Document
... formed? SHOW ALL WORK 12. A 12.2 g sample of X reacts with a sample of Y to form 78.9 g XY. What is the mass of Y that reacted? SHOW ALL WORK 13. Describe the structure of a typical atom. Identify where each subatomic particle is located. 14. Describe the separation technique that could be used to s ...
... formed? SHOW ALL WORK 12. A 12.2 g sample of X reacts with a sample of Y to form 78.9 g XY. What is the mass of Y that reacted? SHOW ALL WORK 13. Describe the structure of a typical atom. Identify where each subatomic particle is located. 14. Describe the separation technique that could be used to s ...
Time-dependent current-density-functional theory for metals
... frequency range. This is typically handled by using some model extrapolation for the optical constants outside the measured frequency range. More accurate and more reproducible than the conventional reflection measurements are ellipsometry measurements. In this technique one obtains directly the com ...
... frequency range. This is typically handled by using some model extrapolation for the optical constants outside the measured frequency range. More accurate and more reproducible than the conventional reflection measurements are ellipsometry measurements. In this technique one obtains directly the com ...
Presentation - Dagotto Group
... If a Group 3 element is used it is p-type doping If a Group 5 element is used it is n-type ...
... If a Group 3 element is used it is p-type doping If a Group 5 element is used it is n-type ...
Principles of Technology
... A. The efficiency of a heat engine depends on its operating temperatures. B. A heat engine would reach 100 percent efficiency only if its “cold” temperature were below absolute zero (0 K) such as -150 K. C. Since such an engine cannot be completely efficient, it follows that a temperature of absolut ...
... A. The efficiency of a heat engine depends on its operating temperatures. B. A heat engine would reach 100 percent efficiency only if its “cold” temperature were below absolute zero (0 K) such as -150 K. C. Since such an engine cannot be completely efficient, it follows that a temperature of absolut ...
Physics Final Exam Review
... 47. ______ Matter that has a definite volume and a definite shape: a. solid b. liquid c. gas d. plasma 48. ______ Matter in which particles are arranged in repeating geometric patterns: a. solid b. liquid c. gas d. plasma 49. ______ A gas-like mixture with no definite volume or shape that is made up ...
... 47. ______ Matter that has a definite volume and a definite shape: a. solid b. liquid c. gas d. plasma 48. ______ Matter in which particles are arranged in repeating geometric patterns: a. solid b. liquid c. gas d. plasma 49. ______ A gas-like mixture with no definite volume or shape that is made up ...
Topic A Guide
... • A thermosetting polymer is a prepolymer in a soft solid or viscous state that changes irreversibly into a hardened thermoset by curing. • Elastomers are flexible and can be deformed under force but will return to nearly their original shape once the stress is released. • High density polyethene (H ...
... • A thermosetting polymer is a prepolymer in a soft solid or viscous state that changes irreversibly into a hardened thermoset by curing. • Elastomers are flexible and can be deformed under force but will return to nearly their original shape once the stress is released. • High density polyethene (H ...
Mr Alasdair Ross at Southpointe Academy
... The passage of molecules directly from the solid state to the vapour state is called sublimation. The reverse process is called deposition. A dynamic equilibrium is reached when the rates of sublimation and deposition become equal. Like vapour in equilibrium with a liquid, vapour in equilibrium with ...
... The passage of molecules directly from the solid state to the vapour state is called sublimation. The reverse process is called deposition. A dynamic equilibrium is reached when the rates of sublimation and deposition become equal. Like vapour in equilibrium with a liquid, vapour in equilibrium with ...
Chapter 2 Name___________________________________
... C) All of the reactants have been converted to the products of the reaction. D) All of the products have been converted to the reactants of the reaction. E) The concentration of the reactants equals the concentration of the products. ...
... C) All of the reactants have been converted to the products of the reaction. D) All of the products have been converted to the reactants of the reaction. E) The concentration of the reactants equals the concentration of the products. ...
2.26 MB - KFUPM Resources v3
... Three dimensional pattern Large attractive forces between atoms or molecules Molecule at relatively fixed position in solid. ...
... Three dimensional pattern Large attractive forces between atoms or molecules Molecule at relatively fixed position in solid. ...
Creation of an Ultracold Neutral Plasma
... to 艐10 mK by using a laser with a bandwidth equal to the Fourier transform limit of a 10 ns pulse. One may be able to decrease this energy even further by exciting below the ionization limit. In this case, one creates a dense gas of highly excited cold Rydberg atoms for which many-body interactions ...
... to 艐10 mK by using a laser with a bandwidth equal to the Fourier transform limit of a 10 ns pulse. One may be able to decrease this energy even further by exciting below the ionization limit. In this case, one creates a dense gas of highly excited cold Rydberg atoms for which many-body interactions ...
33 C? (1)
... ___ 109. When the vapor pressure of a liquid in an open container equals the atmospheric pressure then the liquid will (1) freeze; (2) crystallize; (3) melt; (4) boil. ___ 110. In a closed system, as the temperature of a liquid increases, the kinetic energy of its molecules (1) decreases; (2) increa ...
... ___ 109. When the vapor pressure of a liquid in an open container equals the atmospheric pressure then the liquid will (1) freeze; (2) crystallize; (3) melt; (4) boil. ___ 110. In a closed system, as the temperature of a liquid increases, the kinetic energy of its molecules (1) decreases; (2) increa ...
thermodynamics and statistical physics
... 38. Consider a system of two single-particle levels with energy 0 and ", respectively. Three particles are placed in these levels. The energy of the levels does not depend on the spin of the particles. The temperature is such that kT = ". Calculate numerical values for the Fermi energy (use " as en ...
... 38. Consider a system of two single-particle levels with energy 0 and ", respectively. Three particles are placed in these levels. The energy of the levels does not depend on the spin of the particles. The temperature is such that kT = ". Calculate numerical values for the Fermi energy (use " as en ...
Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant
... What is it? Is an excess electrical charge (either positive or negative) which cannot move, either because the material is an insulator or it is a conductor which is isolated from “Earth”. The charges cannot move and are therefore static ...
... What is it? Is an excess electrical charge (either positive or negative) which cannot move, either because the material is an insulator or it is a conductor which is isolated from “Earth”. The charges cannot move and are therefore static ...
Physics_A2_Unit4_23_StaticElectricity01
... What is it? Is an excess electrical charge (either positive or negative) which cannot move, either because the material is an insulator or it is a conductor which is isolated from “Earth”. The charges cannot move and are therefore static ...
... What is it? Is an excess electrical charge (either positive or negative) which cannot move, either because the material is an insulator or it is a conductor which is isolated from “Earth”. The charges cannot move and are therefore static ...
Protocol S3: 96-well yeast liquid growth assays
... Scientific, Inc., San Diego, CA). After one to two days, the yeast spots on the solid plates were transferred to fresh non-inducing liquid media containing 96-well plates using a 1.58 mm diameter 96 floating pin tool and incubated 16-18 hours such that yeast grew to OD600 between 0.3-0.5. The liquid ...
... Scientific, Inc., San Diego, CA). After one to two days, the yeast spots on the solid plates were transferred to fresh non-inducing liquid media containing 96-well plates using a 1.58 mm diameter 96 floating pin tool and incubated 16-18 hours such that yeast grew to OD600 between 0.3-0.5. The liquid ...
Energy
... • Both gasses and liquids are fluids. –This is because of weak intermolecular forces. –The molecules can slide easily over each other. ...
... • Both gasses and liquids are fluids. –This is because of weak intermolecular forces. –The molecules can slide easily over each other. ...
chapter 3 - UniMAP Portal
... • Compressed liquid (subcooled liquid): A substance that it is not about to vaporize. • Saturated liquid: A liquid that is about to vaporize. At 1 atm and 20°C, water exists in the liquid phase (compressed liquid). ...
... • Compressed liquid (subcooled liquid): A substance that it is not about to vaporize. • Saturated liquid: A liquid that is about to vaporize. At 1 atm and 20°C, water exists in the liquid phase (compressed liquid). ...
Document
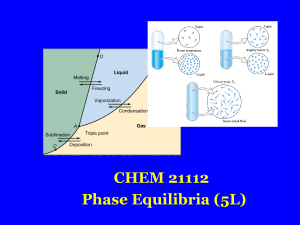
... be changed independently without causing the appearance of a new phase or disappearance of an existing phase ...
... be changed independently without causing the appearance of a new phase or disappearance of an existing phase ...
Untitled
... one extra valence electron • P-type (positive charge carrying) semiconducting: doping with an element with one less valence electron – By adding and removing electrons from structure makes electrons that are available to flow and conduct electricity – Junctions between n-doped and p-doped materials ...
... one extra valence electron • P-type (positive charge carrying) semiconducting: doping with an element with one less valence electron – By adding and removing electrons from structure makes electrons that are available to flow and conduct electricity – Junctions between n-doped and p-doped materials ...
physics - IIT Portal.com
... A capillary tube is immersed vertically in water such that the height of liquid column in it is 5 cm, this arrangement is taken in to a mine of depth 'd' and the height of the liquid, column is found to be 7.5 cm. If R is the radius of the earth, find 'd' in terms of 'R' 1) R/3 ...
... A capillary tube is immersed vertically in water such that the height of liquid column in it is 5 cm, this arrangement is taken in to a mine of depth 'd' and the height of the liquid, column is found to be 7.5 cm. If R is the radius of the earth, find 'd' in terms of 'R' 1) R/3 ...
Superconductivity Is Pair Work - Max-Planck
... BIND THE ELECTRONS This idea is now taking shape. The Cooper pair glue is actually magnetic. Its force originates from spin fluctuations of the heavy fermions. In the general chaos, they form small “bubbles” with short-range magnetic order that form and disappear rapidly. These fluctuations particul ...
... BIND THE ELECTRONS This idea is now taking shape. The Cooper pair glue is actually magnetic. Its force originates from spin fluctuations of the heavy fermions. In the general chaos, they form small “bubbles” with short-range magnetic order that form and disappear rapidly. These fluctuations particul ...
Superconductors: Better levitation through
... in predicting which of these combinations will yield new phases. Most of the elements in the periodic table form solid oxides, so that the number of ways we can combine three oxides is staggeringly large. Furthermore, we cannot always predict which combinations will lead to solid solutions. For exam ...
... in predicting which of these combinations will yield new phases. Most of the elements in the periodic table form solid oxides, so that the number of ways we can combine three oxides is staggeringly large. Furthermore, we cannot always predict which combinations will lead to solid solutions. For exam ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).