
June 2011 review
... 5. Base your answer on the information below. Polonium-210 occurs naturally, but is scarce. Polonium-210 is primarily used in devices designed to eliminate static electricity in machinery. It is also used in brushes to remove dust from camera lenses. Polonium-210 can be created in the laboratory by ...
... 5. Base your answer on the information below. Polonium-210 occurs naturally, but is scarce. Polonium-210 is primarily used in devices designed to eliminate static electricity in machinery. It is also used in brushes to remove dust from camera lenses. Polonium-210 can be created in the laboratory by ...
Solutions
... A solution __________exists when the opposing processes of dissolving the solute in the solvent and of crystallizing the solute from the solvent occur at equal rates. At this point no further solute can be dissolved and the solution is known as ______________. General rule: the solubility of a solid ...
... A solution __________exists when the opposing processes of dissolving the solute in the solvent and of crystallizing the solute from the solvent occur at equal rates. At this point no further solute can be dissolved and the solution is known as ______________. General rule: the solubility of a solid ...
File
... Likewise, for MgCl2 there must be two Chlorine ions for every magnesium ion. Ionic bonds tend to be strong bonds - high bonding energy. (Table 2.3) Ceramics are usually ionically bonded and have high melting points, high hardness, brittle and electrically and thermally insulative (atoms and electron ...
... Likewise, for MgCl2 there must be two Chlorine ions for every magnesium ion. Ionic bonds tend to be strong bonds - high bonding energy. (Table 2.3) Ceramics are usually ionically bonded and have high melting points, high hardness, brittle and electrically and thermally insulative (atoms and electron ...
Modeling Dusty Plasma Discharges of Noble Gases Using a Self
... potential around the dust particle. Charge equilibrium is achieved when the net current to the particle is zero. As a result of dust particle charging, there exists a high electrostatic energy of interaction between individual dust particles, which explains the appearance of ordered crystal structur ...
... potential around the dust particle. Charge equilibrium is achieved when the net current to the particle is zero. As a result of dust particle charging, there exists a high electrostatic energy of interaction between individual dust particles, which explains the appearance of ordered crystal structur ...
Lecture 33 - LSU Physics
... at twice atmospheric pressure (2 atm) as shown. The volume of the water changes from an initial value of 1.0×10‐3 m3 as a liquid to 1.671 m3 as a gas. Here, energy is transferred from the thermal reservoir as heat until the liquid water is changed completely to steam. Work is done by the expandi ...
... at twice atmospheric pressure (2 atm) as shown. The volume of the water changes from an initial value of 1.0×10‐3 m3 as a liquid to 1.671 m3 as a gas. Here, energy is transferred from the thermal reservoir as heat until the liquid water is changed completely to steam. Work is done by the expandi ...
PROPERTIES OF SOLUTIONS
... At the normal boiling point of the pure solvent, the solution has a vapor pressure less than one atm. Therefore, a higher temperature is required to reach a vapor pressure of 1 atm The molal boiling-point-elevation constant, K , expresses how much T boiling changes with molality Tb = Kb m ...
... At the normal boiling point of the pure solvent, the solution has a vapor pressure less than one atm. Therefore, a higher temperature is required to reach a vapor pressure of 1 atm The molal boiling-point-elevation constant, K , expresses how much T boiling changes with molality Tb = Kb m ...
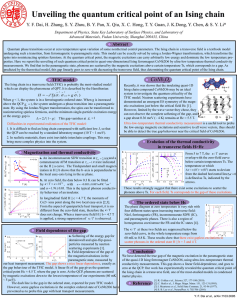
Unveiling the quantum critical point of an Ising chain
... Quantum phase transitions occur at zero temperature upon variation of some nonthermal control parameters. The Ising chain in a transverse field is a textbook model undergoing such a transition, from ferromagnetic to paramagnetic state. This model can be exactly solved by using a Jordan-Wigner transf ...
... Quantum phase transitions occur at zero temperature upon variation of some nonthermal control parameters. The Ising chain in a transverse field is a textbook model undergoing such a transition, from ferromagnetic to paramagnetic state. This model can be exactly solved by using a Jordan-Wigner transf ...
Annual Inventory Report - Risk Management Services
... Date Received Name of Receiver Name of Permit Holder Wipe Test Results of: Outside & Inside of Shipping Container and Vial (CPM) ...
... Date Received Name of Receiver Name of Permit Holder Wipe Test Results of: Outside & Inside of Shipping Container and Vial (CPM) ...
Phase Transformations
... • Provide a fine distribution of alloy carbides during tempering • ↑ resistance to softening on tempering • ↑ corrosion and oxidation resistance • ↑ strength at high temperatures • Strengthen steels that cannot be quenched • Make easier to obtain the properties throughout a larger section • ↑ Elasti ...
... • Provide a fine distribution of alloy carbides during tempering • ↑ resistance to softening on tempering • ↑ corrosion and oxidation resistance • ↑ strength at high temperatures • Strengthen steels that cannot be quenched • Make easier to obtain the properties throughout a larger section • ↑ Elasti ...
Lecture 2: Basics / Lawson
... this electric field (since it would give a zero field) Valid when length scales of the phenomena are larger than the Debye length The current is divergence free The displacement current is neglected (this assumption restricts us to low frequency waves: no light waves). ...
... this electric field (since it would give a zero field) Valid when length scales of the phenomena are larger than the Debye length The current is divergence free The displacement current is neglected (this assumption restricts us to low frequency waves: no light waves). ...
Lecture 38
... The mass of an atom is 1) approximately equally divided between neutrons, protons, and electrons 2) evenly divided between the nucleus and the surrounding electron cloud 3) concentrated in the cloud of electrons surrounding the nucleus 4) concentrated in the nucleus ...
... The mass of an atom is 1) approximately equally divided between neutrons, protons, and electrons 2) evenly divided between the nucleus and the surrounding electron cloud 3) concentrated in the cloud of electrons surrounding the nucleus 4) concentrated in the nucleus ...
Exercises in Statistical Mechanics ====== [A] Ensemble Theory - classical gases
... (d) Show that the isothermal compressibility κT = − V1 ∂V ∂P T is always positive. A16. 1. An ideal gas of classical charged particles with mass m is confined between two capacitor plates of area A, separated by distance L. The capacitors produce a force f perpendicular to the plates which pushes th ...
... (d) Show that the isothermal compressibility κT = − V1 ∂V ∂P T is always positive. A16. 1. An ideal gas of classical charged particles with mass m is confined between two capacitor plates of area A, separated by distance L. The capacitors produce a force f perpendicular to the plates which pushes th ...
Міністерство охорони здоров`я України
... dispersion of substances in the solutions can be different. Particle size is a very important feature which causes many physical and chemical properties of the solutions. According to the particle size solutions can be classified as: 1) true solutions (particle size is less than 10-9 m), which can ...
... dispersion of substances in the solutions can be different. Particle size is a very important feature which causes many physical and chemical properties of the solutions. According to the particle size solutions can be classified as: 1) true solutions (particle size is less than 10-9 m), which can ...
Chemistry COS 2011-2012
... Atoms are made up of a nucleus of protons and neutrons which are surrounded by a cloud of charged electrons. Inside of an atom, neutrons have no charge, while protons are positively charges and electrons are negatively charged. Protons and electrons exist in equal quantities in all atoms, so the ove ...
... Atoms are made up of a nucleus of protons and neutrons which are surrounded by a cloud of charged electrons. Inside of an atom, neutrons have no charge, while protons are positively charges and electrons are negatively charged. Protons and electrons exist in equal quantities in all atoms, so the ove ...
Pressure - Peoria Public Schools
... REACTION OF GASES Gases react in whole-number ratios according to their volumes For example, 2 volumes of hydrogen react with 1 volume of oxygen to yield 2 volumes of water vapor This means that when looking at reactions of gases, the coefficients in a balanced chemical equation reflect the ratio o ...
... REACTION OF GASES Gases react in whole-number ratios according to their volumes For example, 2 volumes of hydrogen react with 1 volume of oxygen to yield 2 volumes of water vapor This means that when looking at reactions of gases, the coefficients in a balanced chemical equation reflect the ratio o ...
Parallel Permittivity Elements for Radio Frequency Waves in
... magnetization parameter. The expressions (28-30) have a natural limit to the corresponding results for tokamaks with elliptic magnetic surfaces (section IV) if d = 0, and circular magnetic surfaces (section V) if b = a and λ → 0. Our dielectric characteristics can be applied for both large and low a ...
... magnetization parameter. The expressions (28-30) have a natural limit to the corresponding results for tokamaks with elliptic magnetic surfaces (section IV) if d = 0, and circular magnetic surfaces (section V) if b = a and λ → 0. Our dielectric characteristics can be applied for both large and low a ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).













![Exercises in Statistical Mechanics ====== [A] Ensemble Theory - classical gases](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008930195_1-676e1e74f116b78f858c4cb735f7e085-300x300.png)







