Helpful PPT on Atoms and Bonding
... Van der Waals Forces • Van der Waals Forces Not all electrons are shared equally when bonds are formed When sharing is unequal, one end of a molecule may be slightly more positive or negative than the other A slight attraction between molecules can develop because of oppositely charged ...
... Van der Waals Forces • Van der Waals Forces Not all electrons are shared equally when bonds are formed When sharing is unequal, one end of a molecule may be slightly more positive or negative than the other A slight attraction between molecules can develop because of oppositely charged ...
EXPLODING BOSE-EINSTEIN CONDENSATES AND - if
... parallel to B, which leads to an effective spin one boson particle as the one described above, having an effective mass as that of neutron mn . Thus, even assuming temperatures of ∼ 108 K, since mn /T ∼ 105 , the system must be considered as highly degenerate, that is, below the critical temperature ...
... parallel to B, which leads to an effective spin one boson particle as the one described above, having an effective mass as that of neutron mn . Thus, even assuming temperatures of ∼ 108 K, since mn /T ∼ 105 , the system must be considered as highly degenerate, that is, below the critical temperature ...
CHAPTER 7 READING GUIDE – IONIC COMPOUNDS AND METALS
... 30. Because a polyatomic ion exists as a unit, never change ________________ of the atoms within the ion. 31. If more than one polyatomic ion is needed, place _____________________ around the ion and write the appropriate subscript outside the parenthesis. 32. ___________________ often form lattices ...
... 30. Because a polyatomic ion exists as a unit, never change ________________ of the atoms within the ion. 31. If more than one polyatomic ion is needed, place _____________________ around the ion and write the appropriate subscript outside the parenthesis. 32. ___________________ often form lattices ...
Science Flipbook 4
... condensation ---------------precipitation ---------------weather ---------------meteorologist ---------------barometer ---------------condensation ---------------precipitation ---------------weather ---------------meteorologist ---------------barometer ...
... condensation ---------------precipitation ---------------weather ---------------meteorologist ---------------barometer ---------------condensation ---------------precipitation ---------------weather ---------------meteorologist ---------------barometer ...
E3060: Magnetic Susceptibility of a Ring
... (2) As χ is a negative constant, it creates a magnetic field opposing the external one and the energy levels rise as a quadratic function of B. (3) The presence of the barrier will weaken the current thus reducing the diamagnetic effect. In the presence of an infinite barrier, that is a disconnected ...
... (2) As χ is a negative constant, it creates a magnetic field opposing the external one and the energy levels rise as a quadratic function of B. (3) The presence of the barrier will weaken the current thus reducing the diamagnetic effect. In the presence of an infinite barrier, that is a disconnected ...
Pure substances
... − Solids have definite volume & definite shape o Particles are limited in their movement and packed close together − Liquids have definite volume but not definite ...
... − Solids have definite volume & definite shape o Particles are limited in their movement and packed close together − Liquids have definite volume but not definite ...
Lecture Notes 1 - Rutgers University
... Gas – atoms or molecules are far apart and moving very fast. Liquid – particles are more closely packed and still moving relatively fast. Solid – held tightly together, usually in definite arrangements, wiggle (vibrate) only slowly in their fixed positions. ...
... Gas – atoms or molecules are far apart and moving very fast. Liquid – particles are more closely packed and still moving relatively fast. Solid – held tightly together, usually in definite arrangements, wiggle (vibrate) only slowly in their fixed positions. ...
Midterm Review Sheet
... 3. Law of Multiple Proportions (Dalton) - if two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of the second element that combine with a fixed mass of the first element are in ratios of small whole numbers. 4. Aufbau Principle - the rule that an electron occupies the lowest energy ...
... 3. Law of Multiple Proportions (Dalton) - if two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of the second element that combine with a fixed mass of the first element are in ratios of small whole numbers. 4. Aufbau Principle - the rule that an electron occupies the lowest energy ...
Tue_10.00-Cadez
... entropy than that of the electrically neutral state at the same energy , many local entropy maxima generate states that are more probable than the state of local charge neutrality. ...
... entropy than that of the electrically neutral state at the same energy , many local entropy maxima generate states that are more probable than the state of local charge neutrality. ...
Change of state - Mrs. Coyle`s College Chemistry
... Molar heats of fusion are generally much smaller than molar heats of vaporization (liquid molecules are packed closer together and more energy need to rearrange from a solid to liquid) ...
... Molar heats of fusion are generally much smaller than molar heats of vaporization (liquid molecules are packed closer together and more energy need to rearrange from a solid to liquid) ...
Final Review Sheet Answers (the 6 page packet)
... 12. Is used to explain why the boiling point of HF is greater than the boiling point of HBr = (A) 14. Is used to explain the fact that the carbon-to-carbon bonds in benzene, C6H6, are identical = (D) Explain each of the following in terms of atomic and molecular structures and/or intermolecular forc ...
... 12. Is used to explain why the boiling point of HF is greater than the boiling point of HBr = (A) 14. Is used to explain the fact that the carbon-to-carbon bonds in benzene, C6H6, are identical = (D) Explain each of the following in terms of atomic and molecular structures and/or intermolecular forc ...
Non-thermal atmospheric plasma treatment in liquid media
... Among the different types of available plasma discharges, we have focused our attention on the development of a dielectric barrier discharge reactor applied to a liquid phase processing. To determine the effects of different chemical characteristics (nature of the gas and solvent) and electrical (vo ...
... Among the different types of available plasma discharges, we have focused our attention on the development of a dielectric barrier discharge reactor applied to a liquid phase processing. To determine the effects of different chemical characteristics (nature of the gas and solvent) and electrical (vo ...
CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER
... In heterogeneous mixtures the distribution of the particles is not uniform; in consequence, the composition is not the same at all points. For example: the mixture of sulphur and iron filings. ...
... In heterogeneous mixtures the distribution of the particles is not uniform; in consequence, the composition is not the same at all points. For example: the mixture of sulphur and iron filings. ...
Matter_Properties_Change
... and carefully filled with pennies. If each penny has a mass of 2.50 g, how many pennies can be added to the boat before it sinks? ...
... and carefully filled with pennies. If each penny has a mass of 2.50 g, how many pennies can be added to the boat before it sinks? ...
Units of Measurement
... – the ratio by mass of the elements in a chemical compound is always the same, regardless of the source of the compound. – The law of constant composition can be used to distinguish between compounds and mixtures of elements: – Compounds have a constant composition; mixtures do not. – Water is alway ...
... – the ratio by mass of the elements in a chemical compound is always the same, regardless of the source of the compound. – The law of constant composition can be used to distinguish between compounds and mixtures of elements: – Compounds have a constant composition; mixtures do not. – Water is alway ...
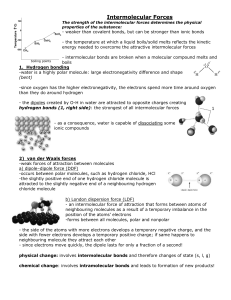
Intermolecular Forces
... The strength of the intermolecular forces determines the physical properties of the substance: ...
... The strength of the intermolecular forces determines the physical properties of the substance: ...
Introducao - Instituto de Física / UFRJ
... 1987 J. G. Bednorz e K. "for their important breakthrough in the discovery of A. Müller superconductivity in ceramic materials". 2003 A. A. Abrikosov, "for pioneering contributions to the theory of V. L. Ginzburg e superconductors and superfluids" A. J. Leggett ...
... 1987 J. G. Bednorz e K. "for their important breakthrough in the discovery of A. Müller superconductivity in ceramic materials". 2003 A. A. Abrikosov, "for pioneering contributions to the theory of V. L. Ginzburg e superconductors and superfluids" A. J. Leggett ...
classification of matter - St. Thomas the Apostle School
... •Physical Property- characteristics of a material which can be observed without changing the identity of the substance in the material. ; examples include color, shape, size, melting point, and ...
... •Physical Property- characteristics of a material which can be observed without changing the identity of the substance in the material. ; examples include color, shape, size, melting point, and ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).