NEURAL ACTIVITY RELATED TO ANTICIPATED REWARD:
... performed a variable-delay version of the memory guided saccade task. A cue presented early in each trial indicated whether the delay intervening before the monkey could make a saccade and receive a reward would be long (2500 ms) or short (500 ms). The essential behavioral finding was that monkeys w ...
... performed a variable-delay version of the memory guided saccade task. A cue presented early in each trial indicated whether the delay intervening before the monkey could make a saccade and receive a reward would be long (2500 ms) or short (500 ms). The essential behavioral finding was that monkeys w ...
Functional Heterogeneity in the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis
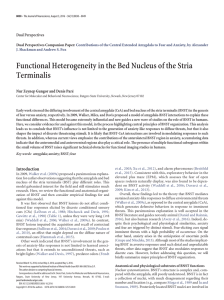
... case of the corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) cells located in the oval nucleus (Sakanaka et al., 1987; Phelix and Paull, 1990), which also express a fast inwardly rectifying K ⫹ conductance (known as Type III cells; Fig. 3C) (Dabrowska et al., 2013a; but see Silberman et al., 2013). It should be ...
... case of the corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) cells located in the oval nucleus (Sakanaka et al., 1987; Phelix and Paull, 1990), which also express a fast inwardly rectifying K ⫹ conductance (known as Type III cells; Fig. 3C) (Dabrowska et al., 2013a; but see Silberman et al., 2013). It should be ...
Module 1 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • neither participants nor researchers know which group is receiving which treatment • Rule 6: Measure – by manipulating the treatment so that the experimental group receives a different treatment than the control group, researchers are able to measure how the independent variable (treatment) affect ...
... • neither participants nor researchers know which group is receiving which treatment • Rule 6: Measure – by manipulating the treatment so that the experimental group receives a different treatment than the control group, researchers are able to measure how the independent variable (treatment) affect ...
What Can an Orbitofrontal Cortex- Endowed Animal
... action potentials to electrical stimulation of the olfactory bulb.5 From electrophysiological recordings in rodents, it is evident that these same structures are involved in olfactory discrimination learning,6,7 lending support to the idea that the OFC of “sub-primate” mammals was chiefly dedicated ...
... action potentials to electrical stimulation of the olfactory bulb.5 From electrophysiological recordings in rodents, it is evident that these same structures are involved in olfactory discrimination learning,6,7 lending support to the idea that the OFC of “sub-primate” mammals was chiefly dedicated ...
World of Children 1st ed
... This multimedia product and its content are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: ...
... This multimedia product and its content are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: ...
The History of the EEG
... • Overall increase of coherence for recalled vs. not recalled nouns • Long range synchronization of frontal and temporal/parietal neuronal assemblies increases for recalled nouns. ...
... • Overall increase of coherence for recalled vs. not recalled nouns • Long range synchronization of frontal and temporal/parietal neuronal assemblies increases for recalled nouns. ...
Takehiro Matsumora, Kowa Koida and Hidehiko Komatsu
... set (color #4) was selected as the point where neural responses sharply changed; in other words, the point where the tuning curve had a large slope. This was because it has been shown that sensory neurons exhibit the greatest ability to discriminate around the point where the tuning curve is steepes ...
... set (color #4) was selected as the point where neural responses sharply changed; in other words, the point where the tuning curve had a large slope. This was because it has been shown that sensory neurons exhibit the greatest ability to discriminate around the point where the tuning curve is steepes ...
The cognitive neuroscience of sustained attention
... lower neural levels of description benefits from neuroscientific research approaches, and that efforts to determine low-level neuronal mechanisms of cognitive functions benefit from cognitive construct-driven research in humans [25,63,76]. Furthermore, it is crucial that evidence in support of neuro ...
... lower neural levels of description benefits from neuroscientific research approaches, and that efforts to determine low-level neuronal mechanisms of cognitive functions benefit from cognitive construct-driven research in humans [25,63,76]. Furthermore, it is crucial that evidence in support of neuro ...
Specificity and Plasticity of Thalamocortical Connections in Sema6A
... A dynamic interplay exists between the processes of cortical arealization and those controlling the guidance and targeting of thalamocortical projections [1–5]. Early in development, both the thalamic field and the cortical sheet appear homogeneous in cytoarchitecture, and connections between them fo ...
... A dynamic interplay exists between the processes of cortical arealization and those controlling the guidance and targeting of thalamocortical projections [1–5]. Early in development, both the thalamic field and the cortical sheet appear homogeneous in cytoarchitecture, and connections between them fo ...
Neuronal polarity: establishing and maintaining the axon initial
... electric signal transfer, however since axons can be much longer than dendrites this transfer must be more faithful and stronger. Therefore axons have a system that boots the electric signal to sustain the same membrane potential as it travels along the axon. This boosted electric signal in the axon ...
... electric signal transfer, however since axons can be much longer than dendrites this transfer must be more faithful and stronger. Therefore axons have a system that boots the electric signal to sustain the same membrane potential as it travels along the axon. This boosted electric signal in the axon ...
Human Biology I - Control and Development
... How Neurons Work Most synapses are chemical synapses. Chemical synapses allow for a finer degree of control. When the action potential reaches the end of the axon, the neuron releases a chemical messenger called a neurotransmitter into the space between the neuron and the target cell. Neurotransmit ...
... How Neurons Work Most synapses are chemical synapses. Chemical synapses allow for a finer degree of control. When the action potential reaches the end of the axon, the neuron releases a chemical messenger called a neurotransmitter into the space between the neuron and the target cell. Neurotransmit ...
Delayed Puberty but Normal Fertility in Mice With Selective Deletion
... plays a pivotal role in the regulation of reproduction. Indeed, insulin has been shown to activate GnRH and LH secretion in vitro (8, 9). Mice that lack insulin signaling in brain neurons (NIRKO mice) exhibit hypothalamic hypogonadism (10) and a delay in puberty (11). Moreover, diabetic rats display ...
... plays a pivotal role in the regulation of reproduction. Indeed, insulin has been shown to activate GnRH and LH secretion in vitro (8, 9). Mice that lack insulin signaling in brain neurons (NIRKO mice) exhibit hypothalamic hypogonadism (10) and a delay in puberty (11). Moreover, diabetic rats display ...
- Wiley Online Library
... specifically from damage to the distal motor axon and not from activation of the cell death pathway (Gould et al. 2006). These studies separate axonal degeneration from neuronal cell death and indicate that axonal degeneration is the leading cause of the disease. Finally, axonal degeneration also occ ...
... specifically from damage to the distal motor axon and not from activation of the cell death pathway (Gould et al. 2006). These studies separate axonal degeneration from neuronal cell death and indicate that axonal degeneration is the leading cause of the disease. Finally, axonal degeneration also occ ...
DCN principal cells respond to spectral edges, which requires additional inhibitory effects in DCN
... sensitivity seen in the ICC could be derived from the DCN. Type IV neurons receive inhibitory inputs from type II interneurons with lower best frequencies (BFs) than the excitatory inputs to type IVs from the auditory nerve (AN) (Voigt and Young, 1990; Spirou and Young, 1991), an arrangement that co ...
... sensitivity seen in the ICC could be derived from the DCN. Type IV neurons receive inhibitory inputs from type II interneurons with lower best frequencies (BFs) than the excitatory inputs to type IVs from the auditory nerve (AN) (Voigt and Young, 1990; Spirou and Young, 1991), an arrangement that co ...
Dopamine Receptor–Mediated Mechanisms Involved in the
... increase of regional blood flow in the putamen and globus pallidus in the process of learning sequential finger movements. Matsumoto et al. (1994) showed that there is a selective impairment of learning arm movement sequences after destruction of the nigrostriatal DA system by local infusion of dopa ...
... increase of regional blood flow in the putamen and globus pallidus in the process of learning sequential finger movements. Matsumoto et al. (1994) showed that there is a selective impairment of learning arm movement sequences after destruction of the nigrostriatal DA system by local infusion of dopa ...
What can mice tell us about how vision works?
... Understanding the neural basis of visual perception is a long-standing fundamental goal of neuroscience. Historically, most vision studies were carried out on humans, macaques and cats. Over the past 5 years, however, a growing number of researchers have begun using mice to parse the mechanisms unde ...
... Understanding the neural basis of visual perception is a long-standing fundamental goal of neuroscience. Historically, most vision studies were carried out on humans, macaques and cats. Over the past 5 years, however, a growing number of researchers have begun using mice to parse the mechanisms unde ...
Open interconnected model of basal ganglia
... neurodegenerative disorder of midlife onset, characterized clinically by prominent motor dysfunction, cognitive deterioration, affective and psychiatric symptoms.1,15,49–51 Despite the recent discovery of the genetic mutation associated with HD, the biochemical basis of HD pathogenesis and of the di ...
... neurodegenerative disorder of midlife onset, characterized clinically by prominent motor dysfunction, cognitive deterioration, affective and psychiatric symptoms.1,15,49–51 Despite the recent discovery of the genetic mutation associated with HD, the biochemical basis of HD pathogenesis and of the di ...
Leptin Receptor Signaling and Action in the Central Nervous System
... db/db mice) in rodents and humans results in increased food intake in combination with a phenotype of reduced energy expenditure reminiscent of the neuroendocrine starvation response (1,2,4). Leptin also regulates insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis by two mechanisms: one by controlling ener ...
... db/db mice) in rodents and humans results in increased food intake in combination with a phenotype of reduced energy expenditure reminiscent of the neuroendocrine starvation response (1,2,4). Leptin also regulates insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis by two mechanisms: one by controlling ener ...
Exposure to As-, Cd-, and Pb-Mixture Induces Ab, Amyloidogenic
... 0.38, 0.098, and 0.22 ppm or 10 times of each, respectively, from gestation-05 to postnatal day-180. We identified dosedependent increase in amyloid-beta (Ab) in frontal cortex and hippocampus as early as post-weaning. The effect was strongly significant during early-adulthood, reaching levels compa ...
... 0.38, 0.098, and 0.22 ppm or 10 times of each, respectively, from gestation-05 to postnatal day-180. We identified dosedependent increase in amyloid-beta (Ab) in frontal cortex and hippocampus as early as post-weaning. The effect was strongly significant during early-adulthood, reaching levels compa ...
- Wiley Online Library
... to individualize owing to its small size and position, which led to the fusion with larger subnuclei. In this case, the intermediate subnucleus was mainly fused to the dorsal subnucleus, which comprised its ventrolateral portion, although fusions with the lateral subnucleus were also frequent. In so ...
... to individualize owing to its small size and position, which led to the fusion with larger subnuclei. In this case, the intermediate subnucleus was mainly fused to the dorsal subnucleus, which comprised its ventrolateral portion, although fusions with the lateral subnucleus were also frequent. In so ...
Essential Roles for GSK-3s and GSK-3
... approach is whether suppression of both GSK-3a and b activities promotes or inhibits axon growth. We have therefore assessed the role of GSK-3s in the regulation of axon morphogenesis by the careful selection of inhibitors, determining effects over a wide range of concentrations, and by constructing ...
... approach is whether suppression of both GSK-3a and b activities promotes or inhibits axon growth. We have therefore assessed the role of GSK-3s in the regulation of axon morphogenesis by the careful selection of inhibitors, determining effects over a wide range of concentrations, and by constructing ...
The Use of Cross-Correlation Mapping in Identifying Backwards Projecting Connections between Visual Cortical Areas
... neural data, the consistently decreasing / converging behavior of CCM output identifies functional connectivity–further evidenced by the lack of convergence in the 0 −− > 4 CCM run–while the values at convergence allow for the ranking of connectivities in a network. In our testing of various network ...
... neural data, the consistently decreasing / converging behavior of CCM output identifies functional connectivity–further evidenced by the lack of convergence in the 0 −− > 4 CCM run–while the values at convergence allow for the ranking of connectivities in a network. In our testing of various network ...
The Three Amnesias - University of Florida College of Public Health
... Despite a few clues in earlier literature, it came as a complete surprise in the early 1950’s that bilateral medial temporal resection caused amnesia. The importance of the thalamus in memory was hardly suspected until the 1970’s and the basal forebrain was an area virtually unknown to clinicians be ...
... Despite a few clues in earlier literature, it came as a complete surprise in the early 1950’s that bilateral medial temporal resection caused amnesia. The importance of the thalamus in memory was hardly suspected until the 1970’s and the basal forebrain was an area virtually unknown to clinicians be ...
Identification of key signaling molecules involved - diss.fu
... Thermoregulation is a crucial homeostatic function orchestrated by the central nervous system for all homothermic animals to obtain an optimal thermal environment. The thermoregulatory center of homothermic animals is located in the preoptic area of the hypothalamus, which not only receives the temp ...
... Thermoregulation is a crucial homeostatic function orchestrated by the central nervous system for all homothermic animals to obtain an optimal thermal environment. The thermoregulatory center of homothermic animals is located in the preoptic area of the hypothalamus, which not only receives the temp ...
Bischoff_Thesis_notes
... internally generated sequences pre-SMA receives connections from prefrontal cortex, area 46 area F5 and anterior cingulate cortex externally generated sequences o Prefrontal learning of new sequences she says that in the DAJ model, prefrontal activity increased as the sequences were lear ...
... internally generated sequences pre-SMA receives connections from prefrontal cortex, area 46 area F5 and anterior cingulate cortex externally generated sequences o Prefrontal learning of new sequences she says that in the DAJ model, prefrontal activity increased as the sequences were lear ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.