Standard Thermodynamic Functions of Reaction
... The standard enthalpy of formation of gaseous formaldehyde H2CO(g) at 307 K, symbolized by is the standard enthalpy change for the process; ...
... The standard enthalpy of formation of gaseous formaldehyde H2CO(g) at 307 K, symbolized by is the standard enthalpy change for the process; ...
Particle detectors - Teaching Advanced Physics
... Getting just the snap you want The trouble with holiday snaps is that often you don’t have your camera ready when something interesting happens. The trouble with cloud and bubble chambers is that they have to be ‘primed’ to be ready (by expanding the gas or reducing the pressure on the liquid). The ...
... Getting just the snap you want The trouble with holiday snaps is that often you don’t have your camera ready when something interesting happens. The trouble with cloud and bubble chambers is that they have to be ‘primed’ to be ready (by expanding the gas or reducing the pressure on the liquid). The ...
The development of Physics and Modern Physics
... electromotive force that could continue to drive electrically charged particles had to await the development of the chemical battery by the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta in 1800. The classical theory of a simple electric circuit assumes that the two terminals of a battery are maintained positiv ...
... electromotive force that could continue to drive electrically charged particles had to await the development of the chemical battery by the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta in 1800. The classical theory of a simple electric circuit assumes that the two terminals of a battery are maintained positiv ...
Physics - USM-Rocks
... electromotive force that could continue to drive electrically charged particles had to await the development of the chemical battery by the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta in 1800. The classical theory of a simple electric circuit assumes that the two terminals of a battery are maintained positiv ...
... electromotive force that could continue to drive electrically charged particles had to await the development of the chemical battery by the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta in 1800. The classical theory of a simple electric circuit assumes that the two terminals of a battery are maintained positiv ...
Lecture Slides - School of Chemical Sciences
... Why Thermodynamics? The macroscopic description of a system of ~1023 particles may involve only a few variables! “Simple systems”: Macroscopically homogeneous, isotropic, uncharged, large enough that surface effects can be neglected, not acted upon by electric, magnetic, or gravitational fields. ...
... Why Thermodynamics? The macroscopic description of a system of ~1023 particles may involve only a few variables! “Simple systems”: Macroscopically homogeneous, isotropic, uncharged, large enough that surface effects can be neglected, not acted upon by electric, magnetic, or gravitational fields. ...
1 MATTER: Anything which occupies space , has volume and can
... Coordination number is the number of nearest neighbours of any particle. CN for simple cubic (SCC) =6, BCC =8, FCC (hcp or ccp) = 12. Q1. A compound formed by elements A and B has a cubic structure in which A atoms are at the corners of the cube and B atoms are at the face centres. Derive the formul ...
... Coordination number is the number of nearest neighbours of any particle. CN for simple cubic (SCC) =6, BCC =8, FCC (hcp or ccp) = 12. Q1. A compound formed by elements A and B has a cubic structure in which A atoms are at the corners of the cube and B atoms are at the face centres. Derive the formul ...
Slide 1
... then increasingly slowly – until its temperature equals that of its surroundings. Similarly, a cool body placed in a warmer environment will increase in temperature until its temperature equals that of its surroundings. Q: What is being exchanged between the body and its surroundings that causes thi ...
... then increasingly slowly – until its temperature equals that of its surroundings. Similarly, a cool body placed in a warmer environment will increase in temperature until its temperature equals that of its surroundings. Q: What is being exchanged between the body and its surroundings that causes thi ...
Solubility Main article: Solvation The ability of one compound to
... interactions are unfavorable, then the free energy decreases with increasing solute concentration. At some point the energy loss outweighs the entropy gain, and no more solute particles can be dissolved; the solution is said to be saturated. However, the point at which a solution can become saturate ...
... interactions are unfavorable, then the free energy decreases with increasing solute concentration. At some point the energy loss outweighs the entropy gain, and no more solute particles can be dissolved; the solution is said to be saturated. However, the point at which a solution can become saturate ...
How do we distinguish substances?
... In a pressure-temperature phase diagram like that shown in Figure 1.5, the transition lines not only define the specific temperature and pressure at which a phase change will occur but they also specify the conditions under which the two phases can simultaneously exist as stable phases. It is common ...
... In a pressure-temperature phase diagram like that shown in Figure 1.5, the transition lines not only define the specific temperature and pressure at which a phase change will occur but they also specify the conditions under which the two phases can simultaneously exist as stable phases. It is common ...
MATERIALS
... F. Inert He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn have 8 electrons in shells 1-6, respectively (except for He). ...
... F. Inert He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn have 8 electrons in shells 1-6, respectively (except for He). ...
WHAT IS A MOLE?
... total number of blood cells found in every human on earth. 1 Liter bottle of Water contains 55.5 moles H20 ...
... total number of blood cells found in every human on earth. 1 Liter bottle of Water contains 55.5 moles H20 ...
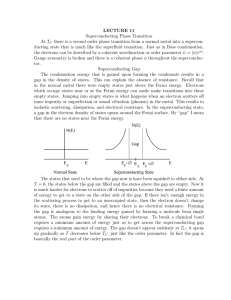
LECTURE 11 Superconducting Phase Transition At TC there is a
... The condensation energy that is gained upon forming the condensate results in a gap in the density of states. This can explain the absence of resistance. Recall that in the normal metal there were empty states just above the Fermi energy. Electrons which occupy states near or at the Fermi energy can ...
... The condensation energy that is gained upon forming the condensate results in a gap in the density of states. This can explain the absence of resistance. Recall that in the normal metal there were empty states just above the Fermi energy. Electrons which occupy states near or at the Fermi energy can ...
Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids
... Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids ...
... Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids ...
Thermionic phenomena and the laws which govern them O W. R
... been got rid of, there may be another more stable emission characteristic of the substance itself. There is a third type which is a direct result of interaction between the heated solid and the surrounding gas. I devoted a good deal of time between 1904 and 1912 to the investigation of these effects ...
... been got rid of, there may be another more stable emission characteristic of the substance itself. There is a third type which is a direct result of interaction between the heated solid and the surrounding gas. I devoted a good deal of time between 1904 and 1912 to the investigation of these effects ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).