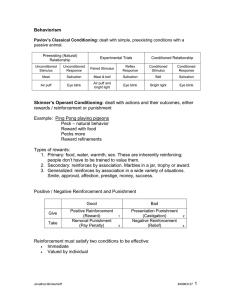
Behaviorism
... 3. Don’t get angry – keep the responsibility where it belongs. Effective: I’m sorry you’ve made the choice to loose part of your recess. Ineffective: How many times will I have to tell you to stop talking? 4. Don’t argue or debate 5. Accept feelings, then state the sad truth. I can see you’re upse ...
... 3. Don’t get angry – keep the responsibility where it belongs. Effective: I’m sorry you’ve made the choice to loose part of your recess. Ineffective: How many times will I have to tell you to stop talking? 4. Don’t argue or debate 5. Accept feelings, then state the sad truth. I can see you’re upse ...
Rat Maze - FTHS Wiki
... response and its consequence Type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment Law of Effect Thorndike’s principle that behaviors ...
... response and its consequence Type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment Law of Effect Thorndike’s principle that behaviors ...
Rat Maze - FTHS Wiki
... response and its consequence Type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment Law of Effect Thorndike’s principle that behaviors ...
... response and its consequence Type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment Law of Effect Thorndike’s principle that behaviors ...
Chapter 8 pt. 2: Operant Conditioning and Social Learning
... Ex: rats that were not reinforced while in a maze could navigate it just as fast when there was a reward put at the end. ...
... Ex: rats that were not reinforced while in a maze could navigate it just as fast when there was a reward put at the end. ...
Operant Conditioning
... Operant Conditioning - Punishments! Punishment: any event that follows a response and decreases its likelihood of occurring again Positive punishment = adding a stimulus, weakens likelihood of re-occurrence Negative punishment = taking away a stimulus, weakens likelihood of re-occurrence ...
... Operant Conditioning - Punishments! Punishment: any event that follows a response and decreases its likelihood of occurring again Positive punishment = adding a stimulus, weakens likelihood of re-occurrence Negative punishment = taking away a stimulus, weakens likelihood of re-occurrence ...
Foundations of Individual Behaviour
... Any relatively permanent change in behaviour that occurs as a result of experience. – First, learning involves change. – Second, the change must be relatively permanent. – Third, our definition is concerned with behavior. – Finally, some form of experience is necessary for learning. ...
... Any relatively permanent change in behaviour that occurs as a result of experience. – First, learning involves change. – Second, the change must be relatively permanent. – Third, our definition is concerned with behavior. – Finally, some form of experience is necessary for learning. ...
Psychology Chapter 19: Group Interaction
... 2. Social Psychologists – study groups and how they influence behavior 3. Developmental Psychologists – study physical, emotional, cognitive and social changes that occur throughout life a) They study children, the elderly and the process of dying for example 4. Educational Psychologists – deal with ...
... 2. Social Psychologists – study groups and how they influence behavior 3. Developmental Psychologists – study physical, emotional, cognitive and social changes that occur throughout life a) They study children, the elderly and the process of dying for example 4. Educational Psychologists – deal with ...
classical conditioning Study Sheet
... Your first question in analyzing a behavior should be whether the behavior is an automatic reflex or a voluntary choice. An automatic reflex is just that: It is triggered automatically by a stimulus and the subject has no control over the response. In most cases, this type of behavior is easy to spo ...
... Your first question in analyzing a behavior should be whether the behavior is an automatic reflex or a voluntary choice. An automatic reflex is just that: It is triggered automatically by a stimulus and the subject has no control over the response. In most cases, this type of behavior is easy to spo ...
07Learning
... • Who developed operant conditioning? • How does operant conditioning differ from classical conditioning? • What is an example of positive and negative reinforcement? • What is an an example of five reinforcement schedules? • What is an example of shaping? ...
... • Who developed operant conditioning? • How does operant conditioning differ from classical conditioning? • What is an example of positive and negative reinforcement? • What is an an example of five reinforcement schedules? • What is an example of shaping? ...
UNIT 6: Learning - Spokane Public Schools
... Taste aversion: classically conditioned avoidance of a certain food or taste that makes/made a person sick Can treat alcoholism using the drug Antabuse 1.physical/medical phenomena = conditioning in order to boost the immune system Chemotherapy as a medical example -anticipating nausea: classically ...
... Taste aversion: classically conditioned avoidance of a certain food or taste that makes/made a person sick Can treat alcoholism using the drug Antabuse 1.physical/medical phenomena = conditioning in order to boost the immune system Chemotherapy as a medical example -anticipating nausea: classically ...
Behaviorism close reading
... role of nature over nurture. For example, chromosomes and hormones (testosterone) influence our behavior too, in addition to the environment. Cognitive psychology states that mediation processes occur between stimulus and response, such as memory, thinking, problem solving etc. Despite these critici ...
... role of nature over nurture. For example, chromosomes and hormones (testosterone) influence our behavior too, in addition to the environment. Cognitive psychology states that mediation processes occur between stimulus and response, such as memory, thinking, problem solving etc. Despite these critici ...
Chapter 9 Applied Behaviorism
... c. minimal attention to larger social systems like society or its culture and institutions 6. How are resources and their flow conceptualized? a. resources include 1. all activities, people, objects, events (and experiences) that can be associated with a behavior as a punisher or reinforcer are pote ...
... c. minimal attention to larger social systems like society or its culture and institutions 6. How are resources and their flow conceptualized? a. resources include 1. all activities, people, objects, events (and experiences) that can be associated with a behavior as a punisher or reinforcer are pote ...
Animal Behavior : Ethology
... • Involves how organisms react (respond) and cope to the stimuli from the environment. Everything an animal does. Two types of Explanations: Proximate Causes: -focuses on the “how” a behavior is formed -triggered by environmental stimuli -involves genetic, physiological, & anatomical mechanisms. Ult ...
... • Involves how organisms react (respond) and cope to the stimuli from the environment. Everything an animal does. Two types of Explanations: Proximate Causes: -focuses on the “how” a behavior is formed -triggered by environmental stimuli -involves genetic, physiological, & anatomical mechanisms. Ult ...
A Brief Explanation of Applied Behavior Analysis
... behavior followed by an aversive consequence is less likely to occur in the future (punishment). The focus of ABA is on the presentation of consequences that will increase the likelihood of the behavior occurring in the future. ABA does not advocate the presentation of aversive stimuli to reduce the ...
... behavior followed by an aversive consequence is less likely to occur in the future (punishment). The focus of ABA is on the presentation of consequences that will increase the likelihood of the behavior occurring in the future. ABA does not advocate the presentation of aversive stimuli to reduce the ...
BEHAVIORISM JOHN BROADUS WATSON (1878
... FIXED RATIO SCHEDULES- a fixed number of correct responses must occur before reinforcement may recur. Ex. The bird will be given food (reinforcer) everytime it presses the bar 5 times. VARIABLE RATIO SCHEDULES- the number of correct repetitions of the correct response for reinforcement varies. Ex, t ...
... FIXED RATIO SCHEDULES- a fixed number of correct responses must occur before reinforcement may recur. Ex. The bird will be given food (reinforcer) everytime it presses the bar 5 times. VARIABLE RATIO SCHEDULES- the number of correct repetitions of the correct response for reinforcement varies. Ex, t ...
File - SSHS AP Psychology
... only after a specified time has elapsed. (e.g., preparing for an exam only when the exam draws close.) ...
... only after a specified time has elapsed. (e.g., preparing for an exam only when the exam draws close.) ...
Learning - Gordon State College
... Punishment: The process by which a consequence decreases the probability of the behavior that it follows. ...
... Punishment: The process by which a consequence decreases the probability of the behavior that it follows. ...
Chapter 6 - learning
... 2. You eat a new food and then get sick because of the flu. However, you develop a dislike for the food and feel nauseated whenever you smell it. 3. An individual receives frequent injections of drugs, which are administered in a small examination room at a clinic. The drug itself causes increased h ...
... 2. You eat a new food and then get sick because of the flu. However, you develop a dislike for the food and feel nauseated whenever you smell it. 3. An individual receives frequent injections of drugs, which are administered in a small examination room at a clinic. The drug itself causes increased h ...
Learning Learning: A relatively permanent change of an organism`s
... organism. For example, wild animal trainers must be vigilant after training animals because the animals may revert to dangerous behaviors. Observational Learning: learning by observation, experience, and examples. --Modeling: the process of observing and imitating a specific behavior. --Mirror Neu ...
... organism. For example, wild animal trainers must be vigilant after training animals because the animals may revert to dangerous behaviors. Observational Learning: learning by observation, experience, and examples. --Modeling: the process of observing and imitating a specific behavior. --Mirror Neu ...
Chapter 6 No Media
... §Scientist who studied digestion by measuring the saliva of dogs §Discovered that dogs “predicted” the arrival of food; led to salivation ...
... §Scientist who studied digestion by measuring the saliva of dogs §Discovered that dogs “predicted” the arrival of food; led to salivation ...
Chapter 2 Figures
... CR, learner often responds to similar stimuli as if they are the original CR. Stimulus discrimination • Ability to differentiate between a particular CS and other significantly different stimuli is stimulus differentiation. ...
... CR, learner often responds to similar stimuli as if they are the original CR. Stimulus discrimination • Ability to differentiate between a particular CS and other significantly different stimuli is stimulus differentiation. ...
Learning – Chapter 5 Learning: process by which experience or
... increases the likelihood of the behavior to recur Example: Moving a student away from someone he or she talks to reinforces the behavior to not talk while the teacher is talking. o Punishers: consequences that decrease the likelihood of the behavior occurring What are some forms of punishment th ...
... increases the likelihood of the behavior to recur Example: Moving a student away from someone he or she talks to reinforces the behavior to not talk while the teacher is talking. o Punishers: consequences that decrease the likelihood of the behavior occurring What are some forms of punishment th ...
Chapter 4 Learning (II)
... Definition — A form of learning in which a behavior becomes more or less probable, depending on its consequences Respondent behavior Operant behavior — behavior that operates on the environment, producing consequences. ...
... Definition — A form of learning in which a behavior becomes more or less probable, depending on its consequences Respondent behavior Operant behavior — behavior that operates on the environment, producing consequences. ...























