
Acids and bases
... Non-aqueous solvents that are good proton acceptors (e.g.NH3) encourage acids to ionize in them. In a basic solvent, all acids are strong. The solvent is said to exhibit a levelling effect on the acid, since the strength of the dissolved acid cannot exceed that of the protonated solvent. In ...
... Non-aqueous solvents that are good proton acceptors (e.g.NH3) encourage acids to ionize in them. In a basic solvent, all acids are strong. The solvent is said to exhibit a levelling effect on the acid, since the strength of the dissolved acid cannot exceed that of the protonated solvent. In ...
2nd Semester Final Review
... 21. What are the values of STP? What is the meaning behind STP? 22. What is the lowest temperature possible? What is it called? Acids and Bases 23. What are the major observable properties of acids, bases, and salt solutions? 24. What gas is produced when an acid reacts with a metal? 25. What is the ...
... 21. What are the values of STP? What is the meaning behind STP? 22. What is the lowest temperature possible? What is it called? Acids and Bases 23. What are the major observable properties of acids, bases, and salt solutions? 24. What gas is produced when an acid reacts with a metal? 25. What is the ...
Chemical laboratories Dipl.-Ing.(FH) Giovanna
... Sugar and lactic acid analysis by HPLC Ultimate 3000 from Dionex ...
... Sugar and lactic acid analysis by HPLC Ultimate 3000 from Dionex ...
Chemistry Chapter 4 Vocabulary 1. Solution 2. Solute 3. Solvent 4
... the amount of solute that is dissolved in a solvent at a particular temperature a solution having a low concentration of solute a solution containing the maximum amount of a solute that can be dissolved in a solvent at a given temperature a substance that can donate a proton to another substance tha ...
... the amount of solute that is dissolved in a solvent at a particular temperature a solution having a low concentration of solute a solution containing the maximum amount of a solute that can be dissolved in a solvent at a given temperature a substance that can donate a proton to another substance tha ...
Chem 1A Practice Final
... volume. Considering only N2 and O2 in air, calculate the density of air at 1.0 atm, 25 oC. a) 0.590 g/L b) 1.18 g/L c) 2.46 g/L d) 14.1 g/L e) None of the above. 24. What kind of gases have low values of a in the van der Waals equation? a. Gases which have no affinity of each other b. Gases with a l ...
... volume. Considering only N2 and O2 in air, calculate the density of air at 1.0 atm, 25 oC. a) 0.590 g/L b) 1.18 g/L c) 2.46 g/L d) 14.1 g/L e) None of the above. 24. What kind of gases have low values of a in the van der Waals equation? a. Gases which have no affinity of each other b. Gases with a l ...
Types of Reactions and Solution Chemistry
... In 1884 Svante Arrhenius proposed the first theoretical model for acids and bases. Prior to that time, these chemically opposite substances were described in properties such as their taste; their effects on metals, carbonates, and dyes (called indicators); their feel to the touch, and their ability ...
... In 1884 Svante Arrhenius proposed the first theoretical model for acids and bases. Prior to that time, these chemically opposite substances were described in properties such as their taste; their effects on metals, carbonates, and dyes (called indicators); their feel to the touch, and their ability ...
The pH Scale…
... pH is the scale that tells you whether a substance is acidic, basic, or neutral. pH=“p” stands for power and “H” stands for hydrogen. The values correspond to the concentration of the hydronium ions. ...
... pH is the scale that tells you whether a substance is acidic, basic, or neutral. pH=“p” stands for power and “H” stands for hydrogen. The values correspond to the concentration of the hydronium ions. ...
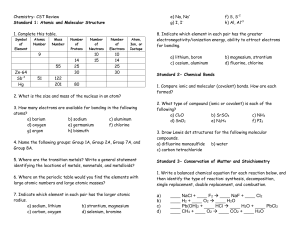
Chemistry- CST Review
... 8. If a sample of gas occupies 6.55 L at 300 °C, what will be its volume at 25 °C if the pressure does not change? 9. A gas at 790 mm Hg and 25 °C occupies a container with an initial volume of 1.20 L. By changing the volume, the pressure of the gas increases to 1500 mm Hg as the temperature is rais ...
... 8. If a sample of gas occupies 6.55 L at 300 °C, what will be its volume at 25 °C if the pressure does not change? 9. A gas at 790 mm Hg and 25 °C occupies a container with an initial volume of 1.20 L. By changing the volume, the pressure of the gas increases to 1500 mm Hg as the temperature is rais ...
Chem. 31 * 9/15 Lecture
... – Example question: An unknown H2SO4 solution is pipeted (25.00 mL) into a flask. It is titrated with KOH until reaching an endpoint (where the equivalence point is observed). It requires 39.1 mL of 0.150 M KOH. What is the concentration of H2SO4 in the unknown ...
... – Example question: An unknown H2SO4 solution is pipeted (25.00 mL) into a flask. It is titrated with KOH until reaching an endpoint (where the equivalence point is observed). It requires 39.1 mL of 0.150 M KOH. What is the concentration of H2SO4 in the unknown ...
+ [H 2 CO 3 ]
... – quick – easy – accurate – portable Indicators – titrations phenolphthalein: pink colourless below pH 8.3 methyl orange: red yellow above pH 4.3 ...
... – quick – easy – accurate – portable Indicators – titrations phenolphthalein: pink colourless below pH 8.3 methyl orange: red yellow above pH 4.3 ...
A-level Paper 1 Practice Paper 8 - A
... Use data from part (a)(ii) and the entropy data given below to calculate the lowest temperature at which the following reaction becomes feasible. BaCl2(s) → Ba(s) + Cl2(g) ...
... Use data from part (a)(ii) and the entropy data given below to calculate the lowest temperature at which the following reaction becomes feasible. BaCl2(s) → Ba(s) + Cl2(g) ...
Final Exam Review – Free Response Section Name: 1. A sample of
... 3. All binary compounds of the halogens (other than F) with metals are soluble, except those of Ag, Hg(I), and Pb. Pb halides are soluble in hot water.) 4. All sulfates are soluble, except those of barium, strontium, calcium, lead, silver, and mercury (I). The latter three are slightly ...
... 3. All binary compounds of the halogens (other than F) with metals are soluble, except those of Ag, Hg(I), and Pb. Pb halides are soluble in hot water.) 4. All sulfates are soluble, except those of barium, strontium, calcium, lead, silver, and mercury (I). The latter three are slightly ...
File
... 58. A 160. mg sample of NaOH, (MM = 40.0 g) is dissolved to prepare an aqueous solution with a volume of 200. mL. What is the molarity of sodium hydroxide in 40. mL of this solution? A) 0.00400 M B) 0.0160 M C) 0.0200 M D) 0.0800 M E) 0.100 M 59. The ionization constant, Kb, of the base HONH2 is 1. ...
... 58. A 160. mg sample of NaOH, (MM = 40.0 g) is dissolved to prepare an aqueous solution with a volume of 200. mL. What is the molarity of sodium hydroxide in 40. mL of this solution? A) 0.00400 M B) 0.0160 M C) 0.0200 M D) 0.0800 M E) 0.100 M 59. The ionization constant, Kb, of the base HONH2 is 1. ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry 2 ed William H. Brown
... Copyright © 2000 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... Copyright © 2000 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
CHM_101_ASSIGNMENT_COPY_1_2
... 7. Differentiate between ionic and covalent compounds. 8. (a) 3.0g of 2-hydroxybenzoic acid is reflux with 6.5g of ethanoic anhydride to produce aspirin and ethanoic acid. (I) Which one of the two reagents is the limiting reagent? (II) How much of excess reagent (in grams) is left at the end of the ...
... 7. Differentiate between ionic and covalent compounds. 8. (a) 3.0g of 2-hydroxybenzoic acid is reflux with 6.5g of ethanoic anhydride to produce aspirin and ethanoic acid. (I) Which one of the two reagents is the limiting reagent? (II) How much of excess reagent (in grams) is left at the end of the ...















![+ [H 2 CO 3 ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001130480_1-81612c04e4e5fb35027131a7b7feb9b6-300x300.png)






