HW4 - SMU Physics
... Beginning in 1906, Ernest Rutherford carried out a famous series of experiments at McGill University in which he bombarded thin gold foil with alpha particles having a mass of 6.68×10−27 kg and a charge of +2e. Most of the particles whizzed right through the foil, some were slightly deflected, and a ...
... Beginning in 1906, Ernest Rutherford carried out a famous series of experiments at McGill University in which he bombarded thin gold foil with alpha particles having a mass of 6.68×10−27 kg and a charge of +2e. Most of the particles whizzed right through the foil, some were slightly deflected, and a ...
Chapter 2- alternate assignment for Changes Matters Lab
... 18. Applying Concepts Develop a set of questions that would be useful when identifying an unknown substance. The substance may be a liquid, a gas, or a solid. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _____________ ...
... 18. Applying Concepts Develop a set of questions that would be useful when identifying an unknown substance. The substance may be a liquid, a gas, or a solid. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _____________ ...
Lecture I
... • The very low critical pressure and temperature of helium, reflecting the very small intermolecular attractions of this atom. • Tc of the noble gas elements increases with atomic number. • Hydrogen gas cannot be liquified above 33 K; this poses a major difficulty in the use of hydrogen as an automo ...
... • The very low critical pressure and temperature of helium, reflecting the very small intermolecular attractions of this atom. • Tc of the noble gas elements increases with atomic number. • Hydrogen gas cannot be liquified above 33 K; this poses a major difficulty in the use of hydrogen as an automo ...
IB 1 CHEMISTRY
... The SI (Systeme International d´Unités) system has seven base units. All the other units are derived from them. The gram was originally defined in 1795 as the mass of one cubic centimeter of water at 4 °C, making the kilogram equal to the mass of one liter of water. The prototype kilogram, manufactu ...
... The SI (Systeme International d´Unités) system has seven base units. All the other units are derived from them. The gram was originally defined in 1795 as the mass of one cubic centimeter of water at 4 °C, making the kilogram equal to the mass of one liter of water. The prototype kilogram, manufactu ...
The Atomic Zoo
... Atomic nuclei are hard to hit After J.J. Thomson had discovered the electron in 1896, people thought that the negative electrons were equally distributed within the corresponding positive charge in the atom – like currants in a pudding. However, in 1909, E. Rutherford bombarded thin gold foil with a ...
... Atomic nuclei are hard to hit After J.J. Thomson had discovered the electron in 1896, people thought that the negative electrons were equally distributed within the corresponding positive charge in the atom – like currants in a pudding. However, in 1909, E. Rutherford bombarded thin gold foil with a ...
L59 SOLID QUARK STARS? RX XU ABSTRACT It is
... in the stellar volume and (2) a less oblate equilibrium shape. Both should result in the decrease of the moment of inertia, but the star’s rigidity resists the stresses until the star cracks when the stresses reach a critical value. Such a “starquake,” an analog of an earthquake, rearranges the stel ...
... in the stellar volume and (2) a less oblate equilibrium shape. Both should result in the decrease of the moment of inertia, but the star’s rigidity resists the stresses until the star cracks when the stresses reach a critical value. Such a “starquake,” an analog of an earthquake, rearranges the stel ...
Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms and Ions
... Matter is composed of empty space through which atoms move Atoms are solid, homogeneous, indestructible, indivisible Atoms come in different sizes and shapes which creates different properties Changes in matter result from changes in groupings of atoms, not in the atoms themselves ...
... Matter is composed of empty space through which atoms move Atoms are solid, homogeneous, indestructible, indivisible Atoms come in different sizes and shapes which creates different properties Changes in matter result from changes in groupings of atoms, not in the atoms themselves ...
Document
... amount of protons and neutrons) elements atomic numbers 20 to 83 are heavy elements and nuclei ratio is not 1:1, the reason is because of the repulsive force between protons, the stronger the repulsive force, the more neutrons are needed to stabilize the nuclei Belt of stability ...
... amount of protons and neutrons) elements atomic numbers 20 to 83 are heavy elements and nuclei ratio is not 1:1, the reason is because of the repulsive force between protons, the stronger the repulsive force, the more neutrons are needed to stabilize the nuclei Belt of stability ...
Thermal and Statistical Physics (Part II) Examples Sheet 1
... in a water-glycerine solution of viscosity 2.78×10−3 kg m−1 s−1 , at a temperature of 292 K. The observed value of ⟨x2 ⟩ was 3.3×10−12 m2 in a 10-second interval. Use these data to determine a value of the Boltzmann constant, kB , and compare it with the modern value. 31. The famous ratchet and pawl ...
... in a water-glycerine solution of viscosity 2.78×10−3 kg m−1 s−1 , at a temperature of 292 K. The observed value of ⟨x2 ⟩ was 3.3×10−12 m2 in a 10-second interval. Use these data to determine a value of the Boltzmann constant, kB , and compare it with the modern value. 31. The famous ratchet and pawl ...
File
... The stream of atoms divided into two separate paths. This division would not be observed with atoms of A) Cu B) Cr C) Mg D) K E) Al ___D___29. The Pauli exclusion principle states that A) the velocity of all electromagnetic radiation equals the speed of light B) all particles with mass also have a w ...
... The stream of atoms divided into two separate paths. This division would not be observed with atoms of A) Cu B) Cr C) Mg D) K E) Al ___D___29. The Pauli exclusion principle states that A) the velocity of all electromagnetic radiation equals the speed of light B) all particles with mass also have a w ...
Home Work Problem Set 9
... magnetic moment due to the rotating charge has magnitude (b) What is the direction of this magnetic moment if the charge is positive? (HRW 32-60) 9-3 Consider a solid containing N atoms per unit volume, each atom having a magnetic dipole momentμ. Suppose the direction ofμcan be only parallel or anti ...
... magnetic moment due to the rotating charge has magnitude (b) What is the direction of this magnetic moment if the charge is positive? (HRW 32-60) 9-3 Consider a solid containing N atoms per unit volume, each atom having a magnetic dipole momentμ. Suppose the direction ofμcan be only parallel or anti ...
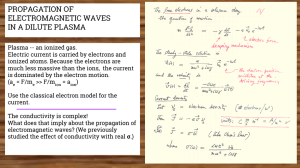
PROPAGATION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES IN A DILUTE PLASMA
... Plasma -- an ionized gas. Electric current is carried by electrons and ionized atoms. Because the electrons are much less massive than the ions, the current is dominated by the electron motion. (ae = F/me >> F/mion = aion) Use the classical electron model for the current. The conductivity is complex ...
... Plasma -- an ionized gas. Electric current is carried by electrons and ionized atoms. Because the electrons are much less massive than the ions, the current is dominated by the electron motion. (ae = F/me >> F/mion = aion) Use the classical electron model for the current. The conductivity is complex ...
Midterm Examination
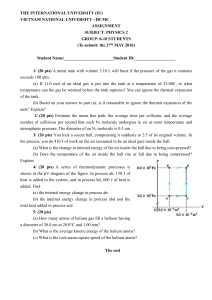
... number of collisions per second that each N2 molecule undergoes in air at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. The diameter of an N2 molecule is 0.3 nm. 3/ (20 pts) You kick a soccer ball, compressing it suddenly to 2/3 of its original volume. In the process, you do 410 J of work on the air (a ...
... number of collisions per second that each N2 molecule undergoes in air at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. The diameter of an N2 molecule is 0.3 nm. 3/ (20 pts) You kick a soccer ball, compressing it suddenly to 2/3 of its original volume. In the process, you do 410 J of work on the air (a ...
1-3 - University of Reading
... • We discovered this without knowing anything about our gas – it must be true in general for monatomic gases or more specifically a “perfect” or “ideal” gas. ...
... • We discovered this without knowing anything about our gas – it must be true in general for monatomic gases or more specifically a “perfect” or “ideal” gas. ...
Document
... Include your observations about matter interactions in an open vs closed container. CO2 + H2O --> H2CO3 --> H+ + HCO3- making the solution acidic. ...
... Include your observations about matter interactions in an open vs closed container. CO2 + H2O --> H2CO3 --> H+ + HCO3- making the solution acidic. ...
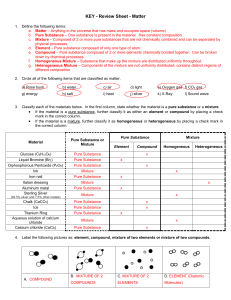
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).