LECTURE_Solutions2013(1)
... Dissolving Covalent Compounds • C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) • NO dissociation because NO ions • Sucrose dissolves in water because sugar is polar (-OH group), but dissociation does not occur. Sucrose molecules are simply separated from each other. No ions are formed ...
... Dissolving Covalent Compounds • C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) • NO dissociation because NO ions • Sucrose dissolves in water because sugar is polar (-OH group), but dissociation does not occur. Sucrose molecules are simply separated from each other. No ions are formed ...
File
... 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge on the ion. Example: Mg2+ has the oxidation number of +2. 3. The more electronegative element in a binary compound is assigned the number equal to the charge it would have if it were an ion. 4. The oxidation number of fluorine in a compoun ...
... 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge on the ion. Example: Mg2+ has the oxidation number of +2. 3. The more electronegative element in a binary compound is assigned the number equal to the charge it would have if it were an ion. 4. The oxidation number of fluorine in a compoun ...
Technical Data Sheet (E
... E-Phos 660 is a calcium-modified formula which produces fine-grained crystalline coatings on iron and steel with a medium coating weight of 600 mg/ft2. The zinc phosphate coating remains fine-grained regardless of the cleaning method used prior to application. It can be applied by either immersion o ...
... E-Phos 660 is a calcium-modified formula which produces fine-grained crystalline coatings on iron and steel with a medium coating weight of 600 mg/ft2. The zinc phosphate coating remains fine-grained regardless of the cleaning method used prior to application. It can be applied by either immersion o ...
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND SOLUTION CHEMISTRY
... 6. The recombination produces _________, which is soluble so it remains _____ and _____. These species are spectator ions. 7. The _____ and the _____ cannot coexist in solution because water is a nonelectrolyte. ...
... 6. The recombination produces _________, which is soluble so it remains _____ and _____. These species are spectator ions. 7. The _____ and the _____ cannot coexist in solution because water is a nonelectrolyte. ...
Challenge - ChemistryIBWYA
... they react with the solvent to form ions. Instead of a simple dissociation, the chemical reaction produces the charged particles. A solution of hydrochloric acid in water is one such example: Substances that tend to ionize completely include strong acids, strong bases, and ionic compounds (salts). S ...
... they react with the solvent to form ions. Instead of a simple dissociation, the chemical reaction produces the charged particles. A solution of hydrochloric acid in water is one such example: Substances that tend to ionize completely include strong acids, strong bases, and ionic compounds (salts). S ...
honors final key
... 17. Convert the following a. 4.58 mol to particles of Al = 2.76x1024 b. 4.58 mol to grams of Al = 124g c. 901.49 g to particles of Carbon dioxide = 1.23x 1025 d. 901.49 g to L of carbon dioxide = 458.9 18. Define molar mass. The mass of a mole of a substance, equal to the atomic mass in grams 19. Gi ...
... 17. Convert the following a. 4.58 mol to particles of Al = 2.76x1024 b. 4.58 mol to grams of Al = 124g c. 901.49 g to particles of Carbon dioxide = 1.23x 1025 d. 901.49 g to L of carbon dioxide = 458.9 18. Define molar mass. The mass of a mole of a substance, equal to the atomic mass in grams 19. Gi ...
Intro to Soln Stoich
... Water is the “universal solvent” ◦ O-H bonds are covalent, e- not shared equally ◦ Oxygen has a slight negative, hydrogen slight positive Polar molecule Oxygen has a strong attraction to cations, hydrogen to anions ...
... Water is the “universal solvent” ◦ O-H bonds are covalent, e- not shared equally ◦ Oxygen has a slight negative, hydrogen slight positive Polar molecule Oxygen has a strong attraction to cations, hydrogen to anions ...
AP Review Chp 1 and Chp 2 Wed 10/9/2013 1. Near room
... A copper(II) sulfate solution is mixed by dissolving 25.000 g of copper(II) sulfate, and then it is treated with an excess of magnesium metal. The mass of copper collected is 8.786 g after drying. Calculate the percent yield of copper. II) In a particular experiment, 225 g of phosphorus, P4, reacted ...
... A copper(II) sulfate solution is mixed by dissolving 25.000 g of copper(II) sulfate, and then it is treated with an excess of magnesium metal. The mass of copper collected is 8.786 g after drying. Calculate the percent yield of copper. II) In a particular experiment, 225 g of phosphorus, P4, reacted ...
Second Semester Final Review Guide
... atoms and not compounds!) a. SiO2 + 2 C → Si + 2 CO ______________________________________ b. 2 Fe + 3 F2 → 2 FeF3 _______________________________________ 7. Write the reducing half reaction for the following equations. (Remember this involves single atoms and not compounds!) a. 2 H2SO4 + C → CO2 + ...
... atoms and not compounds!) a. SiO2 + 2 C → Si + 2 CO ______________________________________ b. 2 Fe + 3 F2 → 2 FeF3 _______________________________________ 7. Write the reducing half reaction for the following equations. (Remember this involves single atoms and not compounds!) a. 2 H2SO4 + C → CO2 + ...
makeup2
... 58. A solution of a non-electrolyte, x, contains 84 grams of x per kilogram of water and freezes at -1.46°C. What is the molecular weight of x? (Kf = 1.86) (A) 84 x 1.86 x 1.46 = 222 g/mol (B) 84 x (1.86 / 1.46) = 107 g/mol (C) 84 x (1.46 / 1.86) = 66 g/mol (D) 1.46 x (1.86 / 84) = 0.032 g/mol 59. ...
... 58. A solution of a non-electrolyte, x, contains 84 grams of x per kilogram of water and freezes at -1.46°C. What is the molecular weight of x? (Kf = 1.86) (A) 84 x 1.86 x 1.46 = 222 g/mol (B) 84 x (1.86 / 1.46) = 107 g/mol (C) 84 x (1.46 / 1.86) = 66 g/mol (D) 1.46 x (1.86 / 84) = 0.032 g/mol 59. ...
ELECTROLYTES: NONELECTROLYTES
... conduct a current rather than re-forming a solid. The reason for this is the polar nature of the water molecule… Positive ions associate with the negative end of the water dipole (oxygen). Negative ions associate with the positive end of the water dipole (hydrogen). ...
... conduct a current rather than re-forming a solid. The reason for this is the polar nature of the water molecule… Positive ions associate with the negative end of the water dipole (oxygen). Negative ions associate with the positive end of the water dipole (hydrogen). ...
chemistry 103 - chem.uwec.edu
... containing 1.0 M CH3CO2H and 1.0 M NaCH3CO2. What is the pH of the buffer after the addition of 0.10 moles of gaseous HCl to 1.00 liter of the buffer solution? The Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 x 10-5. Because acetic acid is a weak acid, we can ignore the small amount of dissociation and assume at equil ...
... containing 1.0 M CH3CO2H and 1.0 M NaCH3CO2. What is the pH of the buffer after the addition of 0.10 moles of gaseous HCl to 1.00 liter of the buffer solution? The Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 x 10-5. Because acetic acid is a weak acid, we can ignore the small amount of dissociation and assume at equil ...
Chem 1411 Chapt2
... ‘ide’. Also, one uses prefixes (mono, di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, hepta, octa, nona, deca) to indicate the number of atoms of each element. If there is only one atom of the more electropositive element, do not use the prefix ‘mono’. Example: CO carbon monoxide; CO2 carbon dioxide NO2 nitrogen dioxi ...
... ‘ide’. Also, one uses prefixes (mono, di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, hepta, octa, nona, deca) to indicate the number of atoms of each element. If there is only one atom of the more electropositive element, do not use the prefix ‘mono’. Example: CO carbon monoxide; CO2 carbon dioxide NO2 nitrogen dioxi ...
+ H 2 O(l) - Cloudfront.net
... predict reactions • Activity series can be used to predict reactions between metals and metal salts or acids. ...
... predict reactions • Activity series can be used to predict reactions between metals and metal salts or acids. ...
Water Chemistry 3
... IAP = KSP SI = 0 (-0.2 < SI < 0.2) water is saturated with the mineral IAP < KSP SI < 0 water is undersaturated with the mineral Reaction is proceeding from left to right (dissolution) IAP > KSP SI > 0 water is supersaturated with the mineral Reaction is proceeding from right to left (precipitation) ...
... IAP = KSP SI = 0 (-0.2 < SI < 0.2) water is saturated with the mineral IAP < KSP SI < 0 water is undersaturated with the mineral Reaction is proceeding from left to right (dissolution) IAP > KSP SI > 0 water is supersaturated with the mineral Reaction is proceeding from right to left (precipitation) ...
Barnard Castle School Chemistry Department
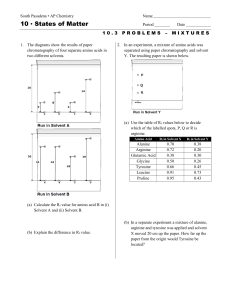
... example of a mixture is air, which contains elements such as oxygen and nitrogen and compounds such as carbon dioxide. Mixtures can contain any amount of the substances in it. The substances in a mixture behave the same way as they would on their own. It is easier to separate the substances in a mix ...
... example of a mixture is air, which contains elements such as oxygen and nitrogen and compounds such as carbon dioxide. Mixtures can contain any amount of the substances in it. The substances in a mixture behave the same way as they would on their own. It is easier to separate the substances in a mix ...
Oxidation-reduction reactions and electrochemistry
... This unit is primarily for science students who intend to major in Chemistry or proceed with Level 2 chemistry major units. During the semester the integrated laboratory/lecture programme is concerned with physical and inorganic chemistry. Content includes categories of chemical reaction in aqueous ...
... This unit is primarily for science students who intend to major in Chemistry or proceed with Level 2 chemistry major units. During the semester the integrated laboratory/lecture programme is concerned with physical and inorganic chemistry. Content includes categories of chemical reaction in aqueous ...