Lecture 29
... Curie law, which is χ = ρ μ2/kT, where μ is the effective moment of the electrons. (This sometimes differs somewhat from μB.) The temperature dependence comes from the fact that temperature tends to randomize the spins. This effect competes with the aligning effect of the field. The result is the Cu ...
... Curie law, which is χ = ρ μ2/kT, where μ is the effective moment of the electrons. (This sometimes differs somewhat from μB.) The temperature dependence comes from the fact that temperature tends to randomize the spins. This effect competes with the aligning effect of the field. The result is the Cu ...
Experiment 4 Separation of a Mixture
... We will at the beginning of lab talked extensively about the different separation techniques and the above table, after which time you will be asked to design a flow chart that will be used to separate the different components of an unknown mixture. Your flow chart will be rather general to begin w ...
... We will at the beginning of lab talked extensively about the different separation techniques and the above table, after which time you will be asked to design a flow chart that will be used to separate the different components of an unknown mixture. Your flow chart will be rather general to begin w ...
Lecture 19 - University of Windsor
... temperature makes the compositions of the immiscible phases fixed When P = 1, F & = 2 (two liquids are fully mixed) both temperature and composition can be changed 1 Add small amt. of B to A at 290 K, it dissolves completely, single phase, P=1 2 Add more B to the point where B no ...
... temperature makes the compositions of the immiscible phases fixed When P = 1, F & = 2 (two liquids are fully mixed) both temperature and composition can be changed 1 Add small amt. of B to A at 290 K, it dissolves completely, single phase, P=1 2 Add more B to the point where B no ...
Materials Science 4 - Clarkson University
... • Three mechanisms for heat transfer in solids: 1. Lattice vibrations. Important with strong bonding, as in diamond. 2. Electron motion. Important when there are many free electrons, e.g. metals 3. Radiation. When the material does not absorb the radiation. Depends on the material composition, the p ...
... • Three mechanisms for heat transfer in solids: 1. Lattice vibrations. Important with strong bonding, as in diamond. 2. Electron motion. Important when there are many free electrons, e.g. metals 3. Radiation. When the material does not absorb the radiation. Depends on the material composition, the p ...
Class Activity
... Write a balanced chemical equations from the following word equations. Include the physical state of each of the element or compound a. Sodium metal plus water yields hydrogen gas and an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution b. An aqueous phosphoric acid solution plus an aqueous calcium hydroxide soluti ...
... Write a balanced chemical equations from the following word equations. Include the physical state of each of the element or compound a. Sodium metal plus water yields hydrogen gas and an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution b. An aqueous phosphoric acid solution plus an aqueous calcium hydroxide soluti ...
NSCC Chem 121 chapter6
... KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF MATTER • The kinetic molecular theory of matter is a useful tool for explaining the observed properties of matter in the three different states of solid, liquid and gas. • Postulate 1: Matter is made up of tiny particles called molecules. • Postulate 2: The particles of ...
... KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF MATTER • The kinetic molecular theory of matter is a useful tool for explaining the observed properties of matter in the three different states of solid, liquid and gas. • Postulate 1: Matter is made up of tiny particles called molecules. • Postulate 2: The particles of ...
κ1 κ2 d2 d1 width = w V L1 L2 x - Electrical and Computer Engineering
... dielectric. NOTE: because the dielectric in this device is non-linear, the usual capacitance cannot be defined. Instead, you must use the integral form of Gauss’s Law to find a terminal relation between the net charge and the voltage and mechanical displacement. This relation will be non-linear but ...
... dielectric. NOTE: because the dielectric in this device is non-linear, the usual capacitance cannot be defined. Instead, you must use the integral form of Gauss’s Law to find a terminal relation between the net charge and the voltage and mechanical displacement. This relation will be non-linear but ...
Advanced oxidation processes for water purification
... Different air flow rates will be applied with the help of an air flowmeter. Plasma discharge will be applied to the surface of the test solution from various distances. By doing these experiments we will optimise the best conditions which are most efficient to degrade the pollutants in the test solu ...
... Different air flow rates will be applied with the help of an air flowmeter. Plasma discharge will be applied to the surface of the test solution from various distances. By doing these experiments we will optimise the best conditions which are most efficient to degrade the pollutants in the test solu ...
Hazardous Material Information Sheet
... Note: You must provide a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for each chemical. Most MSDS's can be obtained by accessing Environmental Health and Safety's website: http://ehs.ucdavis.edu/ ...
... Note: You must provide a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for each chemical. Most MSDS's can be obtained by accessing Environmental Health and Safety's website: http://ehs.ucdavis.edu/ ...
Chapter 41: Quantization of Angular Momentum and of Energy Values
... particles such as electrons, obey the Pauli exclusion principle. Bosons, which are particles with integer spin (s=0,1,2…), on the other hand are not only allowed to share the same quantum state, but prefer to all be in the same quantum state. Examples of bosons: Photons (s=0) 4He (s=n, where n is an ...
... particles such as electrons, obey the Pauli exclusion principle. Bosons, which are particles with integer spin (s=0,1,2…), on the other hand are not only allowed to share the same quantum state, but prefer to all be in the same quantum state. Examples of bosons: Photons (s=0) 4He (s=n, where n is an ...
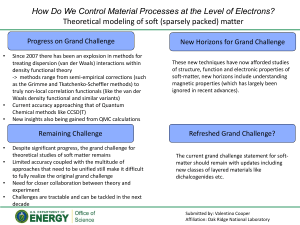
How Do We Control Material Processes at the Level of Electrons? (V
... Limited accuracy coupled with the multitude of approaches that need to be unified still make it difficult to fully realize the original grand challenge Need for closer collaboration between theory and experiment Challenges are tractable and can be tackled in the next decade ...
... Limited accuracy coupled with the multitude of approaches that need to be unified still make it difficult to fully realize the original grand challenge Need for closer collaboration between theory and experiment Challenges are tractable and can be tackled in the next decade ...
Pressure Distribution in Uniform Linear Acceleration
... fluid element equal to zero. The same ideas are applied in this section to a moving fluid by equating the sum of the forces acting on a fluid element to the element's acceleration, according to Newton's second law. The resulting equation is Euler's equation, which can be used to predict pressure var ...
... fluid element equal to zero. The same ideas are applied in this section to a moving fluid by equating the sum of the forces acting on a fluid element to the element's acceleration, according to Newton's second law. The resulting equation is Euler's equation, which can be used to predict pressure var ...
here
... Other Unit expressible as products or quotients of base units. Student should understand and use the conventions for indicating units and for labelling graph axes and table columns as set out in the current ASE Report SI Units, Signs, Symbols and Abbreviations. Use of units or dimensions to check ho ...
... Other Unit expressible as products or quotients of base units. Student should understand and use the conventions for indicating units and for labelling graph axes and table columns as set out in the current ASE Report SI Units, Signs, Symbols and Abbreviations. Use of units or dimensions to check ho ...
Chapter 40
... This principle applies not only to electrons but also to protons and neutrons, all of which have s=½. The principle is known as the Pauli exclusion principle after Wolfgang Pauli, who formulated it in 1925 ...
... This principle applies not only to electrons but also to protons and neutrons, all of which have s=½. The principle is known as the Pauli exclusion principle after Wolfgang Pauli, who formulated it in 1925 ...
Expt. 5: Binary Phase Diagram CHEM 366 V-1 Binary Solid
... may behave more or less independent of each other but merely diluted, i.e., an ideal solution or mixture, or there may be substantial chemical interaction or complex formation between the constituents. The study of such mixtures can lead to an understanding of the most fundamental intermolecular int ...
... may behave more or less independent of each other but merely diluted, i.e., an ideal solution or mixture, or there may be substantial chemical interaction or complex formation between the constituents. The study of such mixtures can lead to an understanding of the most fundamental intermolecular int ...
Unit 2 - Classifying Matter
... i. What is left of the solution? Compare its properties with the original salt. ii. Were you able to get the salt from the solution? How? What kind of matter is salt? iii. Where did the water go? What type of matter was left in the dish? iv. Which of the systems is a mixture? Why? v. Define a (1) s ...
... i. What is left of the solution? Compare its properties with the original salt. ii. Were you able to get the salt from the solution? How? What kind of matter is salt? iii. Where did the water go? What type of matter was left in the dish? iv. Which of the systems is a mixture? Why? v. Define a (1) s ...
6-First Law
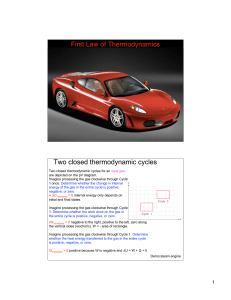
... Two closed thermodynamic cycles Two closed thermodynamic cycles for an ideal gas are depicted on the pV diagram. Imagine processing the gas clockwise through Cycle 1 once. Determine whether the change in internal energy of the gas in the entire cycle is positive, negative, or zero. • ΔU1clockwise = ...
... Two closed thermodynamic cycles Two closed thermodynamic cycles for an ideal gas are depicted on the pV diagram. Imagine processing the gas clockwise through Cycle 1 once. Determine whether the change in internal energy of the gas in the entire cycle is positive, negative, or zero. • ΔU1clockwise = ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).