
... Covalent Compounds • Covalent bonds only appear in non-metal compounds like water (H2O) and Carbon dioxide(CO2) • The compounds are also known as molecules and the covalent bonds are very strong between the non-metal atoms. • Between all the molecules there is weak forces holding them together. ...
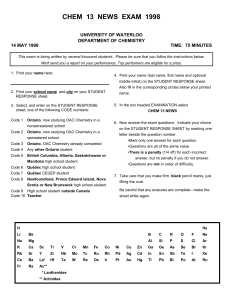
CHEM 13 NEWS EXAM 1998 - University of Waterloo
... middle initial) on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet. Also fill in the corresponding circles below your printed ...
... middle initial) on the STUDENT RESPONSE sheet. Also fill in the corresponding circles below your printed ...
use-2012_review_sheettest_form_c_reactions
... If an ionic compound dissolves in water, it is said to be ________________ and gets the designation of ______________ state of matter in a chemical equation. If an ionic compound does NOT dissolve in water, it is said to be _________________ and will get the designation of ____________________ state ...
... If an ionic compound dissolves in water, it is said to be ________________ and gets the designation of ______________ state of matter in a chemical equation. If an ionic compound does NOT dissolve in water, it is said to be _________________ and will get the designation of ____________________ state ...
Pre-Board Examination2016 Class : XII MM: 70 Subject : Chemistry
... questions and carry 1 mark each, (i) All questions are compulsory (ii) ) Question no . 1 to 5 are short answer questions and carry 1mark each (iii) Question no . 6 to 10 are short answer questions and carry 2 marks each . (iv) Question no . 11 to 22 are also short answer questions and carry 3 marks ...
... questions and carry 1 mark each, (i) All questions are compulsory (ii) ) Question no . 1 to 5 are short answer questions and carry 1mark each (iii) Question no . 6 to 10 are short answer questions and carry 2 marks each . (iv) Question no . 11 to 22 are also short answer questions and carry 3 marks ...
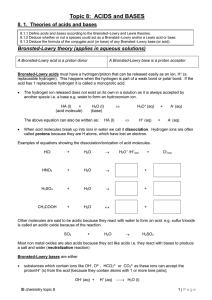
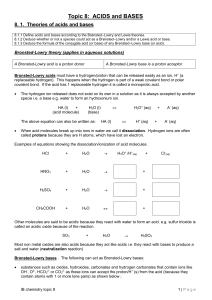
Topic 8: ACIDS and BASES
... Some substances can act as both and they are called amphoteric; what they behave like (either acid or base) depends on the other chemical in the reaction. For instance if the other specie is a stronger acid than our specie in question acts as a base, if the other specie is a stronger base than it wi ...
... Some substances can act as both and they are called amphoteric; what they behave like (either acid or base) depends on the other chemical in the reaction. For instance if the other specie is a stronger acid than our specie in question acts as a base, if the other specie is a stronger base than it wi ...
Topic 8: ACIDS and BASES
... Some substances can act as both and they are called amphoteric; what they behave like (either acid or base) depends on the other chemical in the reaction. For instance if the other specie is a stronger acid than our specie in question acts as a base, if the other specie is a stronger base than it wi ...
... Some substances can act as both and they are called amphoteric; what they behave like (either acid or base) depends on the other chemical in the reaction. For instance if the other specie is a stronger acid than our specie in question acts as a base, if the other specie is a stronger base than it wi ...
Lecture 21 – Cations, Anions and Hydrolysis in
... (water). Metal ions in aqueous solution behave as Lewis acids. The positive charge on the metal ion draws electron density from the O-H bond in the water. This increases the bond's polarity making it easier to break. When the O-H bond breaks, an aqueous proton is released producing an acidic solutio ...
... (water). Metal ions in aqueous solution behave as Lewis acids. The positive charge on the metal ion draws electron density from the O-H bond in the water. This increases the bond's polarity making it easier to break. When the O-H bond breaks, an aqueous proton is released producing an acidic solutio ...
Final Review Answers
... How does each of the following affect the solubility of (a) a solid dissolved in a liquid, and (b) a gas dissolved in a liquid. a. an increase in temperature (a) more collisions between particles causing an increase in dissolving particles (b) decreases solubility, as T increases more dissolved gas ...
... How does each of the following affect the solubility of (a) a solid dissolved in a liquid, and (b) a gas dissolved in a liquid. a. an increase in temperature (a) more collisions between particles causing an increase in dissolving particles (b) decreases solubility, as T increases more dissolved gas ...
Chemistry Section 2
... however, that water is always there. In fact, as you’ll see in the next section, the pH scale ranks solutions based not so much on the acids or bases themselves, but on how those acids or bases influence the equilibrium for the ionization of water. o ...
... however, that water is always there. In fact, as you’ll see in the next section, the pH scale ranks solutions based not so much on the acids or bases themselves, but on how those acids or bases influence the equilibrium for the ionization of water. o ...
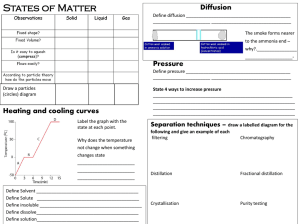
Unit 5 • What Do Atoms Look Like
... great examples of a Brønsted-Lowry acid and base. Arrhenius only dealt with aqueous solutions. When NH3 and HCl meet in the air, a proton (H+) is transferred from the HCl to the NH3. The two resulting ions immediately are attracted to each other to form the solid, NH4Cl(s) which we see as smoke. HCl ...
... great examples of a Brønsted-Lowry acid and base. Arrhenius only dealt with aqueous solutions. When NH3 and HCl meet in the air, a proton (H+) is transferred from the HCl to the NH3. The two resulting ions immediately are attracted to each other to form the solid, NH4Cl(s) which we see as smoke. HCl ...
Participation #1 - Alan`s Chemistry Page
... 1. Nitroglycerin decomposes according to the following equation: 4C3H5N3O9(l) → 6N2(g) + 12CO2(g) + 10H2O(g) + O2(g) a. Calculate the molar masses for nitroglycerin, carbon dioxide, and water. ...
... 1. Nitroglycerin decomposes according to the following equation: 4C3H5N3O9(l) → 6N2(g) + 12CO2(g) + 10H2O(g) + O2(g) a. Calculate the molar masses for nitroglycerin, carbon dioxide, and water. ...