Fluid Properties (three types)
... the water column can be found by summing all forces acting on the water column as a free body diagram. (This is a statics problem since there is no acceleration.) ...
... the water column can be found by summing all forces acting on the water column as a free body diagram. (This is a statics problem since there is no acceleration.) ...
CYL100 2013–14 I semester Homework 1 Solutions August 9, 2013
... Finally, correct the false statement with a clarifying phrase that makes the statement true. (i) The internal energy of a system and its surroundings is not conserved during an irreversible process, but it is conserved for reversible processes. False. Energy is conserved no matter what process, reve ...
... Finally, correct the false statement with a clarifying phrase that makes the statement true. (i) The internal energy of a system and its surroundings is not conserved during an irreversible process, but it is conserved for reversible processes. False. Energy is conserved no matter what process, reve ...
Properties of Gases
... 4. Avogadro’s Law (Relationship between Volume and number of moles or molecules) This law states that equal volumes (V) of all gases at the similar conditions of temperature (T) and pressure (P) contain equal number of molecules (N). ...
... 4. Avogadro’s Law (Relationship between Volume and number of moles or molecules) This law states that equal volumes (V) of all gases at the similar conditions of temperature (T) and pressure (P) contain equal number of molecules (N). ...
Chemical Bonds
... • Bonds form as a result of lowering of the total energy (energy of separated species is higher than that of bonded species) • Bond formation is accompanied by rearrangement of valence electrons – complete transfer of electrons – formation of ions (ionic bonding) – sharing of electrons – formation o ...
... • Bonds form as a result of lowering of the total energy (energy of separated species is higher than that of bonded species) • Bond formation is accompanied by rearrangement of valence electrons – complete transfer of electrons – formation of ions (ionic bonding) – sharing of electrons – formation o ...
File
... The three phases of matter (solids, liquids, and gases) have different properties. (3.1kk) A pure substance (element or compound) has a constant composition and constant properties throughout a given sample, and from sample to sample. (3.1r) Elements cannot be broken down by chemical change. (3.1u) ...
... The three phases of matter (solids, liquids, and gases) have different properties. (3.1kk) A pure substance (element or compound) has a constant composition and constant properties throughout a given sample, and from sample to sample. (3.1r) Elements cannot be broken down by chemical change. (3.1u) ...
1 MATTER—ITS PROPERTIES AND MEASUREMENT
... 3. A 400 g sample of sucrose is to be produced by evaporating to dryness a solution containing 9.5 % sucrose by mass. What volume of solution must be evaporated? 4. A 2.0 gal flask weighs 4.0 lbs when empty. When it is filled with liquid, the flask weighs 4536.0 g. What is the density of the liquid ...
... 3. A 400 g sample of sucrose is to be produced by evaporating to dryness a solution containing 9.5 % sucrose by mass. What volume of solution must be evaporated? 4. A 2.0 gal flask weighs 4.0 lbs when empty. When it is filled with liquid, the flask weighs 4536.0 g. What is the density of the liquid ...
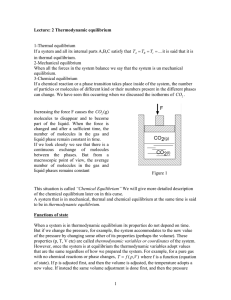
1 Lecture: 2 Thermodynamic equilibrium 1
... it completely converted into heat at the system, we see that the final temperature T2 can be reached after some time. Once the system has reached T2 it is indistinguishable from the system at T2 obtained by lowering the mass m through a difference in height of h. We can also supply some mechanical w ...
... it completely converted into heat at the system, we see that the final temperature T2 can be reached after some time. Once the system has reached T2 it is indistinguishable from the system at T2 obtained by lowering the mass m through a difference in height of h. We can also supply some mechanical w ...
CHAPTER 2 STRUCTURE OF ATOM • Atom is the smallest
... Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle rules out the existence of definite pathsor trajectories of electrons and other similar particles Failure of Bohr’s model: a. It ignores the dual behavior of matter. b. It contradicts Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. Classical mechanics is based on Newton’s laws ...
... Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle rules out the existence of definite pathsor trajectories of electrons and other similar particles Failure of Bohr’s model: a. It ignores the dual behavior of matter. b. It contradicts Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. Classical mechanics is based on Newton’s laws ...
Molar Mass by Freezing Point Depression
... significantly. A few “quick-and-dirty” experiments with the unknown and a few different solvents will often save a great deal of wasted effort. A good rule of thumb is that the freezing point should be lower with a 12% (w/w) solution than with a 10% solution. Otherwise the solute is precipitating at ...
... significantly. A few “quick-and-dirty” experiments with the unknown and a few different solvents will often save a great deal of wasted effort. A good rule of thumb is that the freezing point should be lower with a 12% (w/w) solution than with a 10% solution. Otherwise the solute is precipitating at ...
Physical Chemistry
... Application of 1st law thermodynamics Thermochemistry Standard enthalpy change Hess’ law Equilibrium condition Phase stability of pure substance P-T diagram for pure substance (phase diagram) The Clayperon equation for vapor pressure Phase rule Course material week 1 - 6 ...
... Application of 1st law thermodynamics Thermochemistry Standard enthalpy change Hess’ law Equilibrium condition Phase stability of pure substance P-T diagram for pure substance (phase diagram) The Clayperon equation for vapor pressure Phase rule Course material week 1 - 6 ...
Chemistry Review Fill in the blank
... 5. Cations are _________________ charged ions. They are formed by __________________ electrons. 6. Anions are _________________ charged ions. They are formed by __________________ electrons. 7. The periodic table is arranged by ______________________________________. 8. The periodic table is mostly ...
... 5. Cations are _________________ charged ions. They are formed by __________________ electrons. 6. Anions are _________________ charged ions. They are formed by __________________ electrons. 7. The periodic table is arranged by ______________________________________. 8. The periodic table is mostly ...
Gas Laws - myersparkphysics
... The container holds a very large number N of identical molecules. Each molecule has a mass m, and behaves as a point particle. The molecules move about the container in a random manner. They obey Newton’s laws of motion at all times. When the molecules hit the walls of the container or collide with ...
... The container holds a very large number N of identical molecules. Each molecule has a mass m, and behaves as a point particle. The molecules move about the container in a random manner. They obey Newton’s laws of motion at all times. When the molecules hit the walls of the container or collide with ...
the third law of thermodynamics and the low temperature
... This additional mode is associated with the conservation of mass (11). Assuming for simplicity only one kind of atoms there are 8 hydrodynamic variables associated with the Hamiltonian in Eq. ( 8 ) : The momentum density, the energy density, and the mass density. In addition we have three broken sym ...
... This additional mode is associated with the conservation of mass (11). Assuming for simplicity only one kind of atoms there are 8 hydrodynamic variables associated with the Hamiltonian in Eq. ( 8 ) : The momentum density, the energy density, and the mass density. In addition we have three broken sym ...
PFC_MOF_McKellar_crsytengcomm_refereeresponses
... data decreased rapidly (≈ 1.3 Å). Nevertheless, the sample could still be confirmed as being in the crystalline monoclinic phase. This work is the first example of a penetrating (CO2) and a nonpenetrating (FC-77) medium being used simultaneously, so it is therefore interesting to speculate on the co ...
... data decreased rapidly (≈ 1.3 Å). Nevertheless, the sample could still be confirmed as being in the crystalline monoclinic phase. This work is the first example of a penetrating (CO2) and a nonpenetrating (FC-77) medium being used simultaneously, so it is therefore interesting to speculate on the co ...
Memorize Colors
... Blue Yellow to red-orange (depending on anion and charge of Fe); in rare cases, can form complex ion with a deep blue color yellow-green (depending on the anion) orange-red (depending on the anion) Pink Violet (Cr(NO3)3 to Green (CrCl3) Green Pink blue-green (Pb2+ and Pb4+ are colorless) violet blue ...
... Blue Yellow to red-orange (depending on anion and charge of Fe); in rare cases, can form complex ion with a deep blue color yellow-green (depending on the anion) orange-red (depending on the anion) Pink Violet (Cr(NO3)3 to Green (CrCl3) Green Pink blue-green (Pb2+ and Pb4+ are colorless) violet blue ...
File
... • Ultra filtration: colloidal sols are filtered through ultra-filtrers. pore size of filter paper is decreased such that it will restrict the passage of colloidal particles. • Ultra-centrifugation: Centrifugation is carried out at very high speeds such that the colloidal particles settle down at the ...
... • Ultra filtration: colloidal sols are filtered through ultra-filtrers. pore size of filter paper is decreased such that it will restrict the passage of colloidal particles. • Ultra-centrifugation: Centrifugation is carried out at very high speeds such that the colloidal particles settle down at the ...
File - ever y thin g ismateria l ,,,,
... and molecules, after impinging onto the growth surface, assemble into crystal structure one after another. ...
... and molecules, after impinging onto the growth surface, assemble into crystal structure one after another. ...
Home Work Problem Set 11
... (b) What is the direction of this magnetic moment if the charge is positive? (HRW 32-60) 11-6 Consider a solid containing N atoms per unit volume, each atom having a magnetic dipole momentμ. Suppose the direction ofμcan be only parallel or antiparallel to an externally applied magnetic field B (this ...
... (b) What is the direction of this magnetic moment if the charge is positive? (HRW 32-60) 11-6 Consider a solid containing N atoms per unit volume, each atom having a magnetic dipole momentμ. Suppose the direction ofμcan be only parallel or antiparallel to an externally applied magnetic field B (this ...
Andrew York
... an interesting application of Quantum Field Theory. The Hall fluid is an example of one such fluid, and describes a system in which a collection of electrons move in a plane in the presence of a magnetic field B directed normal to the plane. The magnetic field is strong enough to align all the elect ...
... an interesting application of Quantum Field Theory. The Hall fluid is an example of one such fluid, and describes a system in which a collection of electrons move in a plane in the presence of a magnetic field B directed normal to the plane. The magnetic field is strong enough to align all the elect ...
stable structure - Rothschild Science
... Electrostatic force - the force that occurs when a + charge is attracted to a - charge (causes the bonds!) Salt- another name for ionic compounds Formula unit- One molecule of an ionic compound ...
... Electrostatic force - the force that occurs when a + charge is attracted to a - charge (causes the bonds!) Salt- another name for ionic compounds Formula unit- One molecule of an ionic compound ...
Chapter 1 Matter and Energy Classifying Matter – An Exercise
... Symbols Used in Chemistry • Symbols for physical states – are found in parenthesis by the elemental symbol or chemical formula – designate the physical state [ex. solid, liquid, gas, aqueous] – Also see Table 1.3 ...
... Symbols Used in Chemistry • Symbols for physical states – are found in parenthesis by the elemental symbol or chemical formula – designate the physical state [ex. solid, liquid, gas, aqueous] – Also see Table 1.3 ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).