* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chem 11, Notes – Unit 3 – Properties of Matter
Thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Franck–Condon principle wikipedia , lookup
Vapor–liquid equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
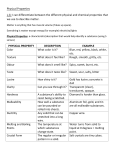
Chemistry 11 Properties of Substances Definitions in Science What is the difference between a hypothesis, a theory, and a law? • A hypothesis is a statement that is unproven that is yet to be tested • A theory is a set of hypotheses that come from observations from the natural world o A theory has been repeatedly tested and is widely accepted explains phenomena • A law will state the results of experiments and state what will happen in specific situations o A law will not explain phenomena What is the difference between an observation and an interpretation? • When you observe, you are using your senses to collect data • When you make an interpretation, you are putting meaning to your observations Chemistry 11 Properties of Substances Physical Properties of Matter What is the difference between a physical and chemical property? • A physical property of a pure substance is anything that can be observed without changing the identity of the substance o An intensive physical property depends upon the nature of the substance o An extensive physical property depends on the amount of substance present • A chemical property is a characteristic which is exhibited as one substance is chemically transformed into another What is matter made up of? • Matter consists of three states: o Solid – particles that are very ordered and are not able to compress o Liquid – particles with greater kinetic energy than solids and are not able to compress Chemistry 11 Properties of Substances o Gas – particles with wide separation and are able to compress How can we classify matter? • There are two classification schemes o Classification by phase see Hebden p. 50 o Classification by composition see Classification of Matter handout How can we separate a mixture? • We look at the property of each substance and use those properties to separate substances o Hand separation/filtration particle size o Evaporation/distillation boiling point o Solvent extraction/recrystallization differing solubilities o Gravity separation density o Chromatography differing solubilities Chemistry 11 Properties of Substances Phase Change Diagrams What happens when a substance goes through a physical change? • In a chemical change, new substances are formed • In a physical change, the phase of a substance changes • When a substance changes phase, energy is added (heating) or removed (cooling) • When a substance cools, the substance exhibits this behaviour Temperature g l s Time Chemistry 11 Properties of Substances On the sloping portion of the graph energy is removed from the substance as it cools • On the plateaus energy removed is used to change phase so temperature does not decrease • On the plateau portions, the substance is in transition phase between phases • What happens to the molecules through a phase change? • Molecules are constantly in motion • As a substance is heated, the amount of energy present in the molecules increase • The three types of kinetic energy a molecule can possess are o Rotational energy – energy which causes a molecule to rotate about an axis (frisbee) o Vibrational energy – energy which causes the length of a bond to change (slinky toy) o Translational energy – energy which causes a molecule to move about in space (thrown ball) Chemistry 11 Properties of Substances • When a substance is heated, translational energy causes bonds to break which hold a substance together • As a substance is continually heated, all three types of energy increase, but it is the increase in translational energy that allows for a phase change Chemistry 11 Properties of Substances What occurs at the plateaus? • When a substance is being heated or cooled, there is a part of the curve that plateaus • These plateaus indicates a constant temperature where an intensive property of the substance is displayed • Boiling point: the temperature where a substance changes from a liquid to a gas • Freezing point: the temperature where a substance changes from a liquid to a solid • Melting point: the temperature where a substance changes from solid to a liquid Note: these changes and properties are applicable only to physical changes a chemical change occurs when a new substance with new properties results Physical change: water is heated from liquid form to form steam Chemical change: water is electrolysed and separated into oxygen gas and hydrogen gas