File
... D) An observation explains why nature does something. E) A scientific law summarizes a series of related observations 3) Which of the following statements about the phases of matter is TRUE? A) In both solids and liquids, the atoms or molecules pack closely to one another. B) Solids are highly compr ...
... D) An observation explains why nature does something. E) A scientific law summarizes a series of related observations 3) Which of the following statements about the phases of matter is TRUE? A) In both solids and liquids, the atoms or molecules pack closely to one another. B) Solids are highly compr ...
Gas Sampler
... them algebraically. These equations can then be used to solve for any of the four variables when the other three are known and expressed in the proper units. P ‗ nRT V ...
... them algebraically. These equations can then be used to solve for any of the four variables when the other three are known and expressed in the proper units. P ‗ nRT V ...
Document
... 13. Entropy vs. Energy • Phase transitions occur because of this competition. • Generally decreasing the temperature leads to transitions to phases with lower internal energy and lower entropy. ...
... 13. Entropy vs. Energy • Phase transitions occur because of this competition. • Generally decreasing the temperature leads to transitions to phases with lower internal energy and lower entropy. ...
New Microsoft Office Word Document
... H=U+PV ∆H=∆U+P∆V ∆H=U+∆nRT ∆H is positive for endothermic reactions ∆H is negative for exothermic reactions Enthalpy depends on the state of the system, allotropic forms of matter, composition of system, amount of reactants and temperature too ...
... H=U+PV ∆H=∆U+P∆V ∆H=U+∆nRT ∆H is positive for endothermic reactions ∆H is negative for exothermic reactions Enthalpy depends on the state of the system, allotropic forms of matter, composition of system, amount of reactants and temperature too ...
An essay on condensed matter physics in the twentieth century
... inconsistencies and had only very limited success. A crucial feature was the (correct) postulate that in a metal some atomic electrons are not attached to specific atoms but roam throughout the entire system. Their scattering by the atomic nuclei was regarded as the cause of electrical resistance. H ...
... inconsistencies and had only very limited success. A crucial feature was the (correct) postulate that in a metal some atomic electrons are not attached to specific atoms but roam throughout the entire system. Their scattering by the atomic nuclei was regarded as the cause of electrical resistance. H ...
TD9 Statistical Physics (M1)
... Bi is the magnetic field acting on the ith spin. 1) Write the expression of the partition function ZN({Bi}) of the N spins in the canonical ensemble, for a given set of {Bi} (1≤i≤N). 2) Write, , and the total magnetization M of the system as a function of partial
derivatives of the free ...
... Bi is the magnetic field acting on the ith spin. 1) Write the expression of the partition function ZN({Bi}) of the N spins in the canonical ensemble, for a given set of {Bi} (1≤i≤N). 2) Write
Tutorial Questions
... is unchanged at 7000 kg m-3 and the bulk modulus is constant and equal to 95 GPa. 10. How much work is done in compressing a van der Waals gas to one-third of its initial volume under isothermal conditions? 11. Steel rails (with a length of 10 metres) are placed end to end on a rail line with a gap ...
... is unchanged at 7000 kg m-3 and the bulk modulus is constant and equal to 95 GPa. 10. How much work is done in compressing a van der Waals gas to one-third of its initial volume under isothermal conditions? 11. Steel rails (with a length of 10 metres) are placed end to end on a rail line with a gap ...
Atomic Structure
... (540 cal/g), which means that it requires a large amount of energy for the liquid to break the hydrogen bonds and leave the liquid state The molecules left behind on the surface thus have a lower kinetic energy and have a lower temperature Evaporative cooling stabilizes temperatures in aquatic ecosy ...
... (540 cal/g), which means that it requires a large amount of energy for the liquid to break the hydrogen bonds and leave the liquid state The molecules left behind on the surface thus have a lower kinetic energy and have a lower temperature Evaporative cooling stabilizes temperatures in aquatic ecosy ...
Introduction to Entropy - key
... 5. Are you more or less likely to have ordered states in a blackjack dealers “shoe” – a device that can contain six or more decks of cards, all shuffled together? There would be fewer ordered states in a blackjack dealers shoe because there would be more cards to randomly place at any one position i ...
... 5. Are you more or less likely to have ordered states in a blackjack dealers “shoe” – a device that can contain six or more decks of cards, all shuffled together? There would be fewer ordered states in a blackjack dealers shoe because there would be more cards to randomly place at any one position i ...
Document
... normally have random spin orientations. In the presence of a strong magnetic field, they become aligned with a component paralell to the field. A brief radio signal flips the spins; as their components reorient paralell to the field, they emit signals that are picked up by sensitive detectors. The d ...
... normally have random spin orientations. In the presence of a strong magnetic field, they become aligned with a component paralell to the field. A brief radio signal flips the spins; as their components reorient paralell to the field, they emit signals that are picked up by sensitive detectors. The d ...
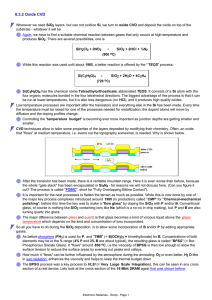
6.3.2 Oxide CVD
... metallization, we want to come down with the temperature for the oxide (or other) CVD processes. One way for doing this is to supply the necessary energy for the chemical reaction not by heating everything evenly, but just the gas. The way to do this is to pump electrical energy into the gas by expo ...
... metallization, we want to come down with the temperature for the oxide (or other) CVD processes. One way for doing this is to supply the necessary energy for the chemical reaction not by heating everything evenly, but just the gas. The way to do this is to pump electrical energy into the gas by expo ...
93essay - PLK Vicwood KT Chong Sixth Form College
... - The diameter of the tube is large compared with the diameters of ball-bearings so that streamline conditions are satisfied. - Marker A is far enough below the liquid surface for the ball-bearing to have its terminal velocity at A - Dip the ball-bearing in the liquid and thereby coated, before drop ...
... - The diameter of the tube is large compared with the diameters of ball-bearings so that streamline conditions are satisfied. - Marker A is far enough below the liquid surface for the ball-bearing to have its terminal velocity at A - Dip the ball-bearing in the liquid and thereby coated, before drop ...
FoundationsofChemistryppt
... as a material undergoes chemical change and changes identity. • Signs of possible chemical change include bubbles, energy change, and change in odor or color. • Chemical equations show the reactants and products of a chemical reaction and that mass is conserved. ...
... as a material undergoes chemical change and changes identity. • Signs of possible chemical change include bubbles, energy change, and change in odor or color. • Chemical equations show the reactants and products of a chemical reaction and that mass is conserved. ...
Midterm review
... 1. Total number of valence electrons is sum of valence electrons of each atom minus the overall charge 2. Arrange the atoms in a structure and distribute the electrons so that each atom has 8 electrons around it (exceptions, H has 2, B can have 6 and third row and lower atoms can have more than 8). ...
... 1. Total number of valence electrons is sum of valence electrons of each atom minus the overall charge 2. Arrange the atoms in a structure and distribute the electrons so that each atom has 8 electrons around it (exceptions, H has 2, B can have 6 and third row and lower atoms can have more than 8). ...
Temperature
... Suppose you have that same cylinder with a piston in the top allowing volume to change, and a heating/cooling element allowing for changing temperature. The force on the piston head is constant to maintain pressure, and the cylinder is contained so the amount of gas is constant. An increase in temp ...
... Suppose you have that same cylinder with a piston in the top allowing volume to change, and a heating/cooling element allowing for changing temperature. The force on the piston head is constant to maintain pressure, and the cylinder is contained so the amount of gas is constant. An increase in temp ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).