Document
... you to a birthday party! 50 years ago, Illinois alumnus Nick Holonyak Jr. demonstrated the first visible light-emitting diode (LED) while working at GE. Holonyak returned to Illinois as a professor in 1963, and has been unveiling new inventions on our campus ever since. Today, the LED he demonstrate ...
... you to a birthday party! 50 years ago, Illinois alumnus Nick Holonyak Jr. demonstrated the first visible light-emitting diode (LED) while working at GE. Holonyak returned to Illinois as a professor in 1963, and has been unveiling new inventions on our campus ever since. Today, the LED he demonstrate ...
The Gaseous State - Soegijapranata Catholic University
... • Ionic compounds can’t be present in gas state under normal condition (25oC, 1atm). But they can be converted to gas at high temperature. Ex: NaCl • Molecular compounds such as CO, CO2, HCl, NH3, CH4 are gases. The majority of molecular compounds are solid or liquid under room temp. Heating can con ...
... • Ionic compounds can’t be present in gas state under normal condition (25oC, 1atm). But they can be converted to gas at high temperature. Ex: NaCl • Molecular compounds such as CO, CO2, HCl, NH3, CH4 are gases. The majority of molecular compounds are solid or liquid under room temp. Heating can con ...
Statistical Physics Problem Sets 3–4: Kinetic Theory xford hysics
... 4.6 a) Obtain an expression for the thermal conductivity of a classical ideal gas. Show that it depends only on temperature and the properties of individual gas molecules. b) The thermal conductivity of argon (atomic weight 40) at S.T.P. is 1.6×10−2 Wm−1 K−1 . Use this to calculate the mean free pat ...
... 4.6 a) Obtain an expression for the thermal conductivity of a classical ideal gas. Show that it depends only on temperature and the properties of individual gas molecules. b) The thermal conductivity of argon (atomic weight 40) at S.T.P. is 1.6×10−2 Wm−1 K−1 . Use this to calculate the mean free pat ...
Surface chemistry Surface chemistry deals with phenomena that
... is prevented by some suitable means, it is observed that the dispersion medium begins to move in an electric field. This phenomenon is termed electroosmosis. (vii) Coagulation or precipitation: The process of settling of colloidal particles is called coagulation or precipitation of the sol. Protecti ...
... is prevented by some suitable means, it is observed that the dispersion medium begins to move in an electric field. This phenomenon is termed electroosmosis. (vii) Coagulation or precipitation: The process of settling of colloidal particles is called coagulation or precipitation of the sol. Protecti ...
Molecular Models Lab
... pair of "dots" or a pair of electrons is used to represent a single covalent bond. The hydrogen molecule is shown a H:H. In structural formulas, a single covalent bond is represented by a straight line. The hydrogen molecule is H-H. Although such "models" help us in understanding the structure of mo ...
... pair of "dots" or a pair of electrons is used to represent a single covalent bond. The hydrogen molecule is shown a H:H. In structural formulas, a single covalent bond is represented by a straight line. The hydrogen molecule is H-H. Although such "models" help us in understanding the structure of mo ...
PPT
... Example: Nuclear Spin and MRI Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) depends on the absorption of electromagnetic radiation by the nuclear spin of the hydrogen atoms in our bodies. The nucleus is a proton with spin ½, so in a magnetic field B there are two energy states. The proton’s magnetic moment is m ...
... Example: Nuclear Spin and MRI Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) depends on the absorption of electromagnetic radiation by the nuclear spin of the hydrogen atoms in our bodies. The nucleus is a proton with spin ½, so in a magnetic field B there are two energy states. The proton’s magnetic moment is m ...
Motivation and Objectives
... magnetic fields. The radial magnetic field acts to impede the flow of electrons from cathode to anode. The electrons are trapped near the exit of a coaxial acceleration channel. The crossed fields produce a net Hall electron current. The trapped electrons act as a volumetric zone of ionization for n ...
... magnetic fields. The radial magnetic field acts to impede the flow of electrons from cathode to anode. The electrons are trapped near the exit of a coaxial acceleration channel. The crossed fields produce a net Hall electron current. The trapped electrons act as a volumetric zone of ionization for n ...
EFFECT OF EXTERNAL FIELDS ON THE
... value can not only lead to a relative change in the characteristic quantities (for example, the osmotic pressure and the latent heat of transition) that is approximately 100 times greater than in(ll but also cause qualitative changes: if the solution in the absence of the field was endothermal (exot ...
... value can not only lead to a relative change in the characteristic quantities (for example, the osmotic pressure and the latent heat of transition) that is approximately 100 times greater than in(ll but also cause qualitative changes: if the solution in the absence of the field was endothermal (exot ...
Magnetic properties of materials Part 1. Introduction to magnetism
... into the crystal structure and does not respond to an applied magnetic field (this is known as quenching of the orbital moment). Such environmental effects can be bundled into the electron g-factor, so this takes values that will differ slightly from 2, depending on the precise environment of the el ...
... into the crystal structure and does not respond to an applied magnetic field (this is known as quenching of the orbital moment). Such environmental effects can be bundled into the electron g-factor, so this takes values that will differ slightly from 2, depending on the precise environment of the el ...
September 6th, 2007
... The first two, intrinsic electron spin and orbital momentum both are “permanent” magnetic moments and magnetization occurs when these align with the external field. The last source of magnetic moment leads to diamagnetism. The relationship between an applied field and the magnetization is the magnet ...
... The first two, intrinsic electron spin and orbital momentum both are “permanent” magnetic moments and magnetization occurs when these align with the external field. The last source of magnetic moment leads to diamagnetism. The relationship between an applied field and the magnetization is the magnet ...
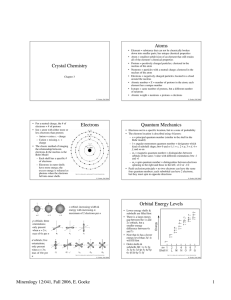
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Bonding: Ionic vs
... Guidelines for Drawing Lewis Structures Underlying criteria: “Octet Rule”: Kind of like the Pirate Code General Scheme: (CH2Cl2 and CO2 as examples) 1. Determine arrangement of atoms (skeletal structure)…HOW? • Central vs peripheral (terminal) atoms 2. Determine total # of valence e-…HOW? 3. Draw s ...
... Guidelines for Drawing Lewis Structures Underlying criteria: “Octet Rule”: Kind of like the Pirate Code General Scheme: (CH2Cl2 and CO2 as examples) 1. Determine arrangement of atoms (skeletal structure)…HOW? • Central vs peripheral (terminal) atoms 2. Determine total # of valence e-…HOW? 3. Draw s ...
1 mole
... the number of atoms in 16 g of oxygen, in 4 grams of He, in 32 g of sulfur, etc. the number of molecules in the molecular weight, in grams, of any compound. the number of molecules in 18 g of water, in 40 g of lithium carbide. Much later, a mole, that equal number, was found to be 6.022 x 1023(repre ...
... the number of atoms in 16 g of oxygen, in 4 grams of He, in 32 g of sulfur, etc. the number of molecules in the molecular weight, in grams, of any compound. the number of molecules in 18 g of water, in 40 g of lithium carbide. Much later, a mole, that equal number, was found to be 6.022 x 1023(repre ...
Bennett - Materials Computation Center
... newly discovered form of matter called a Bose-Einstein condensate may point the way ahead.” The Economist: 5-6-2006, Vol. 379 Issue 8476, p79-80 “One qubit at a time” ...
... newly discovered form of matter called a Bose-Einstein condensate may point the way ahead.” The Economist: 5-6-2006, Vol. 379 Issue 8476, p79-80 “One qubit at a time” ...
Thursday, January 22
... 2100 cm2 (2 significant figures) 2060 cm2 (3 significant figures) 2.10 x 103 cm2 (3 significant figures) 2060. cm2 (4 significant figures) ...
... 2100 cm2 (2 significant figures) 2060 cm2 (3 significant figures) 2.10 x 103 cm2 (3 significant figures) 2060. cm2 (4 significant figures) ...
Introduction to Nanoscience
... A nanodevice that often appears in science fiction is a nanocamera. This is used to view the inside of the body or in other confined spaces where an ordinary camera would not fit. Unfortunately, it is not possible to make such a camera using conventional far field optics. Light sources and light det ...
... A nanodevice that often appears in science fiction is a nanocamera. This is used to view the inside of the body or in other confined spaces where an ordinary camera would not fit. Unfortunately, it is not possible to make such a camera using conventional far field optics. Light sources and light det ...
rapid recombination of plasma jets
... tially no change in ionization, the gas density N atoms or ions with several discrete levels, the and temperature T are related by TN 1- 'Y = canst. populations of which are much smaller than those For a monatomic gas and for a fully ionized plasma given by the Saha formula for a given density N and ...
... tially no change in ionization, the gas density N atoms or ions with several discrete levels, the and temperature T are related by TN 1- 'Y = canst. populations of which are much smaller than those For a monatomic gas and for a fully ionized plasma given by the Saha formula for a given density N and ...
Dr. Ali Abadi Lecture 1 Materials Properties CH. 1: Structure of
... electron → high electronegativity. Metals are electropositive – they can give up their few valence electrons to become positively charged ions. The electron volt (eV) – energy unit convenient for description of atomic bonding Electron volt - the energy lost / gained by an electron when it is taken t ...
... electron → high electronegativity. Metals are electropositive – they can give up their few valence electrons to become positively charged ions. The electron volt (eV) – energy unit convenient for description of atomic bonding Electron volt - the energy lost / gained by an electron when it is taken t ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).