Qualifying Questionnaire for Liquid Handling Workstation
... tissue, cells, human, plant, animal, etc..). What is the expected pipeting range or volume you will be working with (ex: 10 uL to 250 uL, 50 uL to 1 mL, etc...) Do you have time limitations on how quickly you need to prep your samples on the liquid handler (ex: 2 hours of liquid handling time to com ...
... tissue, cells, human, plant, animal, etc..). What is the expected pipeting range or volume you will be working with (ex: 10 uL to 250 uL, 50 uL to 1 mL, etc...) Do you have time limitations on how quickly you need to prep your samples on the liquid handler (ex: 2 hours of liquid handling time to com ...
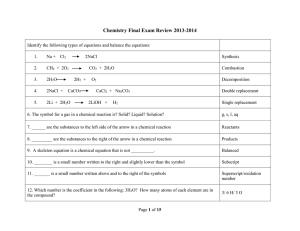
Type Of Chemical Reaction
... 13. Which law states that the number of each type of atom in the reactants must equal the number of atoms of each type in the product? ...
... 13. Which law states that the number of each type of atom in the reactants must equal the number of atoms of each type in the product? ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI –600 034 B.Sc., DEGREE EXAMINATION - CHEMISTRY
... 12. Internal energy and enthalpy remain constant in the isothermal expansion of an ideal gas Explain. 13. For the reaction N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) 2 NH3(g). Kp is 1.64 x 10-4 at 673 k. Calculate G when the partial pressure of N2, H2 and NH3 are 10 atm, 30 atm and 3 atm respectively. Is the reaction spon ...
... 12. Internal energy and enthalpy remain constant in the isothermal expansion of an ideal gas Explain. 13. For the reaction N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) 2 NH3(g). Kp is 1.64 x 10-4 at 673 k. Calculate G when the partial pressure of N2, H2 and NH3 are 10 atm, 30 atm and 3 atm respectively. Is the reaction spon ...
Matter and Measurement
... • Compounds- are substances that can be broken down by chemical methods • When they are broken down, the pieces have completely different properties than the compound. • Made of molecules- two or more atoms ...
... • Compounds- are substances that can be broken down by chemical methods • When they are broken down, the pieces have completely different properties than the compound. • Made of molecules- two or more atoms ...
File
... space (volume) and it also has mass (it is made up of carbon dioxide, oxygen, and nitrogen - all things that have mass to them). Chemistry is a subject that studies many facets of the world around us and almost everyone studies chemistry in high school. It is such an important topic to learn because ...
... space (volume) and it also has mass (it is made up of carbon dioxide, oxygen, and nitrogen - all things that have mass to them). Chemistry is a subject that studies many facets of the world around us and almost everyone studies chemistry in high school. It is such an important topic to learn because ...
Representation of gas-condensate wells in reservoir simulations
... The thermodynamic independent system is monovariant: all the thermodynamic variables depend on pressure only The new thermodynamic model is valid along streamlines ...
... The thermodynamic independent system is monovariant: all the thermodynamic variables depend on pressure only The new thermodynamic model is valid along streamlines ...
File
... NaOH is needed to titrate the sample to the equivalence point. What is the molar mass of the acid? A) 50.0 g B) 62.5 g C) 125 g D) 200 g E) 250 g 63. The pH of a solution prepared by adding 10.0 mL of 0.020 molar KOH (aq) to 10.0 mL of distilled water is closest to A) 13 B) 12 C) 11 D) 3 E) 2 64. Fa ...
... NaOH is needed to titrate the sample to the equivalence point. What is the molar mass of the acid? A) 50.0 g B) 62.5 g C) 125 g D) 200 g E) 250 g 63. The pH of a solution prepared by adding 10.0 mL of 0.020 molar KOH (aq) to 10.0 mL of distilled water is closest to A) 13 B) 12 C) 11 D) 3 E) 2 64. Fa ...
2nd Grade
... Three pocket folders (plain, solid color). One of each color: blue, green, and purple Twelve(12) pencils PLEASE no mechanical pencils Twelve (12) small white glue sticks- for personal use Crayons (limit to 48 count) Two (2) Marble Composition books One(1) school box One(1) pair of scis ...
... Three pocket folders (plain, solid color). One of each color: blue, green, and purple Twelve(12) pencils PLEASE no mechanical pencils Twelve (12) small white glue sticks- for personal use Crayons (limit to 48 count) Two (2) Marble Composition books One(1) school box One(1) pair of scis ...
Solution
... 3- The particles exhibit continuous random motion owing to their kinetic energy. The average kinetic energy, E, is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas. 4- The molecules exhibit perfect elasticity; that is, there is no net loss of speed or transfer of energy after they collid ...
... 3- The particles exhibit continuous random motion owing to their kinetic energy. The average kinetic energy, E, is directly proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas. 4- The molecules exhibit perfect elasticity; that is, there is no net loss of speed or transfer of energy after they collid ...
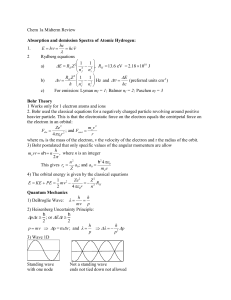
Chem 1a Midterm Review
... Ions: all transition metals when they ionize the first two electrons that are lost are from the ns shell not the (n-1)d shell. Filling orbitals 1. Pauli Principle: Every electron must have a unique set of 4 quantum numbers 2. Aufbau principle: Fill lowest energy orbitals first 3. Hund's Rule: In a d ...
... Ions: all transition metals when they ionize the first two electrons that are lost are from the ns shell not the (n-1)d shell. Filling orbitals 1. Pauli Principle: Every electron must have a unique set of 4 quantum numbers 2. Aufbau principle: Fill lowest energy orbitals first 3. Hund's Rule: In a d ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... The smallest unit of an element Atoms are made of even smaller subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons carry a positive charge, electrons carry a negative charge and neutrons are neutral! ...
... The smallest unit of an element Atoms are made of even smaller subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons carry a positive charge, electrons carry a negative charge and neutrons are neutral! ...
Notes on Atoms and Molecules
... Valency: The combining capacity of an element is known as valency. The combining capacity of the atoms to form molecules either with same or different elements is defined as valency. Atom contains less than four electrons in its outermost shell; the valency of an atom is equal to the number of elect ...
... Valency: The combining capacity of an element is known as valency. The combining capacity of the atoms to form molecules either with same or different elements is defined as valency. Atom contains less than four electrons in its outermost shell; the valency of an atom is equal to the number of elect ...
Aurora Reading
... the atoms to give off light. But why does that happen? To find the answer, we must look further away, to the Sun. The spectacular, "great" auroras in "What do they look like?" are powered by what is called the solar wind. The Sun also has an atmosphere and a magnetic field that extend into space. Th ...
... the atoms to give off light. But why does that happen? To find the answer, we must look further away, to the Sun. The spectacular, "great" auroras in "What do they look like?" are powered by what is called the solar wind. The Sun also has an atmosphere and a magnetic field that extend into space. Th ...
Magnetism
... * Electrons are indistinguishable in quantum mechanics. They cannot be “painted red or blue”. The wave function for two electrons has to change its sign when interchanging their coordinates r1 and r2 , because they are fermions. Bosons, such as photons, are also indistinguishable, but their wave fun ...
... * Electrons are indistinguishable in quantum mechanics. They cannot be “painted red or blue”. The wave function for two electrons has to change its sign when interchanging their coordinates r1 and r2 , because they are fermions. Bosons, such as photons, are also indistinguishable, but their wave fun ...
Phase Transition www.AssignmentPoint.com A phase transition is
... A phase transition is the transformation of a thermodynamic system from one phase or state of matter to another one by heat transfer. The term is most commonly used to describe transitions between solid, liquid and gaseous states of matter, and, in rare cases, plasma. A phase of a thermodynamic sys ...
... A phase transition is the transformation of a thermodynamic system from one phase or state of matter to another one by heat transfer. The term is most commonly used to describe transitions between solid, liquid and gaseous states of matter, and, in rare cases, plasma. A phase of a thermodynamic sys ...
Introduction to Magnetic Neutron Diffraction and Magnetic Structures
... The determination of magnetic structures of crystalline materials using neutron diffraction is one of the major specific applications of the use of neutrons for studying the properties of condensed matter. The knowledge of the magnetic ordering in materials provides important clues for understanding ...
... The determination of magnetic structures of crystalline materials using neutron diffraction is one of the major specific applications of the use of neutrons for studying the properties of condensed matter. The knowledge of the magnetic ordering in materials provides important clues for understanding ...
Problem set #2: AY 254C (Spring 2014) Due March 3, 2014
... Which collisions determine the rate of downward settling? Estimate numerical values for ions in the atmosphere of an 0.6 M white dwarf. (c) Combining (a) and (b), calculate the rate of downward drift of an ion through the white-dwarf atmosphere as a function of the density, temperature, and gravity ...
... Which collisions determine the rate of downward settling? Estimate numerical values for ions in the atmosphere of an 0.6 M white dwarf. (c) Combining (a) and (b), calculate the rate of downward drift of an ion through the white-dwarf atmosphere as a function of the density, temperature, and gravity ...
chapter6
... KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF MATTER • The kinetic molecular theory of matter is a useful tool for explaining the observed properties of matter in the three different states of solid, liquid and gas. • Postulate 1: Matter is made up of tiny particles called molecules. • Postulate 2: The particles of ...
... KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF MATTER • The kinetic molecular theory of matter is a useful tool for explaining the observed properties of matter in the three different states of solid, liquid and gas. • Postulate 1: Matter is made up of tiny particles called molecules. • Postulate 2: The particles of ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).