CHEMISTRY 11 Unit 4 Assignment - The Mole
... a) 6.85 x 1022 molecules of sulphur dioxide take up. (2) ...
... a) 6.85 x 1022 molecules of sulphur dioxide take up. (2) ...
solid metal
... element in Earth’s crust, oceans, and atmosphere. The natural abundance of an element listed as rare is less than 1 mg per metric ton (1000 kg). An element listed as synthetic is made artificially and does not occur naturally. An element listed as unstable often disintegrates in a fraction of a seco ...
... element in Earth’s crust, oceans, and atmosphere. The natural abundance of an element listed as rare is less than 1 mg per metric ton (1000 kg). An element listed as synthetic is made artificially and does not occur naturally. An element listed as unstable often disintegrates in a fraction of a seco ...
HYSTERESIS AND NON-STATIONARY EF- FECTS IN THE
... gas in a highly ionized plasma which result from the fact that the frequency of collisions between electrons and ions falls off sharply with increasing electron velocity.* It was found that in a fixed electric field the electron gas is in a stationary state with respect to the ions only at small val ...
... gas in a highly ionized plasma which result from the fact that the frequency of collisions between electrons and ions falls off sharply with increasing electron velocity.* It was found that in a fixed electric field the electron gas is in a stationary state with respect to the ions only at small val ...
Neutron stars and white dwarfs
... provide charge neutrality and supply the pressure that keeps the star from collapsing under its own weight. Assume Z electrons. Clearly, if N is the number of 4He nuclei, Z = 2N. The mass of the star is then NmHe ≈ 4Nmproton ≡ 4Nm . The electrons are fermions, so in a box of volume Ω large enough to ...
... provide charge neutrality and supply the pressure that keeps the star from collapsing under its own weight. Assume Z electrons. Clearly, if N is the number of 4He nuclei, Z = 2N. The mass of the star is then NmHe ≈ 4Nmproton ≡ 4Nm . The electrons are fermions, so in a box of volume Ω large enough to ...
ch-1-tm-honors
... • A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass regardless of the source of the compound. • Example: A molecule of pure water (H2O) always is made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Prentice Hall © 2003 ...
... • A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by mass regardless of the source of the compound. • Example: A molecule of pure water (H2O) always is made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Prentice Hall © 2003 ...
Streaming Bounded Hollow Jet Oscillation Under Oblique Varying Magnetic Field
... By insertion of the expansion (12) into the basic equations (4)-(11), the unperturbed system of equations are obtained and solved: ...
... By insertion of the expansion (12) into the basic equations (4)-(11), the unperturbed system of equations are obtained and solved: ...
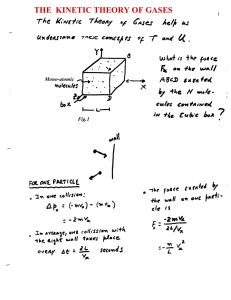
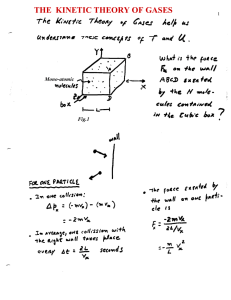
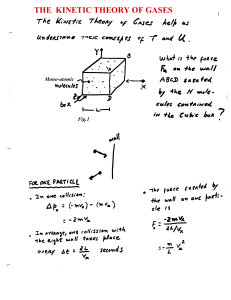
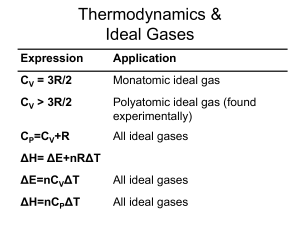
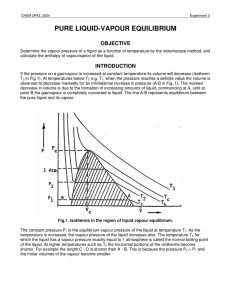
Introduction to Thermodynamics
... dG = dU + PdV + vdP - TdS - SdT Substitute L1, take constant P,T dG = dQ - TdS This is always less than zero by L2. ...
... dG = dU + PdV + vdP - TdS - SdT Substitute L1, take constant P,T dG = dQ - TdS This is always less than zero by L2. ...
Science Final Review
... Which of the following occurs when a liquid becomes a gas? A. The particles break away from each other. B. The particles give off energy. C. The particles slow down. D. The particles move closer together ...
... Which of the following occurs when a liquid becomes a gas? A. The particles break away from each other. B. The particles give off energy. C. The particles slow down. D. The particles move closer together ...
ΔE=nC V ΔT
... iron at 200 oC into a large coffee cup calorimeter containing 250 grams of water at 25 oC. What will the final temperature be inside the cup? The specific heats of iron and water are 0.45 and 4.18 J-K-1-g-1. If the density of the water changes from 0.993 to 0.985 g/ml will your answer change? What a ...
... iron at 200 oC into a large coffee cup calorimeter containing 250 grams of water at 25 oC. What will the final temperature be inside the cup? The specific heats of iron and water are 0.45 and 4.18 J-K-1-g-1. If the density of the water changes from 0.993 to 0.985 g/ml will your answer change? What a ...
View Product Label
... *THIS STATEMENT HAS NOT BEEN EVALUATED BY THE FOOD & DRUG ADMINISTRATION. THIS PRODUCT IS NOT INTENDED TO DIAGNOSE, TREAT, CURE OR PREVENT ANY DISEASE. ...
... *THIS STATEMENT HAS NOT BEEN EVALUATED BY THE FOOD & DRUG ADMINISTRATION. THIS PRODUCT IS NOT INTENDED TO DIAGNOSE, TREAT, CURE OR PREVENT ANY DISEASE. ...
Solutions!
... – visibly different regions – can be separated depending on particle sizes – scatters light ...
... – visibly different regions – can be separated depending on particle sizes – scatters light ...
PowerPoint Chapter 14 - Preparatory Chemistry
... • whether a chemical bond is nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. • which atom in a polar covalent bond is partial negative and which is partial positive. • which atom in an ionic bond forms the cation and which forms the anion. • which of two covalent bonds are more polar. ...
... • whether a chemical bond is nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. • which atom in a polar covalent bond is partial negative and which is partial positive. • which atom in an ionic bond forms the cation and which forms the anion. • which of two covalent bonds are more polar. ...
Multi-electron atoms
... Outside the above experiments, the electron spin is usually too weak to play a major role in atomic or molecular properties directly. The major role of spin is in the Pauli Exclusion Principle No two electrons in an atom can have the same values of all four quantum numbers (n, l, ml , and ms .) The ...
... Outside the above experiments, the electron spin is usually too weak to play a major role in atomic or molecular properties directly. The major role of spin is in the Pauli Exclusion Principle No two electrons in an atom can have the same values of all four quantum numbers (n, l, ml , and ms .) The ...
Plasma Ball Lesson Plan
... ● Charges have associated electric fields which create electric potentials that systems can interact with. Placing your hand on the bulb changes the electric field at that point and allows a stream of electrons to flow from the inner ball to the point of contact on the bulb. Note the electrons do no ...
... ● Charges have associated electric fields which create electric potentials that systems can interact with. Placing your hand on the bulb changes the electric field at that point and allows a stream of electrons to flow from the inner ball to the point of contact on the bulb. Note the electrons do no ...
Description - University of Southampton
... In recent years there has been much interest in the physics and possible technological applications of colloidal suspensions in a liquid crystal host [1]. As early as 1970, Brochard and de Gennes [2] pointed out that if the colloidal particles possess a permanent magnetic moment, then the orientatio ...
... In recent years there has been much interest in the physics and possible technological applications of colloidal suspensions in a liquid crystal host [1]. As early as 1970, Brochard and de Gennes [2] pointed out that if the colloidal particles possess a permanent magnetic moment, then the orientatio ...
Modeling of a chlorine high-density plasma submitted to a
... 3. Results of the model and comparison with experiments 3.1 Characteristics of neutral species Figure 1 shows the dissociation degree τd of the Cl2 molecules as a function of the initial gas pressure for different values of the magnetic field intensity. For comparison (and testing of the model valid ...
... 3. Results of the model and comparison with experiments 3.1 Characteristics of neutral species Figure 1 shows the dissociation degree τd of the Cl2 molecules as a function of the initial gas pressure for different values of the magnetic field intensity. For comparison (and testing of the model valid ...
4. Atomic Structure
... • Therefore, Thomson theorized that an atom contains small, negatively charged particles called electrons. This theory is referred to as the Plum Pudding Model. In this model, the mass of the rest of the atom was evenly distributed and positively charged, taking up all of the space not occupied by ...
... • Therefore, Thomson theorized that an atom contains small, negatively charged particles called electrons. This theory is referred to as the Plum Pudding Model. In this model, the mass of the rest of the atom was evenly distributed and positively charged, taking up all of the space not occupied by ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).