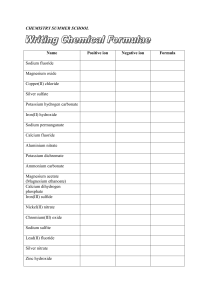
Percent Ionization
... Acid dissociation - acid reacts with water to produce hydronium ion and the conjugate base ion Consider acetic acid HC2H3O2 (aq) + H2O (l) H3O+ + C2H3O2- (aq) - since acetic acid is weak electrolyte, it ionizes only to small amount (about 1% or less/partially ionized) Note: this is not the same thin ...
... Acid dissociation - acid reacts with water to produce hydronium ion and the conjugate base ion Consider acetic acid HC2H3O2 (aq) + H2O (l) H3O+ + C2H3O2- (aq) - since acetic acid is weak electrolyte, it ionizes only to small amount (about 1% or less/partially ionized) Note: this is not the same thin ...
1 - KCSE Online
... (g) (i) Haber process √ 1mk (ii) More of gas X formed √ 1mk lower temperature favours forward reaction √ 1mk in an exothermic reaction . ...
... (g) (i) Haber process √ 1mk (ii) More of gas X formed √ 1mk lower temperature favours forward reaction √ 1mk in an exothermic reaction . ...
CHEMISTRY
... (3) +, +, (4) -,+,- 53. H2(g) +1/2 O2 (g) H298k=-285.8 kJ The molar enthalpy of vapourisation of water at 1 atm and 250C is 44 kJ. The standard enthalpy of formation of 1 mole of water vapour at 250 C is: ...
... (3) +, +, (4) -,+,- 53. H2(g) +1/2 O2 (g) H298k=-285.8 kJ The molar enthalpy of vapourisation of water at 1 atm and 250C is 44 kJ. The standard enthalpy of formation of 1 mole of water vapour at 250 C is: ...
Chemical Reactions: Introduction to Reaction Types
... elements, b) 1 element and 1 binary compound (consisting of 2 elements), or c) 2 binary compounds. The following are examples of combination reactions: The rusting of iron: 4Fe (s) + 3O2 (g) → 2Fe2O3 (s) The formation of one kind of acid rain: SO3 (g) + H2O (l) → H2SO4 (aq) 2. Decomposition: AB → A ...
... elements, b) 1 element and 1 binary compound (consisting of 2 elements), or c) 2 binary compounds. The following are examples of combination reactions: The rusting of iron: 4Fe (s) + 3O2 (g) → 2Fe2O3 (s) The formation of one kind of acid rain: SO3 (g) + H2O (l) → H2SO4 (aq) 2. Decomposition: AB → A ...
Chapter 4 - Aqueous Reactions
... Note that the equation is balanced for both mass and charge!!! ...
... Note that the equation is balanced for both mass and charge!!! ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2H3O2– b) Na+, OH– ...
... double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2H3O2– b) Na+, OH– ...
Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium
... point of the titration • Prior to the equivalence point, the known solution in the flask is in excess, so the pH is closest to its pH • The pH of the equivalence point depends on the pH of the salt solution – equivalence point of neutral salt, pH = 7 – equivalence point of acidic salt, pH < 7 – equi ...
... point of the titration • Prior to the equivalence point, the known solution in the flask is in excess, so the pH is closest to its pH • The pH of the equivalence point depends on the pH of the salt solution – equivalence point of neutral salt, pH = 7 – equivalence point of acidic salt, pH < 7 – equi ...
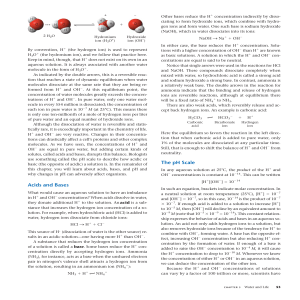
Electrolysis, the Faraday, and Avogadro`s Number
... 1. Determine the exact moles of H2 produced (PV = nRT) under your conditions. 2. Using the elapsed time, determine the amount of charge q in Coulombs that were transferred. 3. Determine the Faraday number F and calculate a percent error. 4. Determine a value for Avogadro’s number using your Faraday ...
... 1. Determine the exact moles of H2 produced (PV = nRT) under your conditions. 2. Using the elapsed time, determine the amount of charge q in Coulombs that were transferred. 3. Determine the Faraday number F and calculate a percent error. 4. Determine a value for Avogadro’s number using your Faraday ...
Acids and Bases The pH Scale
... aqueous solution. It is always associated with another water molecule in the form of H3O!. As indicated by the double arrows, this is a reversible reaction that reaches a state of dynamic equilibrium when water molecules dissociate at the same rate that they are being reformed from H! and OH". At th ...
... aqueous solution. It is always associated with another water molecule in the form of H3O!. As indicated by the double arrows, this is a reversible reaction that reaches a state of dynamic equilibrium when water molecules dissociate at the same rate that they are being reformed from H! and OH". At th ...
Equilibrium Review worksheet
... In a rigid 1.00 L laboratory reaction vessel, a technician places 1.00 mol of each of the four substances involved in this equilibrium. The vessel is heated to 650 °C. Determine the equilibrium amount concentrations of each substance, organizing your values in an ICE table. (Hint: use the value of K ...
... In a rigid 1.00 L laboratory reaction vessel, a technician places 1.00 mol of each of the four substances involved in this equilibrium. The vessel is heated to 650 °C. Determine the equilibrium amount concentrations of each substance, organizing your values in an ICE table. (Hint: use the value of K ...
Solutions, Acids, and Bases
... temperature is said to be saturated. Unsaturated = contains less solute than it can possibly hold Supersaturated = a solution that holds more solute than it should at a given temperature. ...
... temperature is said to be saturated. Unsaturated = contains less solute than it can possibly hold Supersaturated = a solution that holds more solute than it should at a given temperature. ...
Word Pro
... in mol.L–1. What volume of the concentrated sulfuric acid would be required to make 2.50 litres of a 3.0 mol.L–1 solution of the bench acid? What is the mass of the volume of the acid calculated in (b)? Calculate the concentration in mol.L–1 of a sodium hydroxide solution 33.45 mL of which neutraliz ...
... in mol.L–1. What volume of the concentrated sulfuric acid would be required to make 2.50 litres of a 3.0 mol.L–1 solution of the bench acid? What is the mass of the volume of the acid calculated in (b)? Calculate the concentration in mol.L–1 of a sodium hydroxide solution 33.45 mL of which neutraliz ...
Water Kit pH Lesson Teacher Key
... • Describe and produce a physical representation of the dissociation of a strong acid and a strong base. • Associate a high hydronium ion (H3O+) concentration with low pH and a high hydroxide ion (OH-) concentration with a high pH. • Demonstrate how the structure of an amino acid is affected by t ...
... • Describe and produce a physical representation of the dissociation of a strong acid and a strong base. • Associate a high hydronium ion (H3O+) concentration with low pH and a high hydroxide ion (OH-) concentration with a high pH. • Demonstrate how the structure of an amino acid is affected by t ...
CHEM 101 1st Major (Term 161)
... A) Chemical changes always produce substances different from the starting materials. B) Chemical changes provide the only valid basis for identification of a substance. C) Chemical changes are easily reversed by altering the temperature of the system. D) Chemical changes are always associated with e ...
... A) Chemical changes always produce substances different from the starting materials. B) Chemical changes provide the only valid basis for identification of a substance. C) Chemical changes are easily reversed by altering the temperature of the system. D) Chemical changes are always associated with e ...
Last 4 Digits of USC ID:____ ____ ____ ____ Dr.
... 7. (10 pt) What pH must be maintained by a buffer solution so that no more than 0.010% of the Mg2+ present in 0.360 M MgCl2 (aq) remains in solution following precipitation of Mg(OH)2 (s)? Ksp for Mg(OH)2 = 8.9 x 10-12. ...
... 7. (10 pt) What pH must be maintained by a buffer solution so that no more than 0.010% of the Mg2+ present in 0.360 M MgCl2 (aq) remains in solution following precipitation of Mg(OH)2 (s)? Ksp for Mg(OH)2 = 8.9 x 10-12. ...
Acid Spill - Rosshall Academy
... C. An acid that has been neutralised by an alkali D. An acid with the hydrogen ions replaced by ammonium ions 17 The salts formed by nitric acid are called A. chlorides B. ethanoates C. nitrates D. sulphates 18 In the reaction between nitric acid and zinc oxide, one of the products is zinc nitrate, ...
... C. An acid that has been neutralised by an alkali D. An acid with the hydrogen ions replaced by ammonium ions 17 The salts formed by nitric acid are called A. chlorides B. ethanoates C. nitrates D. sulphates 18 In the reaction between nitric acid and zinc oxide, one of the products is zinc nitrate, ...